DEA Extends Telehealth Prescribing Controlled Substances
Dea extends telehealth prescibing controlled substances – DEA Extends Telehealth Prescribing Controlled Substances: Whoa, that’s a big deal! For years, access to controlled substances via telehealth has been a bit of a grey area, with restrictions varying wildly. This recent DEA decision to expand telehealth prescribing for controlled substances is shaking things up, impacting both patients and providers. This post dives into the changes, the implications, and what it all means for the future of healthcare.
The DEA’s move to broaden telehealth prescribing of controlled substances has been a long time coming. Previous limitations, often stemming from concerns about patient safety and potential for misuse, have significantly restricted access for many. Now, with these updated regulations, the landscape is changing dramatically. We’ll explore the specifics of the new rules, the reasons behind them, and what challenges and opportunities lie ahead.
DEA Telehealth Policy Changes
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically accelerated the adoption of telehealth, forcing a rapid reassessment of regulations surrounding healthcare delivery, particularly for controlled substances. Prior to the pandemic, the ability to prescribe controlled substances via telehealth was severely limited, creating significant barriers to access for many patients, especially those in rural or underserved areas. The DEA’s response to this situation has had a profound impact on patient access to necessary medications.The DEA’s response to the increased need for telehealth during the pandemic involved a series of temporary waivers and policy changes that broadened the allowance for telehealth prescribing of controlled substances.
These changes, initially implemented as emergency measures, were later formalized and, in some cases, extended. Specifically, the DEA relaxed requirements around in-person medical evaluations for initial prescriptions of certain controlled substances, allowing for virtual consultations under specific conditions. These conditions often included requirements for a prior in-person visit at some point, but the specifics varied depending on the controlled substance and state regulations.
The temporary waivers ultimately paved the way for more permanent changes, improving access for many patients.
Rationale Behind DEA’s Decision to Extend Telehealth Prescribing Rules
The DEA’s decision to extend and modify telehealth prescribing rules stemmed from several key factors. First, the pandemic highlighted the critical need for flexible healthcare delivery models to ensure patient access, particularly for those with limited mobility or residing in geographically isolated areas. Second, the DEA recognized that telehealth could improve efficiency and convenience for both patients and providers, potentially leading to better medication adherence and overall health outcomes.
Third, data collected during the temporary waiver periods provided evidence that telehealth prescribing of controlled substances could be done safely and effectively, with minimal increase in the risk of misuse or diversion. This data-driven approach helped justify the continued use of telehealth for this purpose.
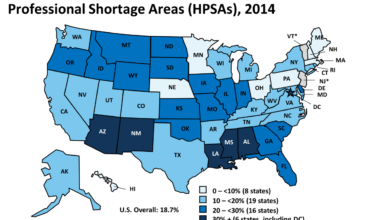
Accessibility of Controlled Substance Prescriptions: Before and After Policy Changes
Before the DEA’s policy changes, accessing controlled substance prescriptions via telehealth was exceptionally challenging. Many patients, especially those in rural areas or with mobility limitations, faced significant hurdles in obtaining necessary medications. Travel distances to in-person appointments, limited availability of specialists, and financial constraints often prevented timely access to care. The policy changes significantly improved access, particularly for patients in underserved communities.
For example, patients in rural areas could now consult with specialists remotely, eliminating the need for lengthy and expensive travel. Similarly, individuals with disabilities or chronic illnesses found it easier to manage their medication needs through convenient telehealth appointments. While the extent of the improved access varies by state and specific medication, the overall impact has been a substantial increase in the availability of controlled substance prescriptions through telehealth for many eligible patients.
Regulatory Requirements and Compliance for Providers
The DEA’s expansion of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances brings significant changes for healthcare providers. Navigating these new regulations requires a thorough understanding of the updated requirements and a proactive approach to compliance. Failure to adhere to these rules can lead to serious consequences, including hefty fines and the potential loss of prescribing privileges.
The new regulations aim to ensure patient safety and prevent the diversion of controlled substances. This involves stricter identification verification procedures, enhanced record-keeping practices, and robust security measures to protect patient data and prevent unauthorized access. Providers must understand these requirements and implement effective strategies to meet them.
Patient Identification and Verification
Accurate patient identification is paramount to prevent prescription fraud and diversion. Providers must utilize reliable methods to verify the identity of telehealth patients before prescribing controlled substances. This may involve using multiple forms of identification, such as driver’s licenses, state-issued identification cards, and passport information. In some cases, a video conference may be used to visually confirm the patient’s identity.
The process must be meticulously documented.
Secure Communication and Data Storage
All communications and data related to telehealth prescribing of controlled substances must be secured using HIPAA-compliant methods. This includes the use of encrypted platforms for video conferencing and secure messaging, as well as the implementation of robust data encryption and access control measures for electronic health records (EHRs). Providers must also adhere to strict data backup and disaster recovery protocols to ensure data integrity and availability.
Record Keeping and Documentation
Maintaining accurate and complete records is crucial for demonstrating compliance. Providers must document all aspects of the telehealth encounter, including patient identification, diagnosis, treatment plan, and the prescribing of controlled substances. This documentation should be readily accessible for audits and inspections by regulatory bodies. The records must be maintained for the period required by state and federal regulations.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Providers may face several challenges in meeting these new requirements. These include the cost of implementing secure technologies, the need for additional staff training, and the complexity of navigating varying state and federal regulations. Furthermore, ensuring reliable internet connectivity in all patient locations can be a hurdle. The integration of new technologies into existing workflows can also present challenges.
Strategies for Ensuring Compliance
To ensure compliance, providers should invest in secure telehealth platforms, train staff on the new regulations, and develop comprehensive compliance policies and procedures. Regular audits and security assessments are essential to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. Collaboration with technology vendors and legal experts can also help providers navigate the complexities of the new regulations. Proactive monitoring of patient data and suspicious activities is crucial for preventing diversion.
Key Compliance Requirements
| Requirement | Description | Compliance Method | Potential Penalty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Identification | Verifying patient identity using multiple forms of identification. | Utilize secure video conferencing, identity verification services, and document all verification steps. | Fines, suspension or revocation of prescribing privileges. |
| Record Keeping | Maintaining accurate and complete records of telehealth encounters, including prescriptions. | Use a secure EHR system, document all aspects of the encounter, and adhere to retention policies. | Fines, sanctions, and legal action. |
| Secure Communication | Using HIPAA-compliant methods for all telehealth communications. | Employ encrypted video conferencing and messaging platforms. | Fines, HIPAA violations, and reputational damage. |
| Security Measures | Implementing robust security measures to protect patient data. | Utilize firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control measures. | Fines, data breaches, legal action, and reputational damage. |
Patient Safety and Monitoring Protocols
The expansion of telehealth for controlled substance prescribing necessitates robust safety measures to mitigate the risks of misuse and diversion. This requires a multi-faceted approach encompassing stringent prescription monitoring, proactive patient engagement, and sophisticated risk assessment strategies. The goal is to leverage technology to enhance patient safety while maintaining access to necessary medications.
Effective patient safety and monitoring protocols are crucial for responsible telehealth prescribing of controlled substances. These protocols must integrate technological solutions with established clinical best practices to ensure that patients receive appropriate care while minimizing the potential for harm. This involves a combination of technological tools, clinical judgment, and patient education.
The DEA’s expansion of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances is a huge step forward for patient access, especially in rural areas. It’s interesting to consider this alongside advancements in AI-powered healthcare, like the Google iCAD AI mammography expansion , which shows how technology can improve diagnosis and care. Both initiatives highlight the potential of technology to bridge gaps in healthcare access and improve outcomes, ultimately making healthcare more efficient and equitable, impacting how the DEA’s changes might be implemented across different healthcare sectors.
Prescription Monitoring and Risk Assessment
Implementing a comprehensive prescription drug monitoring program (PDMP) is paramount. This involves integrating the telehealth platform with state-level PDMPs to access a patient’s complete controlled substance prescription history. This allows providers to identify potential red flags, such as doctor shopping or unusually high dosages, enabling them to make informed decisions about prescribing. Risk assessment tools, incorporating factors like patient history, substance use disorder history, and social determinants of health, can further refine the identification of high-risk patients.
For example, a patient with a history of opioid addiction and a recent overdose attempt would trigger a higher level of monitoring and potentially require additional interventions. Furthermore, algorithms can be employed to flag prescriptions exceeding recommended dosages or those prescribed for unusually long durations.
Telehealth Technology for Patient Monitoring
Telehealth platforms offer several tools for enhancing patient monitoring. These include:
- Electronic medication adherence monitoring: Smart pill bottles or mobile applications can track medication intake, alerting providers to missed doses or inconsistent usage. This allows for timely intervention and addresses potential non-adherence before it leads to adverse outcomes. For example, if a patient consistently misses doses of their pain medication, the provider can initiate a conversation about the reasons for non-adherence and explore strategies to improve compliance.
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM): RPM devices can collect physiological data, such as heart rate and blood pressure, providing insights into a patient’s overall health status and potential adverse effects of medication. This is particularly valuable for patients taking opioids, where monitoring for respiratory depression is crucial. For instance, a significant drop in heart rate or respiratory rate could trigger an immediate alert to the provider, allowing for timely intervention.
- Video conferencing and regular check-ins: Regular virtual visits provide opportunities for providers to assess patients’ physical and mental well-being, assess for signs of misuse or diversion, and provide ongoing education and support. This allows for a more personalized approach to patient care, fostering trust and promoting adherence.
Patient Education and Engagement
Patient education is a critical component of safe controlled substance prescribing via telehealth. Providers should utilize the telehealth platform to provide comprehensive information about the prescribed medication, including its potential benefits, risks, and side effects. Educating patients on proper storage, disposal, and recognizing signs of misuse or diversion is equally crucial. Interactive modules and educational videos can be integrated into the telehealth platform to reinforce key information and ensure patient understanding.
For instance, a patient could be shown a video demonstrating the proper way to dispose of unused medications to prevent accidental ingestion or diversion. Furthermore, clear communication channels should be established to encourage patients to report any concerns or adverse effects promptly.
Risk Assessment Approaches
Different risk assessment approaches can be implemented, ranging from simple questionnaires to sophisticated algorithms incorporating multiple data points. A simple questionnaire might assess factors like prior substance use history, while a more complex algorithm might integrate PDMP data, patient demographics, and clinical factors to generate a risk score. The choice of approach will depend on factors such as available resources, patient population, and the specific type of controlled substance being prescribed.
For example, a clinic specializing in pain management might utilize a more comprehensive algorithm than a primary care clinic prescribing limited quantities of controlled substances. Regardless of the approach, the goal is to identify patients at higher risk of misuse or diversion so that appropriate monitoring and interventions can be implemented.
Technological Infrastructure and Security Considerations
The expansion of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances necessitates a robust and secure technological infrastructure. This goes beyond simply having a video conferencing platform; it demands a comprehensive system designed to protect patient privacy, maintain data integrity, and comply with stringent regulatory requirements. Failure to implement adequate security measures can lead to serious consequences, including legal penalties, reputational damage, and, most importantly, compromised patient safety.The core components of this infrastructure must seamlessly integrate to ensure a secure and compliant process.
This integration requires careful planning and coordination, considering both hardware and software requirements, as well as ongoing maintenance and updates.
Technological Infrastructure Requirements
Secure telehealth prescribing of controlled substances requires a multi-faceted technological approach. This includes reliable high-speed internet connectivity for both the provider and patient, ensuring uninterrupted video and data transmission. The platform itself must be HIPAA-compliant and capable of securely storing and transmitting patient data, including electronic prescriptions for controlled substances (EPCS). This necessitates robust encryption protocols and authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access.
Furthermore, the system should integrate seamlessly with the provider’s electronic health record (EHR) system, facilitating efficient workflow and data management. Finally, the system should include audit trails to track all activities related to the prescription process, enabling thorough record-keeping and compliance monitoring.
Data Security Measures
Protecting patient data is paramount. This requires implementing multiple layers of security. Strong password policies, multi-factor authentication, and access controls limit unauthorized access. Data encryption both in transit and at rest is crucial to prevent data breaches. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments identify and address potential weaknesses in the system.
The system should also incorporate intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor for and respond to malicious activity. Furthermore, comprehensive employee training programs on data security best practices are essential to ensure that all staff understand their responsibilities in protecting patient information. Consider, for example, a scenario where a clinic’s system is breached because an employee reused a password across multiple platforms.
The consequences could be severe.
The Role of Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
EHRs are central to secure telehealth prescribing of controlled substances. They provide a centralized repository for patient information, including medical history, allergies, and current medications. Integration with the telehealth platform allows providers to access this information quickly and securely, facilitating informed decision-making. EHRs also often include EPCS capabilities, streamlining the prescription process and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
The seamless flow of information between the EHR and the telehealth platform minimizes the risk of errors and ensures that all relevant information is readily available to the provider. A well-integrated system allows for efficient tracking of prescriptions and refills, reducing the potential for abuse or diversion.
Security Best Practices for Telehealth Platforms
A comprehensive list of security best practices is crucial.
- Regular software updates and patching to address known vulnerabilities.
- Implementation of robust encryption protocols (e.g., TLS 1.2 or higher) for all data transmission.
- Use of strong password policies and multi-factor authentication for all users.
- Regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address security weaknesses.
- Strict access control measures to limit access to sensitive patient data based on the principle of least privilege.
- Comprehensive employee training programs on data security best practices.
- Implementation of data loss prevention (DLP) measures to prevent unauthorized data exfiltration.
- Regular backups of all data to ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster.
- Compliance with all relevant regulations, including HIPAA and state-specific requirements.
- Regular monitoring of system logs for suspicious activity.
Adherence to these best practices is not merely recommended; it is essential for maintaining patient safety and regulatory compliance in the increasingly prevalent landscape of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances.
The DEA extending telehealth prescribing for controlled substances is huge news for patient access, especially considering the aging population. This increased access is even more critical when you consider that early detection of conditions like dementia is vital; research suggests that a simple eye test might help, as discussed in this fascinating article: can eye test detect dementia risk in older adults.
Ultimately, improved healthcare access, like the DEA’s changes, coupled with early detection methods, could significantly improve the quality of life for many seniors.
Impact on Different Patient Populations
The expansion of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances has profound implications for diverse patient populations, impacting access to care and potentially exacerbating existing health disparities. While offering increased convenience and accessibility, it also presents unique challenges and necessitates careful consideration of potential inequities. This section examines how this policy change affects various groups and explores the complexities of ensuring equitable access to necessary medications.
The shift towards telehealth prescribing has the potential to significantly alter the healthcare landscape for numerous patient populations. Analyzing the experiences of these groups reveals both benefits and drawbacks, highlighting the need for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the policy to maximize positive outcomes and mitigate potential harm.
Rural Patients
Expanding telehealth access to controlled substances offers a lifeline for individuals in rural areas, often characterized by limited access to healthcare providers specializing in pain management or addiction treatment. Before the policy change, these patients faced significant barriers, including long travel distances, limited provider availability, and transportation challenges. Telehealth eliminates many of these obstacles, enabling them to receive timely consultations and prescriptions, potentially improving health outcomes and reducing the burden of chronic pain or substance use disorders.
However, reliable internet access remains a crucial factor; without it, the benefits of telehealth are significantly diminished. For example, a patient in a remote mountain community with unreliable internet service may find telehealth prescribing impractical, perpetuating existing healthcare disparities.
Patients with Disabilities
Telehealth offers considerable advantages for patients with disabilities who may experience difficulty traveling to in-person appointments. Mobility limitations, chronic illnesses, or cognitive impairments can significantly restrict access to traditional healthcare settings. Telehealth allows these patients to receive care from the comfort and safety of their homes, reducing physical and psychological barriers to treatment. However, ensuring that telehealth platforms are accessible to patients with diverse disabilities, including those with visual or auditory impairments, is critical.
For instance, providing real-time captioning or alternative communication methods is essential for inclusivity. Without such accommodations, the promise of improved access remains unrealized for many.
Comparison of Telehealth and In-Person Visits
Patients accessing controlled substances via telehealth generally report increased convenience and reduced travel time compared to in-person visits. The elimination of travel-related expenses and time commitments can be particularly beneficial for those with limited resources or mobility issues. However, some patients may express a preference for the in-person interaction with their provider, finding the personal connection crucial for building trust and rapport, especially when dealing with sensitive health issues.
This highlights the importance of maintaining a balance between telehealth and in-person care, offering patients choices that best suit their individual needs and preferences. Furthermore, the lack of a physical examination in telehealth encounters might lead to concerns regarding proper diagnosis and treatment in some cases.
Geographic and Socioeconomic Disparities, Dea extends telehealth prescibing controlled substances
While telehealth aims to bridge geographical divides in healthcare access, existing socioeconomic disparities can still impede its effectiveness. Reliable internet access and technological literacy are not evenly distributed across the population. Low-income individuals and those in underserved communities may lack the necessary technology or digital skills to participate fully in telehealth programs. This digital divide can exacerbate existing health disparities, limiting the benefits of expanded telehealth prescribing for vulnerable populations.
For instance, a patient in a low-income urban neighborhood without consistent high-speed internet may struggle to engage in telehealth appointments, despite the policy change. Similarly, patients lacking the financial means to acquire necessary technology (such as a computer or smartphone) are also excluded.
Benefits and Limitations for Specific Patient Groups
The benefits of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances vary depending on the specific patient group. For individuals in rural areas or those with mobility limitations, telehealth offers improved access to essential care, potentially leading to better health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. However, concerns regarding patient monitoring, the potential for misuse or diversion, and the need for robust security measures remain crucial considerations.
For patients with substance use disorders, telehealth can facilitate remote monitoring and support, reducing the risk of relapse. However, the lack of direct observation and potential difficulties in verifying patient identity present challenges. The potential for over-prescribing and the need for careful assessment and monitoring remain key limitations.
Future Directions and Challenges
Source: inquirer.com
The expansion of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. Successfully navigating this new landscape requires a proactive approach focused on addressing potential pitfalls while capitalizing on technological advancements to enhance patient safety and access to care. This necessitates ongoing research, robust regulatory frameworks, and a commitment to continuous improvement.The integration of telehealth into controlled substance prescribing is still relatively new, leaving many aspects ripe for further development and refinement.
The DEA’s expansion of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances is a big deal, impacting access to care nationwide. This shift in healthcare delivery comes at a time when healthcare systems are making tough decisions, like Kaiser Permanente’s recent choice to scrap a $500 million Seattle bed tower, as reported in this article. It makes you wonder how these budgetary shifts will further influence the implementation and accessibility of the DEA’s new telehealth rules.
Several key areas require focused attention to ensure the long-term success and safety of this practice.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Security and Efficiency
Technological innovation holds the key to improving the security and efficiency of telehealth prescribing. Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to patient records and prescriptions. Blockchain technology, with its inherent security features, offers the potential to create tamper-proof records of prescriptions, enhancing transparency and accountability. Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) can be leveraged to develop sophisticated monitoring systems that detect potential prescription drug abuse or diversion patterns, alerting healthcare providers to potential risks in real-time.
For example, an AI-powered system could analyze patient data, including prescription history, demographics, and even social media activity (with appropriate patient consent), to flag unusual patterns that warrant further investigation. This proactive approach could significantly improve patient safety and reduce the risk of misuse.
Ongoing Research and Evaluation of Effectiveness and Safety
Rigorous research and ongoing evaluation are crucial to understanding the long-term impact of telehealth prescribing on patient outcomes and public health. Studies should focus on comparing the effectiveness and safety of telehealth prescribing to traditional in-person methods, paying close attention to patient adherence, treatment efficacy, and the incidence of adverse events. This data is essential for informing policy decisions and ensuring the responsible implementation of telehealth prescribing practices.
For instance, a large-scale randomized controlled trial comparing telehealth and in-person opioid prescribing for chronic pain patients could provide valuable insights into the relative effectiveness and safety of each approach, including differences in pain management, medication adherence, and potential for misuse. This data would inform best practices and potentially refine guidelines for future implementation.
Policy Improvements to Optimize Benefits and Mitigate Risks
Policy improvements are essential to optimize the benefits and mitigate the risks associated with telehealth prescribing of controlled substances. Clear and consistent regulations are needed to ensure provider compliance and patient safety. These regulations should address issues such as provider credentialing, patient identification and verification, prescription monitoring program integration, and data security. Furthermore, policies should encourage the development and implementation of best practices for telehealth prescribing, including guidelines for patient education, risk assessment, and ongoing monitoring.
For example, mandatory continuing education for providers on the appropriate use of telehealth for controlled substance prescribing, incorporating the latest research and best practices, could help ensure high-quality care and reduce risks. Similarly, establishing standardized protocols for documenting telehealth encounters and integrating these records into electronic health records (EHRs) could improve data collection and facilitate monitoring of patient outcomes.
Final Conclusion

Source: qtxasset.com
The DEA’s expansion of telehealth prescribing for controlled substances marks a significant shift in healthcare delivery. While concerns about misuse and diversion remain valid, the potential benefits for patients, especially those in rural areas or with limited mobility, are substantial. Successfully navigating this new landscape requires careful attention to regulatory compliance, robust security measures, and a commitment to patient safety.
The coming years will be crucial in evaluating the long-term impact of this decision and refining best practices to ensure responsible and effective care.
FAQ Explained: Dea Extends Telehealth Prescibing Controlled Substances
What types of controlled substances are now eligible for telehealth prescribing?
The specific schedules of controlled substances allowed for telehealth prescribing vary based on state and federal laws. It’s crucial to check the latest guidelines from both the DEA and your state’s board of medicine.
How does the DEA ensure patient safety with telehealth prescribing?
The DEA’s updated regulations emphasize robust security measures, including secure electronic prescribing systems, strong patient identification protocols, and regular monitoring of prescription patterns to detect potential misuse or diversion.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with these new regulations?
Penalties for non-compliance can be severe and range from fines and license suspension to criminal charges, depending on the severity of the violation. It’s vital for providers to thoroughly understand and adhere to all applicable regulations.
Are there specific training requirements for providers prescribing controlled substances via telehealth?
Many states require additional training or certifications for providers who wish to prescribe controlled substances via telehealth. Check with your state’s licensing board for specific requirements.