Medicaid Cuts Meeting Republican Budget Goals?
Medicaid cuts necessary meet republican budget target CBO – that’s the headline grabbing everyone’s attention, and rightfully so. This isn’t just about numbers on a spreadsheet; it’s about real people, real healthcare, and the very fabric of our social safety net. We’re diving deep into the proposed cuts, examining their potential impact on access to care, the economy, and the political landscape.
Get ready for a no-nonsense look at the complex realities behind this controversial budget proposal.
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) has projected a significant budget deficit under current spending levels. Republicans are proposing substantial cuts to Medicaid to help close this gap. This has ignited a fierce debate, pitting concerns about fiscal responsibility against the vital need for healthcare access for millions of low-income Americans. We’ll explore the details of the Republican budget proposal, analyzing the potential consequences of these cuts across different demographics and geographic locations.
We’ll also examine alternative approaches to controlling Medicaid spending that don’t involve direct cuts to benefits.
Medicaid Spending and the Republican Budget Proposal
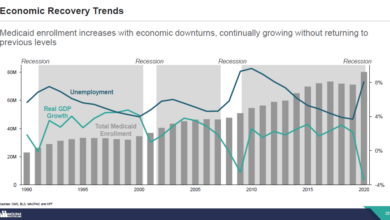
The debate surrounding Medicaid spending and its role in the federal budget is a complex and often contentious one. Understanding the current levels of spending, projected growth, and the implications of proposed cuts is crucial for evaluating the Republican budget proposal and its potential impact on millions of Americans. This analysis focuses on the factual aspects of the situation, avoiding partisan commentary.
Medicaid, a joint federal and state government program, provides healthcare coverage to millions of low-income individuals and families. Current spending on Medicaid is substantial, representing a significant portion of the overall federal budget. Projected growth in Medicaid spending is influenced by factors such as the aging population, rising healthcare costs, and changes in eligibility criteria. The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) regularly provides updated projections of Medicaid spending, which are vital for policymakers in making budgetary decisions.
Republican Budget Proposal’s Spending Reduction Targets
The Republican budget proposal typically aims to reduce federal spending across various programs, and Medicaid is often a target for significant cuts. These proposals usually involve a combination of strategies, such as altering eligibility requirements, reducing federal matching rates, and implementing block grants instead of the current open-ended funding mechanism. The specific targets for Medicaid spending reductions vary depending on the specific proposal, but they generally represent a substantial percentage decrease compared to projected spending under current law.
For example, a hypothetical Republican budget might propose a 10% reduction in Medicaid spending over the next five years, translating into billions of dollars in savings. The rationale behind these proposals often centers on fiscal responsibility and controlling the growth of the national debt.
CBO’s Projected Budget Deficit Comparison, Medicaid cuts necessary meet republican budget target cbo
The CBO plays a critical role in analyzing the budgetary implications of different policy proposals, including those impacting Medicaid. The CBO regularly publishes reports comparing the projected budget deficit under current law with the projected deficit under alternative scenarios, such as those incorporating proposed Republican budget cuts to Medicaid. These comparisons highlight the potential impact of proposed cuts on the overall federal budget deficit.
For instance, a CBO analysis might show that implementing a specific Republican Medicaid cut proposal would reduce the projected deficit by a certain amount over a specified timeframe, but this reduction would come at the cost of reduced healthcare access for some beneficiaries. The CBO also provides detailed analysis of the potential effects on various demographic groups.
Projected Impact of Medicaid Cuts on Various Demographics
The impact of Medicaid cuts is not uniform across all demographics. Cuts disproportionately affect certain populations, exacerbating existing health disparities.
| Demographic | Projected Impact (Hypothetical Example) | Potential Consequences | Geographic Impact (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elderly (65+) | Loss of coverage for 5% of beneficiaries | Increased hospitalizations, reduced access to preventative care | Higher impact in rural areas with limited healthcare access |
| Children | Reduced access to preventative care and immunizations | Increased rates of preventable illnesses | Disproportionate impact in states with high child poverty rates |
| Low-income Adults | Increased uninsured rate | Delayed or forgone healthcare, leading to worse health outcomes | Greater impact in states with stricter eligibility criteria |
| Individuals with Disabilities | Loss of access to crucial services | Reduced quality of life, increased institutionalization | Varied impact depending on state-level disability support programs |
Impact of Proposed Medicaid Cuts on Healthcare Access
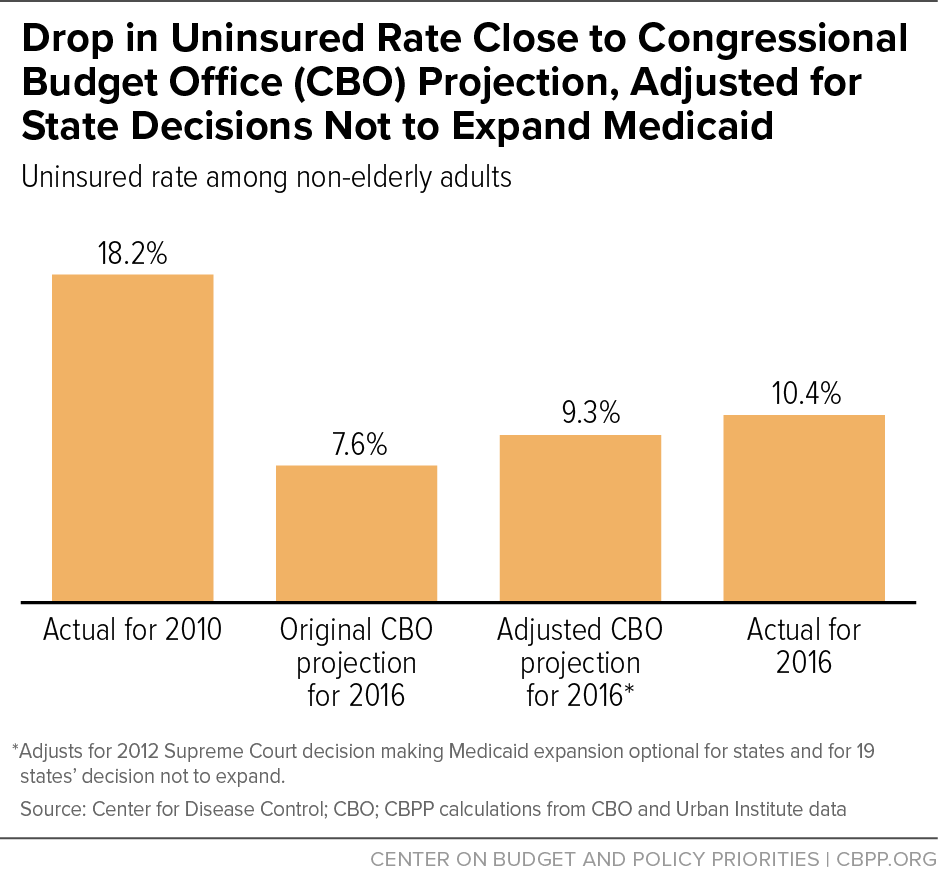
Source: cbpp.org
Proposed cuts to Medicaid funding represent a significant threat to healthcare access for millions of low-income Americans. These cuts would drastically reduce the availability and affordability of essential medical services, potentially leading to devastating consequences for individuals and communities alike. The impact will be felt across various aspects of healthcare, from preventative care to emergency services.Medicaid cuts will severely limit access to vital healthcare services for low-income individuals.
The reduced funding will ripple through the healthcare system, impacting hospitals, clinics, and individual providers. This will inevitably lead to longer wait times for appointments, fewer available providers, and potentially the closure of facilities in underserved areas. The consequences will be disproportionately felt by those already facing significant barriers to accessing quality care.
Impact on Specific Healthcare Services
Reduced Medicaid funding will directly impact a wide range of healthcare services. For example, preventative care, such as annual check-ups, screenings for chronic diseases (like diabetes and hypertension), and vaccinations, will likely be curtailed. Access to mental health services, substance abuse treatment, and specialized care for chronic conditions will also be significantly reduced. Furthermore, the availability of prescription medications, especially those with high costs, may be compromised, forcing individuals to choose between medication and other necessities.
Imagine a scenario where a diabetic patient, reliant on Medicaid for insulin, can no longer afford their medication due to reduced coverage. This is a realistic possibility under proposed cuts. Similarly, a child requiring regular asthma treatment might face interrupted care, leading to serious health complications.
Consequences of Reduced Access to Preventative Care
The reduction in preventative care access has particularly dire long-term health implications. Preventative care is crucial for early detection and treatment of diseases, significantly reducing the risk of severe illness and hospitalization later on. Without access to regular check-ups and screenings, many conditions will go undiagnosed and untreated until they reach a critical stage, necessitating more expensive and extensive treatment in the long run.
The CBO’s report on the Republican budget highlights the need for drastic Medicaid cuts, a move that’s sparking serious debate. Access to affordable healthcare is already a struggle for many, and these cuts could exacerbate the problem. This makes the expansion of options like the convenient humana centerwell primary care centers walmart even more critical, especially for those relying on Medicaid.
Ultimately, the impact of these proposed Medicaid cuts will be felt far and wide, potentially leaving many without necessary medical care.
This will not only place a heavier burden on individuals and their families but will also strain the overall healthcare system. For example, delayed diagnosis of hypertension can lead to heart attacks or strokes, resulting in far greater healthcare costs and diminished quality of life.
Potential Consequences for Vulnerable Populations
The potential consequences of limited access to healthcare for vulnerable populations are far-reaching and devastating.
- Increased rates of preventable hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
- Higher mortality rates, particularly among individuals with chronic conditions.
- Exacerbation of existing health disparities among racial and ethnic minorities and rural populations.
- Increased financial burdens on individuals and families due to unexpected medical expenses.
- Reduced workforce participation due to illness and disability.
- Increased strain on the overall healthcare system, leading to higher costs in the long run.
Alternative Approaches to Reducing Medicaid Spending
Source: cbo.gov
Reducing Medicaid spending without compromising access to care requires a multifaceted approach that moves beyond simple benefit cuts. This necessitates a shift towards strategies that improve efficiency, promote preventative care, and address the underlying social determinants of health that drive healthcare costs. Focusing on these areas can lead to long-term cost savings while maintaining or even improving health outcomes.
Improving Medicaid Program Efficiency
Streamlining administrative processes and reducing bureaucratic inefficiencies can free up significant funds. This could involve consolidating administrative functions, implementing more effective claims processing systems, and utilizing technology to improve data management and reduce paperwork. For example, states could explore using telehealth platforms to reduce the need for costly in-person visits, especially for routine check-ups or monitoring of chronic conditions.
The potential savings from reduced administrative overhead and increased efficiency can be substantial, freeing up resources for patient care. One example is the implementation of automated eligibility systems that have been shown to reduce administrative costs and improve the accuracy of enrollment.
Investing in Preventative Care and Health Promotion
Investing in preventative care and health promotion programs is a cost-effective way to reduce long-term healthcare expenditures. Early detection and intervention for chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease can prevent costly hospitalizations and long-term care needs. These programs could include initiatives to promote healthy lifestyles, such as smoking cessation programs, nutrition education, and increased access to physical activity.
Similarly, expanding access to preventive services like vaccinations and screenings can significantly reduce the incidence of preventable illnesses. The state of Oregon, for instance, has shown success in reducing hospital readmissions through a comprehensive program focused on post-discharge care coordination and patient education.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health
Social determinants of health, such as poverty, lack of access to healthy food, and unsafe housing, significantly impact health outcomes and drive up healthcare costs. Addressing these factors through targeted investments in social services can lead to significant long-term cost savings. This could include initiatives to improve housing conditions, expand access to healthy food options, and address transportation barriers to healthcare access.
For example, initiatives that provide housing assistance and support services for individuals experiencing homelessness have demonstrated a reduction in healthcare utilization and costs. Similarly, community-based programs that address food insecurity and provide nutrition education have been shown to improve health outcomes and reduce the need for expensive medical interventions.
Negotiating Lower Drug Prices
High prescription drug costs represent a substantial portion of Medicaid spending. States can explore strategies to negotiate lower drug prices, such as bulk purchasing agreements or utilizing generic medications whenever possible. Furthermore, promoting the use of biosimilars—similar to brand-name biologics but at lower cost—could significantly reduce expenses. Several states have successfully implemented bulk purchasing programs that have led to significant savings on prescription drugs.
The potential savings from these strategies can be substantial, freeing up resources to improve access to care for other services.
Policy Brief: Strategies for Medicaid Reform
A balanced approach to Medicaid reform requires a strategic combination of the approaches discussed above. A policy brief outlining potential strategies could focus on: (1) Implementing comprehensive efficiency improvements within Medicaid administration, (2) Expanding access to preventative care and health promotion programs, (3) Investing in initiatives to address social determinants of health, and (4) Implementing strategies to negotiate lower drug prices.
This multifaceted approach would ensure that budget concerns are addressed while maintaining, and potentially even improving, access to quality healthcare for Medicaid beneficiaries. The brief should also emphasize the need for ongoing evaluation and data-driven adjustments to ensure the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and maximize the return on investment. This iterative approach will be crucial for long-term sustainability and success.
Economic Consequences of Medicaid Cuts
Medicaid cuts, driven by budgetary constraints, have far-reaching economic consequences that extend beyond the immediate impact on healthcare recipients. These cuts create a ripple effect, impacting healthcare providers, local economies, and the overall national economy. Understanding these economic ramifications is crucial for evaluating the long-term sustainability and societal impact of such policy decisions.The healthcare industry is particularly vulnerable to Medicaid funding reductions.
Hospitals and clinics that rely heavily on Medicaid reimbursements face significant financial challenges. Reduced revenue streams directly translate to decreased capacity for providing care, potentially leading to job losses among healthcare professionals, administrative staff, and support personnel. This loss of employment impacts not only individual livelihoods but also contributes to reduced consumer spending within the community. In extreme cases, hospitals, particularly those in underserved areas, might be forced to close their doors, leaving communities without essential healthcare services.
Impact on Healthcare Providers and Employment
The reduction in Medicaid funding directly translates into lower reimbursements for healthcare providers. This shortfall forces hospitals and clinics to make difficult choices, often involving staff reductions. For example, a rural hospital heavily reliant on Medicaid patients might be forced to lay off nurses and doctors, reducing its capacity to serve the community. This reduction in healthcare workers contributes to a shortage of qualified professionals across the region, further limiting access to care.
The resulting job losses contribute to a decrease in local tax revenue and overall economic activity. The closure of a hospital, as seen in several rural communities following similar funding cuts, can have devastating consequences, leaving residents with limited or no access to essential healthcare services. These closures often result in population displacement as individuals seek healthcare elsewhere, further impacting the local economy.
The proposed Medicaid cuts to meet the Republican budget target, as projected by the CBO, are deeply concerning. These cuts could impact access to crucial healthcare, potentially even delaying treatment for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome. If you’re struggling with this painful condition, exploring non-surgical options is vital; check out this helpful resource on ways to treat carpal tunnel syndrome without surgery to learn more.
Ultimately, the impact of these budget decisions will ripple through the healthcare system, affecting everyone, regardless of their condition.
Ripple Effects on Local and National Economies
The economic consequences of Medicaid cuts are not confined to the healthcare sector. Reduced healthcare spending leads to decreased economic activity in the communities served by these facilities. Job losses in the healthcare sector translate into reduced consumer spending, affecting local businesses such as restaurants, retail stores, and other service providers. This domino effect can significantly weaken local economies, especially in areas with high Medicaid enrollment rates.
On a national level, reduced healthcare spending can negatively impact economic growth by lowering overall consumer demand and potentially increasing healthcare costs for the insured population due to market shifts and increased demand on private insurance.
Impact on the Overall Healthcare Market and Insurance Premiums
Reduced Medicaid funding can lead to a shift in the healthcare market. As Medicaid patients seek care elsewhere, the burden on private insurance providers may increase, potentially leading to higher premiums for individuals and families with private insurance. This is because a reduced number of providers willing to accept Medicaid patients leads to increased demand on private healthcare services, driving up costs.
The proposed Medicaid cuts to meet the Republican budget target, as projected by the CBO, are deeply concerning. It’s a stark contrast to the advancements in healthcare technology, like those discussed in an article about Salesforce’s healthcare AI initiatives led by Sean Kennedy: salesforce healthcare ai sean kennedy. These advancements, while promising, won’t help those left without access due to the cuts, highlighting the urgent need for a more equitable healthcare system.
Furthermore, an increased number of uninsured individuals due to Medicaid cuts can lead to an increase in uncompensated care for private hospitals, further increasing healthcare costs and potentially leading to higher premiums. The resulting instability in the healthcare market can discourage investment in healthcare infrastructure and innovation. This scenario was observed in several states after previous rounds of Medicaid cuts.
For instance, [insert specific example of a state and the impact of Medicaid cuts on premiums].
Visual Representation of Medicaid Funding and Consequences
Imagine a circular flow diagram. At the center is the Medicaid fund, depicted as a large reservoir. Arrows flow outwards representing the disbursement of funds to hospitals, clinics, and healthcare providers. From these providers, arrows flow back to the central fund, representing reimbursements for services. Another set of arrows flows from the providers to the local economy, representing salaries and expenditures.
Now, imagine a scenario where the reservoir (Medicaid fund) shrinks significantly due to cuts. The arrows flowing outwards become thinner, indicating reduced funding for providers. This leads to thinner arrows flowing back to the fund (reduced reimbursements) and thinner arrows flowing to the local economy (reduced employment and spending). The overall flow slows down significantly, illustrating the reduced economic activity and the negative consequences of Medicaid cuts.
The diagram clearly shows the interconnectedness between Medicaid funding, healthcare providers, and the overall economy, highlighting the ripple effects of reduced funding.
Political Implications of Medicaid Cuts: Medicaid Cuts Necessary Meet Republican Budget Target Cbo
Proposed Medicaid cuts carry significant political weight, potentially reshaping the political landscape and influencing upcoming elections. The debate surrounding these cuts highlights deep divisions within the electorate and exposes the complex interplay between healthcare policy, fiscal responsibility, and partisan politics.The ramifications extend far beyond budget numbers; they impact voters’ perceptions of candidates and parties, influencing electoral outcomes at local, state, and national levels.
The debate often centers around the balance between fiscal conservatism and the social safety net, with differing opinions on the effectiveness and necessity of Medicaid.
Arguments For and Against Medicaid Cuts
The debate over Medicaid cuts is sharply divided along partisan lines. Republicans generally advocate for cuts, framing them as necessary to control spending and reduce the national debt. They often propose reforms to streamline the program and encourage work, arguing that current levels of spending are unsustainable. Conversely, Democrats strongly oppose significant cuts, emphasizing the crucial role Medicaid plays in providing healthcare access to vulnerable populations, including children, seniors, and people with disabilities.
They argue that cuts would lead to devastating consequences, including increased healthcare costs for individuals and the broader economy. Independent voices often fall somewhere in between, suggesting targeted reforms rather than broad cuts, prioritizing cost-effectiveness and efficiency improvements.
Public Opinion on Medicaid Cuts Across Demographic Groups
Public opinion on Medicaid cuts varies significantly across demographic groups. Generally, there’s stronger support for Medicaid among lower-income individuals and those who have personally benefited from the program. Older Americans and those with pre-existing conditions also tend to express greater concern about potential cuts. Conversely, higher-income individuals and those who are generally healthier might be less concerned about the program’s impact.
These differing perspectives reflect the uneven distribution of benefits and burdens associated with Medicaid. Polling data consistently shows a strong correlation between individual experiences with the healthcare system and opinions on Medicaid cuts. For example, surveys consistently reveal that individuals who have personally relied on Medicaid are significantly more likely to oppose cuts than those who haven’t.
Potential Political Consequences of Implementing or Failing to Implement Cuts
The political consequences of Medicaid cuts are far-reaching. Implementing significant cuts could alienate key voting blocs, potentially costing the Republican party support among moderate voters and those concerned about healthcare access. This could lead to electoral losses in key states and districts where Medicaid plays a significant role in the healthcare system. Conversely, failing to implement proposed cuts could damage the Republican party’s credibility on fiscal issues, leading to dissatisfaction among conservative voters who prioritize budget reduction.
This could weaken the party’s standing with its base and create internal divisions. The political fallout from either decision will significantly influence the upcoming election cycle and shape future policy debates. The 2010 Affordable Care Act debates provide a historical parallel, illustrating the political ramifications of major healthcare policy changes. The contentious passage and subsequent challenges to the ACA demonstrate the potential for long-term political consequences related to healthcare policy.
The current debate around Medicaid mirrors these earlier dynamics, highlighting the politically sensitive nature of healthcare access and affordability.
Last Word
The proposed Medicaid cuts to meet the Republican budget target, as analyzed by the CBO, present a complex challenge. Balancing fiscal responsibility with the critical need for healthcare access requires careful consideration of the potential economic and social consequences. While reducing spending is a legitimate goal, the potential negative impacts on vulnerable populations and the healthcare industry cannot be ignored.
Ultimately, the debate highlights the need for innovative and sustainable solutions that ensure both fiscal health and the well-being of our communities. This isn’t just about dollars and cents; it’s about the health and future of millions.
Quick FAQs
What specific services might be affected by Medicaid cuts?
Services like preventative care (check-ups, screenings), mental health services, prescription drugs, and long-term care could all face reduced access or availability.
How might these cuts affect rural communities?
Rural areas often have fewer healthcare providers and limited access to begin with. Medicaid cuts could exacerbate these existing disparities, leading to even greater health inequities.
Are there any states that have successfully implemented cost-saving Medicaid reforms without cutting benefits?
Yes, some states have implemented managed care programs, focused on preventative care, and used technology to improve efficiency, achieving cost savings without significant benefit reductions. However, these models vary and may not be easily replicated nationwide.
What is the public opinion on these proposed cuts?
Public opinion is highly divided, with strong support and opposition depending on political affiliation and personal experiences with the healthcare system. Polls often show significant concern about the potential negative impacts of the cuts on vulnerable populations.