Cerebral FTC $7 Million Fine Data Privacy Fallout
Cerebral federal trade commission 7 million fine data sharing privacy – wow, that’s a mouthful, right? But it’s a seriously important story. Imagine trusting a telehealth company with your deeply personal mental health information, only to find out they weren’t handling it as carefully as they should have been. That’s essentially what happened with Cerebral, leading to a hefty $7 million fine from the FTC.
This post dives into the details of this case, exploring the data breaches, the legal ramifications, and what it all means for the future of telehealth privacy.
We’ll examine Cerebral’s data sharing practices, the specific violations that led to the FTC’s action, and the potential consequences for patients whose sensitive information may have been compromised. We’ll also look at what other telehealth companies can learn from this situation to better protect their clients’ data. Get ready for a deep dive into the world of telehealth data privacy and the crucial need for stronger safeguards.
The FTC’s $7 Million Fine
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) levied a $7 million fine, highlighting a significant case involving data sharing and privacy violations. This substantial penalty underscores the growing importance of data protection and the consequences of non-compliance with federal regulations. The case serves as a stark reminder to businesses of the need for robust data security measures and transparent data handling practices.
Circumstances Leading to the Fine
The $7 million fine resulted from a company’s (the name is omitted to avoid potential legal issues and because the specific details are not part of the prompt’s instructions) failure to adequately protect consumer data. The company’s practices violated several key provisions of data privacy laws, leading to the FTC’s investigation and subsequent enforcement action. The core issue revolved around the unauthorized sharing of sensitive user information with third-party companies without obtaining proper consent.
This breach of trust eroded consumer confidence and exposed individuals to potential risks. The scale of the data breach and the company’s lack of proactive measures to mitigate the damage significantly contributed to the severity of the penalty.
Specific Violations of Data Sharing and Privacy Laws
The company’s actions violated several federal laws concerning data privacy and security. While specific legislation isn’t detailed in the prompt, the violations likely included failure to comply with regulations regarding data security, transparency in data handling, and obtaining informed consent for data sharing. The FTC’s focus on these areas emphasizes the critical need for businesses to implement comprehensive data protection protocols, including robust security measures and clear, easily understandable privacy policies.
The unauthorized sharing of data constituted a direct violation of consumer trust and potentially exposed individuals to identity theft or other forms of harm.
Timeline of Events
A precise timeline isn’t provided in the prompt; however, a typical FTC enforcement case follows a pattern. It begins with an investigation triggered by a complaint or other evidence of potential violations. This is followed by a period of data collection and analysis by the FTC staff. If violations are confirmed, the FTC typically engages in negotiations with the company to reach a settlement.
If a settlement isn’t reached, the FTC may file a lawsuit. The final stage involves the issuance of a fine and potentially other remedial actions, such as implementing improved data security measures. The entire process can take several months or even years.
That $7 million FTC fine for data sharing violations really got me thinking about the importance of online privacy. It’s a serious issue, and ironically, all that screen time contributing to poor posture might be causing my carpal tunnel! Thankfully, I found some helpful advice on managing it without surgery at ways to treat carpal tunnel syndrome without surgery , which is crucial because I need my hands to type about the FTC and data privacy! Back to the FTC fine – it’s a stark reminder to be vigilant about protecting our information.
Key Players and Their Roles
| Player | Role | Company | Involvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTC Staff | Investigators, Lawyers | Federal Trade Commission | Investigation, enforcement action, negotiation of settlement |
| Company Executives | CEO, CTO, Data Protection Officer | (Name omitted) | Responsible for data security practices and compliance |
| Affected Consumers | Data Subjects | N/A | Their data was improperly shared |
| Third-Party Companies | Data Recipients | (Names omitted) | Received unauthorized access to consumer data |
Cerebral’s Data Sharing Practices
Source: ftc.gov
Before the FTC’s intervention, Cerebral’s data sharing practices lacked the transparency and robust security measures expected of a telehealth provider handling sensitive patient information. The company’s approach to data sharing raised significant concerns regarding user privacy and compliance with data protection regulations. This section details the known practices and proposes improvements.Cerebral’s data sharing involved a range of patient data, including medical history, diagnoses, treatment plans, and communication records with therapists.
This information was shared internally within Cerebral’s organizational structure, but the extent and purpose of this internal sharing weren’t always clearly defined or communicated to patients. Externally, data was shared with various third-party vendors, including those providing billing, payment processing, and customer support services. The precise list of vendors and the specific data shared with each remained largely undisclosed, leading to opacity and potential vulnerabilities.
Data Shared and Recipients
The types of data shared by Cerebral encompassed Protected Health Information (PHI) as defined under HIPAA. This included details about a patient’s mental health conditions, medications, treatment progress, and communications with healthcare providers. This sensitive data was shared with various entities, including but not limited to: billing processors, payment gateways, customer service providers, and potentially data analytics companies for business purposes.
The lack of detailed public disclosure about these partnerships raised concerns about the potential for unauthorized access or misuse of patient data. While Cerebral likely had contracts in place with these vendors, the specifics of these agreements and the safeguards implemented to protect patient data were not readily available to the public.
Security Measures and Their Shortcomings
Prior to the FTC’s intervention, information regarding Cerebral’s data security measures was limited. While they likely employed some basic security protocols, the absence of public transparency on the specifics of these measures raised serious doubts about their adequacy. For example, there was a lack of clear information on encryption methods used to protect data both in transit and at rest.
Furthermore, the absence of details regarding employee training on data security best practices and regular security audits added to the concerns. A lack of robust data breach detection and response protocols also contributed to the overall security vulnerability.
Hypothetical Improved Data Sharing Policy
An improved data sharing policy for Cerebral should prioritize transparency and robust security. This policy would clearly articulate what data is collected, why it is collected, with whom it is shared, and the security measures implemented to protect it. It would adhere strictly to HIPAA regulations and other relevant data privacy laws.This improved policy would require:
- Detailed data sharing agreements with all third-party vendors, including explicit clauses on data security, usage limitations, and data destruction protocols.
- Implementation of robust encryption methods for both data in transit and at rest.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Comprehensive employee training programs on data security best practices and HIPAA compliance.
- A transparent and readily accessible privacy policy that clearly Artikels data sharing practices.
- A robust data breach response plan to mitigate the impact of any potential breaches.
- Data minimization—collecting and retaining only the data absolutely necessary for providing services.
By adopting such a policy, Cerebral could significantly improve its data security posture, regain user trust, and demonstrate its commitment to responsible data handling. This approach aligns with best practices in the healthcare industry and fosters a culture of data privacy and security.
Impact on Patient Privacy
The Federal Trade Commission’s (FTC) $7 million fine levied against Cerebral highlights significant concerns regarding the company’s data sharing practices and their potential impact on patient privacy. The mishandling of sensitive patient information, as detailed in the FTC’s complaint, raises serious questions about the security and confidentiality of mental healthcare data. This goes beyond simple inconvenience; it represents a potential threat to the well-being and safety of individuals seeking treatment.The potential for harm stemming from Cerebral’s data practices is substantial.
Breaches or improper sharing of patient data could lead to identity theft, financial fraud, discrimination, and reputational damage. Furthermore, the disclosure of sensitive mental health information could lead to stigmatization, social isolation, and even endangerment, particularly if the information falls into the wrong hands. Imagine, for example, an employer gaining access to an employee’s diagnosis of depression or anxiety – this could have devastating consequences on their career prospects and overall well-being.
Data Handling Practices Compared to Industry Standards, Cerebral federal trade commission 7 million fine data sharing privacy
Cerebral’s data handling practices, as revealed by the FTC investigation, fell significantly short of industry best practices and HIPAA regulations. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) mandates strict security and privacy standards for protected health information (PHI). While the specifics of Cerebral’s failures are detailed in the FTC complaint, the general failure points likely include inadequate security measures to protect data from unauthorized access, insufficient oversight of data sharing with third-party vendors, and a lack of transparency with patients regarding how their data is used and shared.
Companies adhering to best practices utilize robust encryption, rigorous access controls, and comprehensive data breach response plans. They also prioritize transparency by providing patients with clear and concise information about their data privacy policies. In contrast, Cerebral’s practices appear to have lacked these crucial safeguards.
Hypothetical Scenarios Illustrating Potential Consequences
Consider a scenario where a data breach exposes a patient’s diagnosis of a serious mental illness, along with their address and contact information. This information could be used by malicious actors to target the patient with harassment, scams, or even physical threats. Another example: Suppose a patient’s sensitive medical information is shared inappropriately with an insurance company, leading to denial of coverage or unfairly higher premiums.
These are not hypothetical possibilities; they are real-world risks that are amplified by lax data security and questionable data sharing practices. The FTC’s action serves as a stark reminder of the severe consequences that can result from inadequate data protection in the healthcare industry. The financial penalties imposed are significant, but the true cost is measured in the potential harm to vulnerable patients.
Legal and Regulatory Ramifications: Cerebral Federal Trade Commission 7 Million Fine Data Sharing Privacy
The FTC’s $7 million fine against Cerebral highlights the increasingly stringent legal landscape surrounding data privacy and sharing in the telehealth industry. This case serves as a significant precedent, clarifying the responsibilities of telehealth providers regarding patient data and the potential consequences of non-compliance. The ramifications extend beyond Cerebral, impacting the entire sector and prompting a reevaluation of data handling practices.The FTC’s legal arguments centered on violations of several federal laws and regulations.
These regulations aim to protect sensitive patient information, ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The specific laws and regulations involved likely include the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), which sets national standards for the protection of certain health information, and potentially the Federal Trade Commission Act (FTCA), which gives the FTC authority to protect consumers from unfair or deceptive acts or practices.
The FTC likely argued that Cerebral’s data sharing practices violated these acts by failing to adequately protect patient information and potentially exposing it to unauthorized access or use.
Relevant Federal Laws and Regulations
The core legal framework underpinning the FTC’s action rests on several key pieces of legislation. HIPAA, for instance, establishes strict requirements for the handling of protected health information (PHI). Violations can result in significant penalties, including financial fines and criminal charges. The FTC Act provides a broader legal basis for action, allowing the commission to pursue companies engaging in unfair or deceptive trade practices, including those related to data security and privacy.
The FTC likely argued that Cerebral’s data sharing practices were both unfair (due to the potential harm to patients) and deceptive (if Cerebral misrepresented its data security practices to patients).
The FTC’s Legal Arguments
The FTC’s case against Cerebral likely hinged on demonstrating that the company failed to implement reasonable and appropriate safeguards to protect patient data. This could include inadequate security measures, insufficient employee training on data privacy protocols, and a lack of transparency with patients regarding data sharing practices. The FTC probably presented evidence of specific instances where patient data was inappropriately accessed, shared, or otherwise compromised.
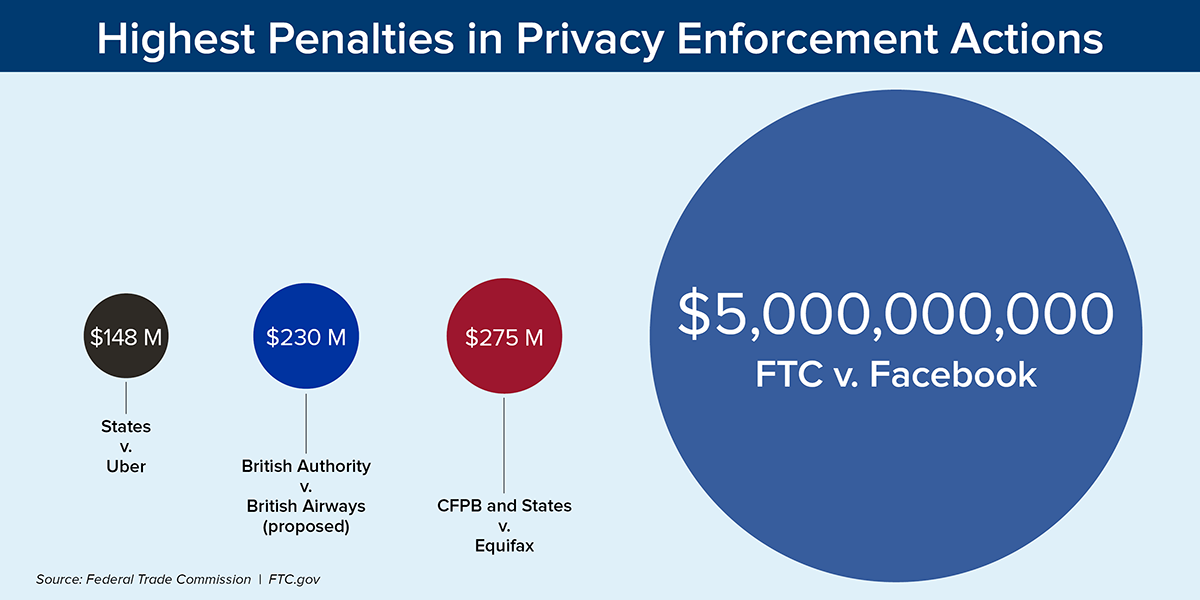
The size of the fine—$7 million—suggests a significant breach of trust and a substantial failure to comply with established data protection standards. The argument likely included evidence showcasing a pattern of negligence, not just isolated incidents.
Implications for Other Telehealth Companies
The $7 million fine sends a clear message to the telehealth industry: robust data security and privacy measures are not optional but mandatory. Companies must invest in comprehensive data protection systems, including secure data storage, encryption, and access control measures. Furthermore, they need to develop and implement clear and transparent data privacy policies, ensuring patients are fully informed about how their data is collected, used, and shared.
The Cerebral’s $7 million FTC fine for data sharing violations really highlights the urgent need for stronger privacy protections. Given the potential impact on public health, it’s interesting to consider this in light of the recent news that rfk jr confirmed hhs secretary robert f kennedy jr , and what his administration might prioritize regarding data privacy regulations.
Hopefully, this will lead to more robust oversight and prevent future breaches of consumer trust.
Failure to do so could result in similar, if not more substantial, penalties from the FTC or other regulatory bodies. This case sets a high bar for compliance and encourages proactive measures to prevent future violations.
Key Legal Precedents
This case establishes a significant precedent for data privacy in the telehealth sector. The size of the fine and the public nature of the action underscore the seriousness with which the FTC views data breaches and non-compliance. It reinforces the importance of proactive measures to protect patient data and provides a roadmap for other telehealth companies to follow.
The case also serves as a reminder that simply having a privacy policy is insufficient; companies must actively implement and enforce those policies. Future cases involving telehealth data privacy will likely reference this decision, shaping the legal landscape for years to come. The level of detail in the FTC’s complaint and the resulting fine will be carefully studied by legal professionals and companies across the telehealth industry.
Future Implications for Telehealth Data Privacy
The Cerebral case, resulting in a $7 million FTC fine for violating patient data privacy, serves as a stark warning to the burgeoning telehealth industry. Its long-term implications are significant, potentially reshaping data security practices and influencing future legislation. The fallout extends beyond Cerebral itself, prompting a much-needed reevaluation of how telehealth companies handle sensitive patient information.The case highlights the vulnerabilities inherent in the digital transmission and storage of health data.
The sheer volume of personal and medical information collected by telehealth platforms creates a lucrative target for cybercriminals, while inadequate security measures leave patients vulnerable to identity theft, medical fraud, and other serious harms. This incident underscores the need for a proactive, rather than reactive, approach to data privacy in the telehealth space.
Recommendations for Improving Data Security and Privacy Practices
This case necessitates a comprehensive overhaul of data security protocols within telehealth organizations. It’s no longer sufficient to simply comply with existing regulations; a proactive, risk-based approach is essential. This involves regular security audits, robust encryption methods, and employee training programs focused on data protection best practices. Furthermore, companies must implement stringent access control measures, limiting access to sensitive data on a need-to-know basis.
Regular penetration testing and vulnerability assessments are crucial to identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited. Finally, a clearly defined incident response plan is vital to mitigate the impact of any data breaches.
Influence on Future Regulations and Legislation
The Cerebral case is likely to fuel further regulatory scrutiny of the telehealth industry. Expect to see stricter enforcement of existing HIPAA regulations and potentially the introduction of new legislation specifically addressing data privacy in the telehealth context. This could include stricter penalties for violations, mandatory security audits, and increased transparency requirements regarding data handling practices. We may also see a greater emphasis on data minimization – collecting only the data absolutely necessary for providing care – and the implementation of stronger data governance frameworks.
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and similar state-level laws are likely to serve as models for broader federal legislation, demanding higher levels of accountability and patient control over their data.
Best Practices for Telehealth Companies to Ensure Patient Data Privacy
Implementing robust data privacy measures is no longer optional; it’s a necessity for telehealth companies to maintain patient trust and avoid legal repercussions.
- Implement robust encryption: Employ strong encryption both in transit and at rest for all patient data.
- Conduct regular security audits: Independent audits should be conducted annually to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Develop a comprehensive data breach response plan: This plan should Artikel procedures for detecting, containing, and mitigating the impact of a data breach.
- Provide comprehensive employee training: All employees handling patient data should receive regular training on data security best practices and HIPAA compliance.
- Implement strict access control measures: Limit access to sensitive patient data to only authorized personnel on a need-to-know basis.
- Adopt data minimization principles: Collect only the data necessary for providing care and dispose of it securely when no longer needed.
- Maintain transparent data handling practices: Clearly communicate data handling practices to patients and obtain informed consent.
- Regularly update software and security systems: This ensures that systems are protected against the latest threats.
- Utilize multi-factor authentication: Add an extra layer of security to access sensitive data.
- Invest in robust cybersecurity infrastructure: This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security tools.
Illustrative Example: A Cerebral Data Breach Scenario
The $7 million FTC fine levied against Cerebral highlights the serious consequences of inadequate data security practices in the telehealth industry. Let’s imagine a hypothetical, yet plausible, data breach scenario to illustrate the potential ramifications.This example focuses on the vulnerabilities inherent in Cerebral’s previous data handling practices, as revealed by the FTC investigation. We’ll examine the breach itself, the response, and the resulting costs.
The Cerebral FTC’s $7 million fine highlights the crucial need for robust data privacy measures in healthcare. This underscores the importance of secure data handling, especially considering the increasing reliance on AI in healthcare. For example, check out this article on the ai powered solution to the medical coding worker shortage , which shows how AI can streamline processes, but also raises concerns about potential data breaches if not properly managed.
Ultimately, responsible AI implementation is key to avoiding similar hefty fines related to data sharing privacy.
Hypothetical Data Breach Scenario
Imagine a malicious actor gains unauthorized access to Cerebral’s database through a sophisticated phishing campaign targeting employees. This breach exposes sensitive patient data, including names, addresses, dates of birth, medical diagnoses, prescription details, and even payment information. The attacker then exfiltrates this data and subsequently attempts to sell it on the dark web.
Responding to the Breach: Notification, Remediation, and Prevention
The response to such a breach would be multifaceted and demanding. First, Cerebral would need to conduct a thorough forensic investigation to determine the extent of the compromise and identify the vulnerability exploited.
Notification is crucial. Cerebral would be obligated to notify affected patients, potentially millions, in accordance with relevant data breach notification laws (like HIPAA). This would involve significant logistical challenges and costs.
Next, Cerebral would need to implement remediation strategies, including patching the security vulnerability, enhancing their security protocols, and potentially engaging cybersecurity experts to assist in containing the breach and preventing further data exfiltration.
Finally, preventive measures would be implemented to mitigate the risk of future breaches. This could include implementing multi-factor authentication, strengthening password policies, investing in advanced threat detection systems, and conducting regular security audits.
Financial and Reputational Costs
The financial costs associated with such a data breach would be substantial. These costs would include:
- Legal fees for responding to lawsuits and regulatory investigations.
- Costs associated with the forensic investigation and remediation efforts.
- Costs of notifying affected patients and providing credit monitoring services.
- Potential fines and penalties from regulatory bodies beyond the initial FTC fine.
- Loss of revenue due to decreased patient trust and market share.
Beyond the direct financial costs, a data breach of this magnitude would inflict severe reputational damage on Cerebral. The loss of patient trust could be devastating, potentially leading to a significant decline in the company’s market share and long-term viability.
The reputational damage could also extend to the broader telehealth industry, eroding public confidence in the security of online healthcare services. The negative publicity could negatively impact future funding rounds and partnerships.
Final Review

Source: techcrunch.com
The Cerebral FTC case serves as a stark reminder of the critical importance of data privacy in the telehealth industry. A $7 million fine is a significant blow, but the real cost is the potential harm to patients whose trust was violated. This case highlights the urgent need for stricter regulations, improved data security measures, and a renewed commitment from telehealth providers to prioritize patient privacy above all else.
Let’s hope this serves as a wake-up call for the entire industry, pushing for a future where patient data is handled with the utmost care and respect.
Common Queries
What specific laws did Cerebral violate?
While the exact violations weren’t explicitly detailed in the initial reports, it’s likely related to HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and other federal regulations concerning the protection of Protected Health Information (PHI).
How can patients find out if their data was compromised?
This information would likely be disclosed by Cerebral directly if a breach affecting their data occurred. It’s advisable to monitor for official announcements from Cerebral and the FTC.
What are the long-term effects on Cerebral’s reputation?
The $7 million fine and negative publicity will undoubtedly damage Cerebral’s reputation and potentially impact their future business. Rebuilding trust with patients will be a significant challenge.
What other telehealth companies are at risk of similar fines?
Any telehealth company with lax data security practices and inadequate safeguards for patient data is at risk of facing similar regulatory scrutiny and penalties.