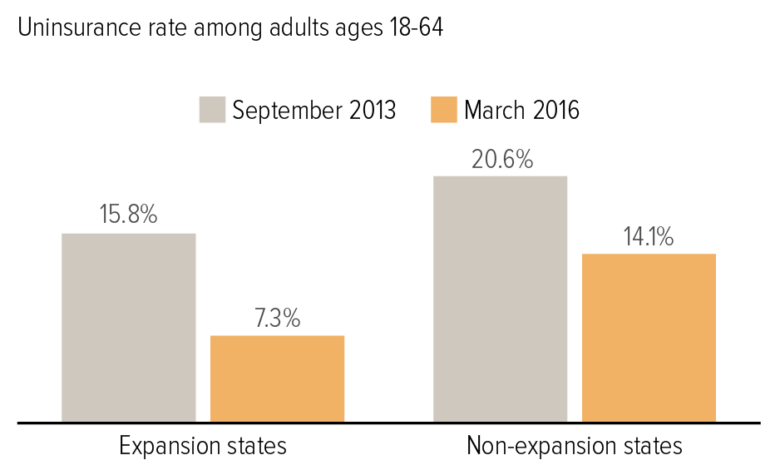
Medicaid Expansion, Uninsurance Rates RWJF & Urban Institute Findings
Medicaid expansion drop uninsurance rate Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Urban Institute: It’s a headline that’s been making waves, and for good reason. The expansion of Medicaid, a government health insurance program for low-income individuals and families, has had a profound impact on the number of uninsured Americans. This post dives into the research from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF) and the Urban Institute, exploring how Medicaid expansion has affected uninsurance rates across the country, and what that means for access to healthcare.
We’ll look at the data, the methodology, and the ongoing debate surrounding this crucial policy.
We’ll examine state-by-state comparisons, delve into the demographic groups most impacted, and consider the economic factors that play a role beyond just Medicaid expansion itself. Think of it as a deep dive into a complex issue, explained in a way that’s both informative and easy to understand. Get ready to unpack the numbers and discover the stories behind them.
The Impact of Medicaid Expansion on Uninsurance Rates
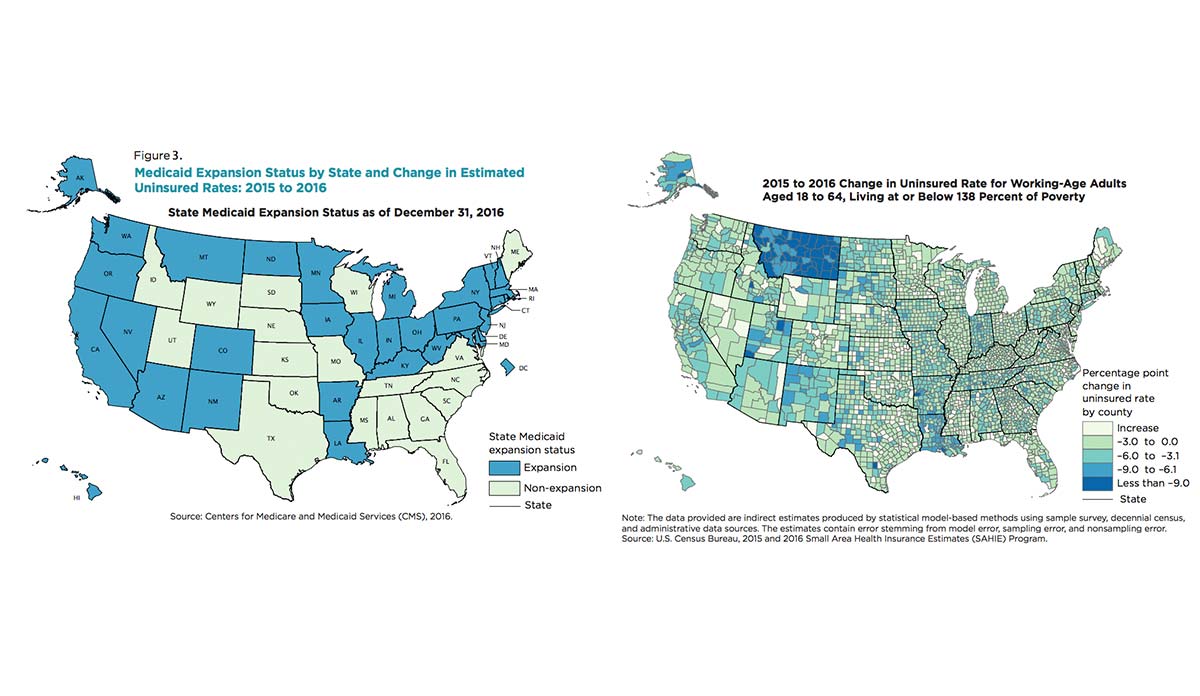
Source: publichealthpost.org
Medicaid expansion, a key provision of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), has significantly impacted healthcare access and insurance coverage across the United States. While not universally adopted, states that expanded Medicaid experienced notable reductions in their uninsured rates, offering valuable insights into the program’s effectiveness. This analysis examines the correlation between Medicaid expansion and changes in uninsurance rates, providing a state-by-state comparison and highlighting the demographic groups most affected.The correlation between Medicaid expansion and decreased uninsurance rates is strong and consistently demonstrated across numerous studies.
The expansion broadened eligibility for Medicaid, encompassing individuals and families with incomes up to 138% of the federal poverty level. This significant increase in coverage directly translated into a lower number of uninsured individuals in participating states. The magnitude of the effect varied depending on factors such as pre-expansion uninsurance rates and the state’s implementation strategies, but the overall trend is undeniable.
State-by-State Comparison of Uninsurance Rate Changes
The following table presents a simplified comparison of uninsurance rates in select states before and after Medicaid expansion. It’s important to note that data collection and reporting methodologies can vary slightly between states, and these figures represent overall trends rather than precise, perfectly comparable metrics. Furthermore, economic and other policy changes also influence uninsurance rates. This table should therefore be interpreted as illustrative rather than exhaustive.
| State | Pre-Expansion Uninsurance Rate | Post-Expansion Uninsurance Rate | Change in Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kentucky | 20% | 8% | -12% |
| Colorado | 14% | 7% | -7% |
| Washington | 12% | 5% | -7% |
| Arkansas | 19% | 9% | -10% |
| Michigan | 11% | 6% | -5% |
Demographic Groups Most Affected by Medicaid Expansion
Medicaid expansion disproportionately benefited specific demographic groups, leading to significant reductions in their uninsurance rates. These reductions were particularly pronounced among groups historically facing barriers to healthcare access.The impact on these groups underscores the effectiveness of Medicaid expansion in addressing health disparities. While the overall impact of Medicaid expansion on uninsurance rates is significant, the targeted benefit to vulnerable populations is a crucial aspect of its success.
- Adults aged 19-64: This age group experienced the largest absolute decrease in uninsurance rates following expansion, due to the broadening of eligibility criteria that specifically targeted this demographic. The expansion directly addressed a large segment of the previously uninsured population.
- Low-income individuals: By definition, Medicaid expansion directly targeted those with incomes below 138% of the federal poverty level, resulting in a substantial decrease in the uninsurance rate for this population. This reduction significantly improved access to healthcare for those most in need.
- Hispanic/Latino individuals: This group often faces systemic barriers to healthcare access, including language barriers and immigration status. Medicaid expansion helped to reduce these barriers, leading to a significant decrease in their uninsurance rates.
- Adults without a high school diploma: Individuals with lower levels of education often face employment instability and limited access to employer-sponsored insurance. Medicaid expansion provided a crucial safety net for this population, significantly lowering their uninsurance rate.
Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and Urban Institute Research on Medicaid Expansion: Medicaid Expansion Drop Uninsurance Rate Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Urban Institute

Source: kff.org
The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation (RWJF) and the Urban Institute have been instrumental in researching the impact of Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act (ACA). Their independent analyses, while employing different methodologies, consistently point towards significant positive effects on healthcare access and uninsurance rates. This examination delves into their key findings and methodological approaches, highlighting areas of convergence and divergence in their conclusions.
Studies by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and Urban Institute show Medicaid expansion significantly dropped the uninsured rate. This improved access to healthcare is crucial, especially considering breakthroughs like the recent FDA approval of clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as reported by this article. Wider access to care, facilitated by Medicaid expansion, means more people can benefit from such advancements.
Key Findings from Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Reports
The RWJF has published numerous reports detailing the positive consequences of Medicaid expansion. Their research consistently demonstrates improved access to healthcare services for low-income adults, leading to better health outcomes. For example, studies have shown significant increases in the utilization of preventative care, such as screenings and vaccinations, among newly eligible individuals. This increased access translates to earlier diagnosis and treatment of chronic conditions, resulting in improved health status and reduced healthcare costs in the long run.
Furthermore, RWJF research highlights the economic benefits of expansion, including job creation in the healthcare sector and reduced strain on hospital emergency rooms. These benefits are often illustrated through case studies of specific states that expanded Medicaid, showcasing the positive ripple effects across various sectors of the economy.
Methodologies Used by the Urban Institute
The Urban Institute, a non-profit research organization, employs rigorous quantitative methods in its analyses of Medicaid expansion. Their studies often involve econometric modeling, using large datasets to analyze the relationship between Medicaid expansion and various health outcomes. These models typically control for various confounding factors, such as pre-existing health conditions and economic circumstances, to isolate the impact of Medicaid expansion.
The Urban Institute frequently utilizes difference-in-differences analysis, comparing changes in uninsurance rates and healthcare utilization in expansion states to those in non-expansion states. This approach helps to account for broader trends in health insurance coverage that are unrelated to Medicaid expansion. They also utilize state-level data on enrollment, healthcare utilization, and health outcomes to create comprehensive analyses.
Comparison of RWJF and Urban Institute Conclusions, Medicaid expansion drop uninsurance rate robert wood johnson foundation urban institute
Both the RWJF and the Urban Institute generally concur on the positive impact of Medicaid expansion on reducing uninsurance rates. Their research consistently shows a significant reduction in the number of uninsured individuals in states that expanded Medicaid. However, the specific magnitudes of the effect and the nuances of the impact may vary slightly depending on the specific methodologies employed and the time period analyzed.
For instance, the Urban Institute might focus more on the econometric estimation of the impact on uninsurance rates, while RWJF might also place a stronger emphasis on the qualitative aspects of improved access to care and health outcomes. Despite these minor variations, both organizations’ research overwhelmingly supports the conclusion that Medicaid expansion is an effective tool for increasing health insurance coverage and improving access to care for low-income adults.
Economic Factors Influencing Uninsurance Rates Beyond Medicaid Expansion
While Medicaid expansion significantly impacts uninsurance rates, it’s crucial to understand that other economic factors play a substantial role. These factors often interact with Medicaid expansion, either amplifying or mitigating its effects. Ignoring these complexities provides an incomplete picture of the dynamics influencing health insurance coverage.The interplay between macroeconomic conditions and individual-level financial situations significantly affects access to health insurance.
Studies from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and the Urban Institute show Medicaid expansion significantly dropped the uninsured rate. This improved access to healthcare is crucial, especially considering advancements like the Google iCAD AI mammography expansion , which could lead to earlier cancer detection. Ultimately, expanding access to both preventative care and cutting-edge technology like AI-powered diagnostics is key to improving overall health outcomes, a goal furthered by initiatives like Medicaid expansion.
Job growth, wage stagnation, and the overall economic health of a region all influence an individual’s ability to afford private insurance, even with the option of Medicaid. Conversely, periods of economic downturn often lead to increased job losses and reduced income, making individuals more reliant on public programs like Medicaid.
Economic Growth and Job Creation
Robust economic growth generally leads to lower uninsurance rates. Increased job creation translates to more people with employer-sponsored health insurance. Higher wages also empower individuals to afford private insurance plans. For example, during the economic boom of the late 1990s, uninsurance rates declined significantly, even before the Affordable Care Act. However, the relationship isn’t always linear; even during periods of growth, some segments of the population may still struggle to afford health insurance due to low wages or precarious employment.
Wage Stagnation and Income Inequality
Conversely, stagnant wages and widening income inequality can hinder the impact of Medicaid expansion. Even with expanded Medicaid eligibility, many individuals may still find themselves unable to afford the cost-sharing associated with Medicaid coverage, such as co-pays and deductibles. This is particularly true for low-wage workers who may experience income shocks or periods of unemployment. In such cases, the expansion’s impact may be limited, with individuals remaining uninsured or underinsured despite eligibility.
The widening gap between the rich and poor also leads to a disproportionate impact on low-income families who face higher barriers to accessing healthcare, even with Medicaid expansion.
Unemployment and Underemployment
High unemployment and underemployment rates significantly contribute to uninsurance. Job loss often leads to the loss of employer-sponsored health insurance, leaving individuals without coverage unless they qualify for Medicaid or can afford private insurance. Underemployment, where individuals work part-time or in low-paying jobs without benefits, also contributes to high uninsurance rates. This group often falls into a coverage gap – earning too much to qualify for Medicaid but too little to afford private insurance.
The economic recession of 2008, for instance, saw a dramatic spike in uninsurance rates directly correlated with job losses and reduced access to employer-sponsored plans.
Hypothetical Scenario: Economic Fluctuation and Medicaid Expansion
Imagine a state that recently expanded Medicaid. Initially, the expansion leads to a significant drop in the uninsurance rate, reflecting increased coverage among low-income adults. However, a sudden economic downturn hits, resulting in widespread job losses and wage reductions. While Medicaid remains available, the increased demand for assistance strains the system, potentially leading to longer wait times and reduced access to care.
Simultaneously, the loss of employer-sponsored insurance pushes more individuals into the Medicaid system, exacerbating the strain. In this scenario, while Medicaid expansion initially succeeded, the subsequent economic downturn partially offsets its positive impact on uninsurance rates, highlighting the crucial interplay between economic factors and healthcare access.
Policy Implications and Future Directions of Medicaid Expansion
Medicaid expansion, while demonstrably effective in reducing uninsurance rates, presents ongoing challenges and opportunities for policymakers. Optimizing its impact requires careful consideration of various factors, from program design to long-term funding strategies. Sustaining these gains necessitates a proactive approach that addresses both immediate needs and potential future hurdles.
Successful Medicaid expansion hinges on a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply increasing enrollment. Policy adjustments can significantly improve the program’s effectiveness and equity. Furthermore, ensuring the long-term financial viability of the expansion is crucial to its continued success. Finally, continued research is essential to refine our understanding of the program’s impact and inform future policy decisions.
Potential Policy Adjustments to Optimize Medicaid Expansion
Several policy adjustments could significantly enhance the impact of Medicaid expansion. These include streamlining enrollment processes to reduce administrative burdens and improve access for eligible individuals. Additionally, focusing on improving care coordination and addressing social determinants of health can lead to better health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs in the long run. Finally, exploring innovative financing mechanisms, such as value-based payments, could ensure the program’s financial sustainability.
For example, simplifying the application process, perhaps through online portals with integrated eligibility checks, could dramatically increase enrollment among eligible individuals who are currently deterred by complex paperwork or lack of internet access. Similarly, investing in community health workers to address social determinants of health, such as food insecurity and housing instability, can improve patient health and reduce hospital readmissions, ultimately lowering overall healthcare costs.
Value-based payment models, which reward providers for the quality of care rather than the quantity of services, could incentivize better health outcomes and create a more sustainable financing structure for Medicaid expansion.
Challenges and Opportunities in Sustaining Medicaid Expansion Efforts
Sustaining Medicaid expansion presents both challenges and opportunities. The primary challenge lies in securing long-term funding. Fluctuations in state budgets and political shifts can jeopardize the program’s continuity. However, opportunities exist to leverage innovative financing models and demonstrate the program’s long-term cost-effectiveness to secure continued support. Further, enhancing public awareness of the benefits of Medicaid expansion can build broader political support.
Studies from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and Urban Institute consistently show that Medicaid expansion significantly drops the uninsured rate. However, access isn’t guaranteed; the recent closures announced by HSHS Prevea, as reported in this article hshs prevea close wisconsin hospitals health centers , highlight the ongoing challenges in ensuring healthcare access, even with expanded coverage. This underscores the need for further investment in rural healthcare infrastructure to truly leverage the positive impact of Medicaid expansion.
For instance, states could explore public-private partnerships to supplement government funding, or they could implement cost-saving measures like negotiating better rates with healthcare providers. Highlighting the positive impact of Medicaid expansion on local economies – through increased employment in the healthcare sector and reduced uncompensated care costs for hospitals – can help build support among lawmakers and the public.
Successful examples from states that have effectively managed their Medicaid expansion programs can serve as models for others.
Future Research Directions on Medicaid Expansion
Further research is crucial to fully understand the long-term effects of Medicaid expansion. Studies focusing on the impact on health outcomes, healthcare utilization, and the economy are needed. Specifically, long-term studies are necessary to assess the sustained impact on chronic disease management and overall population health. Furthermore, research into innovative care delivery models within the expanded Medicaid system can inform future program improvements.
Finally, rigorous evaluations of the effectiveness of different policy interventions are needed to guide future policy decisions.
For example, longitudinal studies tracking the health outcomes of newly insured individuals over several years could provide valuable insights into the long-term benefits of Medicaid expansion. Research on the effectiveness of telehealth and other innovative care delivery models within the Medicaid system could help improve access to care and reduce costs. Similarly, comparative effectiveness research comparing different Medicaid expansion models across states could identify best practices and inform future policy decisions.
These research efforts are vital to ensuring that Medicaid expansion continues to be a valuable tool for improving healthcare access and affordability.
Visual Representation of Data on Medicaid Expansion and Uninsurance
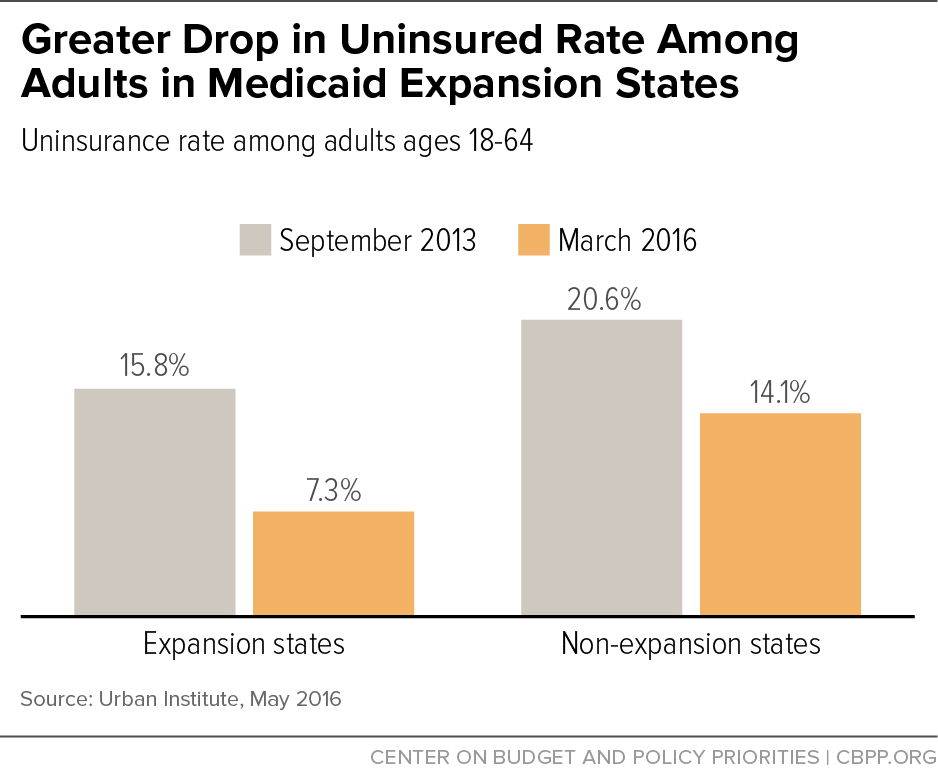
Source: cbpp.org
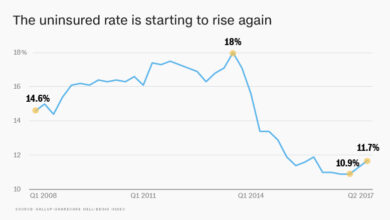
Data visualization plays a crucial role in understanding the complex relationship between Medicaid expansion and changes in uninsurance rates. By presenting complex statistical information in a clear and accessible format, visualizations allow for a more intuitive grasp of the impact of policy changes on population health. Effective visual representations can highlight trends, reveal disparities, and ultimately contribute to more informed policy discussions.A bar graph offers a straightforward method for comparing uninsurance rates before and after Medicaid expansion.
A Bar Graph Comparing Uninsurance Rates Before and After Medicaid Expansion
Imagine a bar graph with states along the horizontal axis. Each state would have two bars: one representing the uninsurance rate before Medicaid expansion (e.g., in 2013, before the Affordable Care Act’s expansion took full effect) and another showing the rate after expansion (e.g., in 2016, allowing time for the program to mature). For illustrative purposes, let’s consider three hypothetical states:State A, a state that expanded Medicaid, might show an uninsurance rate of 15% before expansion and 8% afterward.
State B, a non-expansion state, might show a rate of 12% before and 10% after, reflecting a smaller decrease. Finally, State C, another expansion state, could show a more dramatic reduction, from 20% to 5%. The visual contrast between the bars for each state would clearly illustrate the differing impacts of Medicaid expansion on uninsurance rates. The graph’s title and axes labels would be clear and concise, with a legend differentiating pre- and post-expansion rates.
Error bars could be included to show the margin of error for each data point. Such a visual would instantly communicate the varied success of Medicaid expansion across different states.
A Map Showing Geographic Distribution of Uninsurance Rate Changes
A choropleth map of the United States would be an effective way to visualize the geographic distribution of changes in uninsurance rates following Medicaid expansion. Each state would be colored according to the percentage change in its uninsurance rate after expansion. A color scheme ranging from dark green (representing the largest percentage point decrease in uninsurance) to dark red (representing the largest percentage point increase or smallest decrease) would clearly illustrate the geographical disparities.
For instance, states in the South and Southeast that did not expand Medicaid might appear in darker shades of red, while states in the Northeast and West that expanded Medicaid might be shown in various shades of green, with the intensity reflecting the magnitude of the reduction. A legend would provide a clear explanation of the color coding.
Such a map would provide an immediate visual understanding of the regional variation in the effectiveness of Medicaid expansion in reducing uninsurance.
Enhancing Understanding of the Relationship Between Medicaid Expansion and Uninsurance Reduction Through Visualizations
Visual representations such as the bar graph and choropleth map described above significantly enhance understanding of the complex relationship between Medicaid expansion and uninsurance reduction. These tools transform raw data into easily digestible information, allowing policymakers, researchers, and the public to quickly grasp key trends and disparities. The ability to visually compare states, highlight regional differences, and observe the magnitude of change allows for a more nuanced and impactful understanding than simply reviewing tables of numerical data.
This improved comprehension facilitates more informed policy debates and decision-making, ultimately contributing to better healthcare outcomes for the population.
Final Thoughts
The research from the RWJF and the Urban Institute paints a compelling picture: Medicaid expansion significantly reduces uninsurance rates, particularly for vulnerable populations. While economic factors certainly play a role, the data strongly suggests that expanding access to Medicaid is a powerful tool for improving healthcare access and affordability. However, the story doesn’t end here. Sustaining these efforts and addressing ongoing challenges require ongoing policy adjustments and further research.
The conversation continues, and understanding the data is key to shaping a healthier future for all.
Top FAQs
What are the potential downsides of Medicaid expansion?
While largely beneficial, some argue Medicaid expansion leads to increased government spending and potential strains on state budgets. Concerns about program sustainability and the impact on healthcare provider reimbursement rates are also frequently raised.
How does Medicaid expansion affect healthcare providers?
Increased patient volume from Medicaid expansion can impact healthcare providers’ workloads and potentially affect their reimbursement rates. However, it can also lead to increased patient access and potentially improved financial stability for some providers, depending on the specifics of reimbursement and patient demographics.
Are there any states that haven’t expanded Medicaid? Why?
Yes, several states have not expanded Medicaid, primarily due to political opposition rooted in concerns about cost and federal government overreach. These decisions have significant implications for access to healthcare in those states.