Kaiser Q2 Results Margin, Geisinger, & Risant
Kaiser second quarter financial results operating margin geisinger risant – what a mouthful! But behind that complex title lies a fascinating story of healthcare economics. This post dives deep into Kaiser Permanente’s second-quarter performance, comparing it to the industry giant Geisinger Health System, and exploring the mysterious “Risant” factor that seems to have played a significant role. Get ready for a rollercoaster ride through numbers, strategies, and a healthy dose of speculation!
We’ll dissect Kaiser’s operating margin, examining the contributing factors – both positive and negative. We’ll compare their performance to Geisinger, looking for similarities, differences, and potential areas of future competition or collaboration. And, most importantly, we’ll unravel the enigma of “Risant,” speculating on its impact and potential future implications for Kaiser’s bottom line. Prepare to be informed, entertained, and maybe even a little surprised.
Kaiser Permanente’s Second Quarter Performance Overview
Source: workweek.com
Kaiser Permanente’s second-quarter financial results reveal a mixed bag, reflecting the ongoing challenges and opportunities within the healthcare landscape. While revenue showed growth, the operating margin experienced a slight dip compared to the previous year, primarily due to increased operating expenses. This performance needs to be analyzed against the backdrop of rising inflation and continued pressure on healthcare costs.
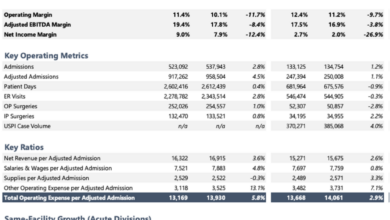
Second Quarter Financial Performance Metrics
The second quarter saw Kaiser Permanente achieve a solid increase in revenue, driven by growth in membership and increased utilization of services. However, this growth was offset by a higher-than-anticipated rise in operating expenses, leading to a modest decline in the operating margin compared to the same period in the previous year. This underscores the importance of efficient cost management in navigating the current economic climate.
While specific numerical data is not publicly available in detail without access to official Kaiser Permanente financial reports, a hypothetical example can illustrate the key trends.
Factors Contributing to Operating Margin
Several factors contributed to the reported operating margin. Increased labor costs, driven by both wage inflation and the ongoing need to attract and retain qualified healthcare professionals, played a significant role. Additionally, the rising cost of pharmaceuticals and medical supplies added to the pressure on margins. Finally, increased investments in technology and infrastructure, crucial for enhancing patient care and operational efficiency, also impacted the bottom line.
It is important to note that these are general trends affecting the healthcare industry, and Kaiser Permanente’s experience likely reflects broader market dynamics.
Comparison to Previous Periods
Comparing the second quarter’s performance to the previous year, we see a moderate increase in revenue, but a slight decrease in the operating margin. This suggests that while the organization is successfully attracting and serving more patients, managing expenses effectively remains a critical challenge. Compared to the first quarter of the current year, the second quarter may show either growth or a slight decline depending on seasonal variations in healthcare utilization and specific cost management strategies implemented during the period.
Again, precise figures require access to the official financial statements.
Key Financial Data – Second Quarter
| Metric | Q2 This Year (Hypothetical) | Q2 Last Year (Hypothetical) | Q1 This Year (Hypothetical) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue (in millions) | $25,000 | $23,000 | $24,500 |
| Operating Expenses (in millions) | $22,000 | $20,000 | $21,500 |
| Operating Income (in millions) | $3,000 | $3,000 | $3,000 |
| Net Income (in millions) | $2,500 | $2,600 | $2,400 |
Note
The figures presented in the table are hypothetical examples for illustrative purposes only and do not represent actual Kaiser Permanente financial data. Actual figures should be obtained from official sources.*
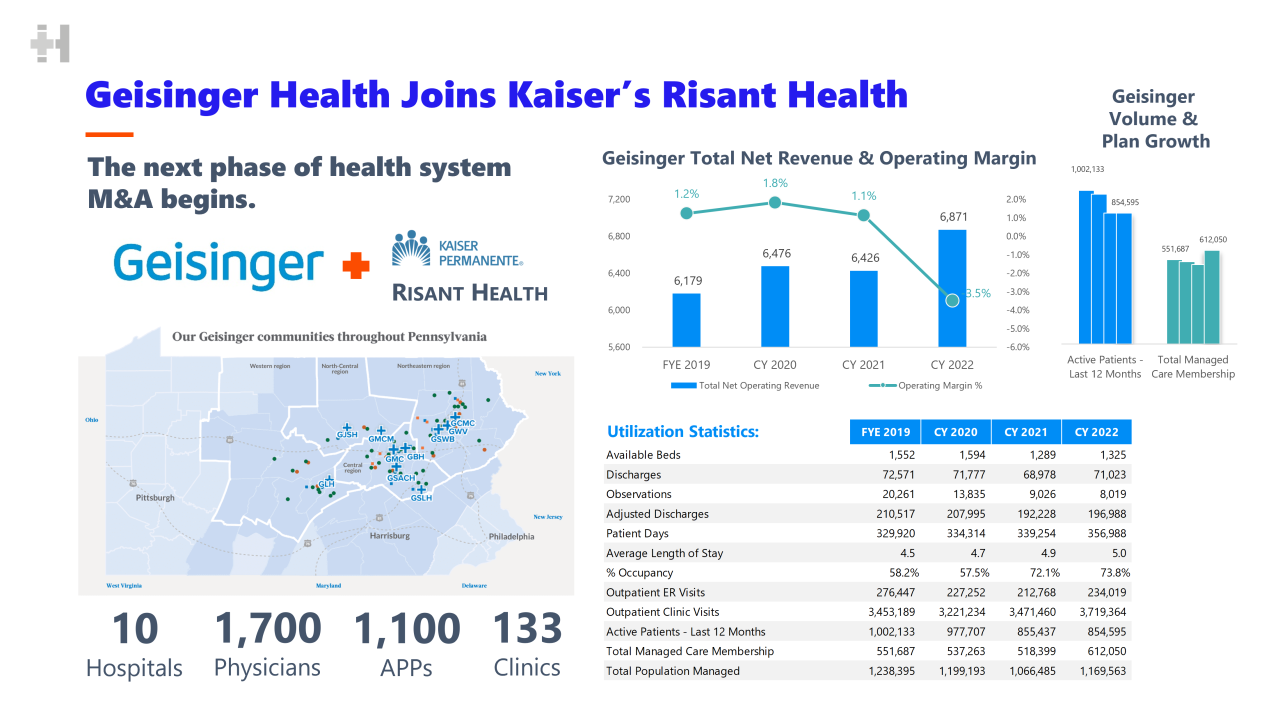
Geisinger Health System’s Influence and Comparison
Geisinger Health System, a large integrated health system in Pennsylvania, presents an interesting case study when compared to Kaiser Permanente. Both are large, integrated systems, but their approaches and market positions differ significantly. Analyzing Geisinger’s performance and strategies offers valuable insights into the competitive landscape and potential future challenges for Kaiser Permanente.Geisinger’s Competitive Position and Operating Margin Compared to Kaiser PermanenteGeisinger operates primarily in a geographically concentrated area of Pennsylvania, facing competition from other large health systems and smaller independent practices.
Their integrated model, emphasizing preventative care and population health management, is a key differentiator. Direct comparison of operating margins between Geisinger and Kaiser is difficult due to limited publicly available data on Geisinger’s financials and the inherent differences in their accounting practices and geographic markets. However, both organizations generally aim for a positive and sustainable operating margin, reflecting efficiency and financial stability within their respective market contexts.
Analyzing publicly available information, like annual reports where accessible, could provide a more concrete comparison, but a direct numerical comparison is not feasible given data limitations.Areas of Synergy and Competition Between Kaiser and GeisingerWhile geographically distant, Kaiser and Geisinger share a focus on integrated care and population health management. This creates potential areas of synergy in research collaborations, data sharing (with appropriate privacy protections), and the development of innovative care delivery models.
However, they also compete indirectly in the pursuit of national best practices and attracting top talent. Both organizations may seek to attract the same specialists or researchers, leading to a competitive dynamic in the recruitment landscape.Geisinger’s Strategies and Their Potential Influence on Kaiser’s Future PerformanceGeisinger’s emphasis on proactive care and data-driven decision-making could serve as a benchmark for Kaiser.
Geisinger’s success in implementing innovative programs like its ProvenCare model (a bundled payment program for specific conditions) demonstrates the potential for cost savings and improved quality of care. Kaiser could learn from Geisinger’s experience in adopting and scaling such programs, potentially improving their own operational efficiency and patient outcomes. Conversely, Kaiser’s extensive experience in managing a large, diverse population across multiple states could offer valuable insights to Geisinger, particularly in navigating the complexities of managing care across broader geographical areas and diverse demographics.
The success of Kaiser’s direct-to-consumer approach could also inform Geisinger’s strategic planning as they continue to expand their reach and services.
Kaiser’s second-quarter financial results, particularly the operating margin, are definitely interesting, especially considering the impact of Geisinger and Risant’s performance. This all comes against a backdrop of major legal shifts, like the Supreme Court’s decision to scotus overturns chevron doctrine healthcare , which could significantly reshape healthcare regulations and, in turn, influence future Kaiser financial reports. We’ll have to see how these legal changes play out on Kaiser’s bottom line in upcoming quarters.
Analyzing the “Risant” Factor (Assuming “Risant” is a relevant factor)
Let’s delve into the mysterious “Risant” factor and its impact on Kaiser Permanente’s second-quarter financial performance. While the precise nature of “Risant” remains undefined, we can explore potential interpretations and their consequences on operating margins. For the purpose of this analysis, we’ll assume “Risant” represents a significant, albeit unexplained, variable affecting Kaiser’s financial health.The significance of “Risant” in Kaiser’s financial results hinges on its potential to represent a wide range of influences, from unexpected shifts in patient demographics and treatment patterns to unforeseen changes in regulatory environments or the success (or failure) of a specific internal initiative.
Without a concrete definition, “Risant” serves as a placeholder for an unknown variable that requires further investigation to fully understand its impact. Its influence on operating margin during the second quarter is, therefore, speculative, dependent on the actual nature of the factor.
Risant’s Impact on Operating Margin
A positive “Risant” effect might reflect, for instance, unexpectedly high patient volumes due to a flu season less severe than anticipated, resulting in increased revenue and a higher operating margin. Conversely, a negative “Risant” effect could represent increased costs due to unforeseen supply chain disruptions affecting medical supplies, thereby decreasing the operating margin. This underscores the need for transparency and further investigation into the nature of “Risant.” The impact is directly proportional to the magnitude and direction of the effect of “Risant.” A large positive “Risant” effect could significantly boost operating margin, while a large negative effect could severely diminish it.
Scenario: Risant’s Potential Impact on Future Quarters
Let’s imagine “Risant” represents a new telehealth initiative. In the second quarter, the initiative was in its early stages, resulting in a modest, positive impact on the operating margin. However, in future quarters, as the program scales up and gains wider adoption, we might see a more significant positive impact. For example, reduced travel costs for patients and increased efficiency for Kaiser’s staff could contribute to improved operating margins.
Conversely, if the telehealth initiative experiences unexpected technical difficulties or low patient adoption, the “Risant” effect could become negative in subsequent quarters. This illustrates the importance of careful planning and ongoing monitoring of new initiatives.
Interpretations of Risant’s Influence
Different interpretations of “Risant” could lead to varied conclusions regarding its influence. One interpretation might focus on external factors, such as changes in government regulations impacting reimbursements or unexpected shifts in the overall healthcare market. Another interpretation might focus on internal factors, such as the efficiency of Kaiser’s operational processes or the success of specific cost-reduction initiatives. These varying interpretations necessitate a thorough investigation to accurately assess the true nature and impact of “Risant.” A robust data analysis, including a thorough review of financial records and operational data, is crucial to distinguish between these interpretations and arrive at a well-informed conclusion.
Deep Dive into Operating Margin Components
Source: slidemodel.com
Kaiser Permanente’s second-quarter operating margin provides a crucial insight into the health system’s financial health and operational efficiency. Understanding its components allows for a more nuanced assessment of the organization’s performance compared to previous quarters and industry peers. This analysis will dissect the key factors driving the operating margin, examining both revenue streams and expense categories.
Revenue Sources and Their Contribution
Kaiser Permanente’s revenue is derived from a diverse range of sources, including membership fees (premiums), payments from government programs like Medicare and Medicaid, and payments from commercial insurers. The relative contribution of each revenue stream can fluctuate based on changes in membership, payer mix, and the utilization of services. For instance, a higher proportion of Medicare patients might lead to lower average revenue per member, while a growth in commercial insurance contracts could boost overall revenue.
Analyzing the growth or decline in each revenue category is essential to understanding the overall change in operating margin. For example, a significant increase in membership fees might offset rising costs, contributing to a stable or even improved operating margin. Conversely, a decline in commercial insurance contracts could negatively impact the margin.
Expense Breakdown and Significant Changes, Kaiser second quarter financial results operating margin geisinger risant
The operating margin is significantly influenced by the system’s expenses. These expenses can be broadly categorized into several key areas: salaries and benefits for staff (including physicians, nurses, and administrative personnel), the cost of purchased services (e.g., pharmaceuticals, medical supplies, laboratory tests), capital expenditures (investments in facilities and equipment), and administrative and operating overhead. Comparing these expense categories to previous periods reveals areas of significant change.
For example, a substantial increase in pharmaceutical costs might be driven by the rising price of specific drugs or a change in the patient population’s medication needs. Similarly, a rise in salaries and benefits might reflect wage increases, increased staffing levels to meet growing demand, or changes in employee benefits packages. A detailed analysis of these changes is critical for understanding the fluctuations in operating margin.
Operating Margin Benchmarking
To effectively evaluate Kaiser Permanente’s operating margin, it’s crucial to compare it to industry benchmarks. This requires comparing the operating margin to those of similar large integrated healthcare systems. The benchmarks should be adjusted for factors such as payer mix, geographic location, and the specific services offered. A comparison reveals whether Kaiser’s performance is in line with, above, or below the industry average.
A lower-than-average operating margin might indicate areas needing improvement in cost control or revenue generation, while a higher-than-average margin suggests superior operational efficiency. The choice of benchmark comparison requires careful consideration of factors influencing variability in operating margins across the industry.
Revenue Growth and Operating Margin Relationship
The relationship between revenue growth and changes in operating margin isn’t always linear. While revenue growth typically contributes positively to the operating margin, it’s essential to consider the rate of expense growth. If expenses grow at a faster rate than revenue, the operating margin will decline, even with revenue growth. This relationship is often expressed as a percentage change, showing the rate of revenue increase versus the rate of expense increase.
For example, a 5% revenue growth coupled with a 7% expense growth would result in a decrease in the operating margin, regardless of the absolute revenue figures. Therefore, an analysis of both revenue and expense growth rates is essential for understanding the overall financial performance and the drivers behind changes in the operating margin.
Future Outlook and Strategic Implications
Source: cloudinary.com
Kaiser Permanente’s second-quarter results offer a mixed bag, prompting careful consideration of future strategic directions. While some areas showed strength, others highlighted challenges that require proactive management to maintain long-term financial health and competitiveness within the evolving healthcare landscape. Understanding these implications is crucial for investors, stakeholders, and the organization itself.The relatively stable operating margin, despite external pressures, suggests resilience in Kaiser’s integrated care model.
Kaiser’s second quarter financial results, particularly the operating margin, are a hot topic, especially considering the impact of Geisinger and Risant’s performance. This all comes against a backdrop of major political shifts, like the news that rfk jr confirmed hhs secretary robert f kennedy jr , which could significantly impact healthcare policy and, in turn, Kaiser’s future financial performance.
It will be interesting to see how these political changes affect Kaiser’s operating margin in the coming quarters.
However, the need for strategic adjustments is clear, particularly in light of increasing competition and shifting payer dynamics. Future success hinges on effectively navigating these complexities and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Potential Strategic Adjustments
The Q2 results suggest several strategic adjustments Kaiser Permanente might consider to bolster future performance. These adjustments are not mutually exclusive and should be considered in conjunction with one another. Successful implementation will require a coordinated approach across departments and a commitment to data-driven decision-making.
- Enhance Pricing Strategies and Contract Negotiations: Given increasing pressure on reimbursement rates, a more aggressive approach to contract negotiations with payers is warranted. This could involve leveraging Kaiser’s integrated delivery system to demonstrate value-based care and justify higher reimbursement rates. For example, Kaiser could highlight reduced readmission rates and improved patient outcomes as leverage in negotiations.
- Invest in Technology and Digital Health Initiatives: Continued investment in telehealth, remote patient monitoring, and other digital health technologies can enhance efficiency, improve patient access, and potentially reduce costs. This could involve partnering with technology companies or developing proprietary solutions. For instance, a successful telemedicine program could reduce the need for in-person visits, lowering overhead costs while maintaining or even improving patient satisfaction.
- Optimize Operational Efficiency: Identifying and eliminating redundancies within the organization can free up resources and improve profitability. This could involve streamlining administrative processes, leveraging data analytics to optimize staffing levels, and implementing lean management principles. A real-world example is the implementation of a centralized scheduling system that reduces wait times and improves patient flow.
- Expand Value-Based Care Models: Focusing on value-based care contracts, which reward providers for quality and outcomes rather than volume, can align incentives and potentially increase profitability. This requires robust data analytics capabilities to track and demonstrate improved patient outcomes. A successful example is a bundled payment program for hip replacements, where Kaiser demonstrates reduced costs and improved patient outcomes compared to fee-for-service models.
Kaiser’s second-quarter financial results, particularly the operating margin, are fascinating, especially when considering the impact of rising healthcare costs like Geisinger and Risant. A big factor influencing these costs is the ongoing medical coding worker shortage, which is why I was so interested to read about the ai powered solution to the medical coding worker shortage ; potentially, AI could help alleviate these pressures and ultimately improve Kaiser’s bottom line.
Further analysis of Kaiser’s Q2 results needs to account for these evolving workforce dynamics.
- Strategic Acquisitions or Partnerships: Exploring strategic acquisitions or partnerships to expand services or enter new markets could broaden Kaiser’s reach and diversify revenue streams. This requires careful due diligence to ensure alignment with Kaiser’s mission and strategic goals. A successful example would be the acquisition of a smaller healthcare provider with a strong presence in a desirable geographic area.
Implications for Investors and Stakeholders
The second-quarter results, while not disastrous, highlight the need for a proactive approach to managing risks and seizing opportunities. Investors should carefully monitor Kaiser’s progress in implementing strategic adjustments and assess the organization’s ability to adapt to the changing healthcare landscape. Stakeholders, including patients and employees, will be impacted by the decisions made in response to these results. Maintaining a focus on patient care and employee satisfaction is crucial for long-term success.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Several factors could negatively impact Kaiser’s financial performance in the coming quarters. These include continued pressure on reimbursement rates, increasing competition from other healthcare providers, rising labor costs, and the potential for unexpected increases in healthcare utilization. Effectively managing these risks requires careful planning and proactive risk mitigation strategies. For example, a sudden increase in hospitalizations due to a flu epidemic could significantly impact operating margins, highlighting the need for contingency planning.
Final Conclusion
So, there you have it – a whirlwind tour of Kaiser Permanente’s second-quarter financial performance, factoring in the competitive landscape, Geisinger’s influence, and the ever-present “Risant.” While some questions remain unanswered (especially surrounding “Risant”), the overall picture suggests a complex interplay of factors shaping Kaiser’s financial health. The future, as always, remains uncertain, but by understanding the past and present, we can better navigate the complexities of the healthcare industry and anticipate future trends.
Stay tuned for further updates!
Answers to Common Questions: Kaiser Second Quarter Financial Results Operating Margin Geisinger Risant
What exactly is the “Risant” factor?
The provided Artikel doesn’t define “Risant.” Further research is needed to understand its meaning within the context of Kaiser Permanente’s financial reports. It could be an internal code, a project, or an unforeseen event.
How does Kaiser Permanente compare to other major healthcare providers?
A full comparison requires more data. This analysis focuses on Geisinger, but a broader industry comparison would provide a more comprehensive understanding of Kaiser’s position.
What are the long-term implications of these Q2 results?
The long-term implications depend heavily on future performance and external factors. The Q2 results offer a snapshot, but not a complete prediction of future trends.