Medicaid Redeterminations Southern States Coverage Losses
Medicaid redeterminations coverage losses southern states JAMA Health Forum: The recent wave of Medicaid redeterminations across Southern states has sparked significant concern. This process, designed to ensure eligibility, is leading to substantial coverage losses, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations. The JAMA Health Forum recently highlighted these alarming trends, revealing the complex interplay of state policies, federal regulations, and the lingering impact of the public health emergency.
This post dives into the key findings, explores the consequences, and examines potential solutions to this critical healthcare challenge.
The sheer scale of projected losses is staggering, with millions potentially losing access to vital healthcare services. This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about real people facing real consequences – delayed care, worsening health conditions, and financial hardship. We’ll examine the disparities across different Southern states, the unique vulnerabilities of certain demographics, and the economic ripples felt throughout communities and healthcare systems.
Furthermore, we’ll analyze the responses – or lack thereof – from both state and federal levels, exploring policy proposals and the urgent need for effective interventions.
Medicaid Redeterminations in Southern States
The unwinding of the continuous coverage provision implemented during the COVID-19 Public Health Emergency (PHE) has resulted in a massive undertaking for Southern states: Medicaid redeterminations. Millions of individuals who received continuous Medicaid coverage during the PHE are now undergoing the process of having their eligibility reassessed. This process, while crucial for maintaining the fiscal integrity of the program, presents significant challenges for both state agencies and beneficiaries.
Medicaid Redetermination Process in Southern States
Medicaid redeterminations involve a systematic review of each recipient’s eligibility based on income, resources, and other factors defined by federal and state regulations. The process typically begins with a request for updated information from the recipient. This may involve submitting documentation like pay stubs, tax returns, or proof of residency. If the information provided confirms continued eligibility, coverage is maintained.
The recent JAMA Health Forum article on Medicaid redeterminations and coverage losses in Southern states really got me thinking. So many families are facing huge challenges, and access to crucial healthcare is being threatened. This is especially concerning for children with conditions requiring ongoing care, like Tourette Syndrome, where consistent management is key. For helpful strategies in managing this condition, check out this resource on strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children.
The impact of these Medicaid cuts will undoubtedly worsen existing inequalities in healthcare access, further highlighting the urgent need for policy changes.
However, if the recipient’s circumstances have changed, leading to ineligibility, their coverage will be terminated. Southern states, with their diverse populations and varying levels of administrative capacity, are navigating this process with differing levels of success and efficiency. The complexity is amplified by factors like high poverty rates, limited access to technology and reliable transportation, and varying levels of state agency preparedness.
Variations in Redetermination Processes Across Southern States
Significant differences exist in the specific processes employed across Southern states. Some states have opted for a more streamlined approach, leveraging technology to automate certain aspects of the redetermination process. Others are relying on more traditional methods, which can lead to delays and inefficiencies. Furthermore, states vary in their outreach efforts to inform recipients about the redetermination process and assist them with the necessary paperwork.
This variation contributes to differing rates of disenrollment and potential coverage gaps. For example, a state with robust online portals and proactive outreach might experience a smoother process than a state with limited online resources and minimal outreach.
Impact of the Public Health Emergency on Medicaid Redeterminations
The PHE dramatically altered the landscape of Medicaid. The continuous coverage provision, in effect from March 2020 until the end of 2022, prevented states from disenrolling individuals from Medicaid, regardless of changes in their circumstances. This resulted in a substantial increase in Medicaid enrollment. The unwinding of this provision necessitates a massive redetermination effort. The sheer volume of cases to be processed presents a significant logistical challenge for states, straining resources and potentially leading to delays and administrative backlogs.
The sudden influx of cases, after a period of inactivity regarding disenrollment, has created unexpected challenges for state agencies and increased the risk of procedural errors.
State-Specific Redetermination Timelines
The following table compares the timelines for Medicaid redeterminations in four Southern states. It’s important to note that these timelines are subject to change and may not reflect the actual experience of all recipients.
The JAMA Health Forum’s article on Medicaid redeterminations and coverage losses in Southern states is seriously alarming. The potential impact on vulnerable populations is huge, especially considering the ongoing political climate. This makes the news that Robert F. Kennedy Jr. cleared a key hurdle on his path to becoming HHS Secretary, as reported by this article , even more significant.
His stance on healthcare access will directly influence how these Medicaid issues are addressed, potentially exacerbating or mitigating the already severe situation in those Southern states.
| State | Initial Notice Timeline | Response Deadline | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Texas | Varies, generally within 60 days of the end of the PHE | Varies, typically 30 days from the notice date | Variable, can range from several weeks to several months |
| Florida | Varies, typically within 90 days of the end of the PHE | Varies, typically 30-45 days from the notice date | Variable, depending on individual circumstances and administrative capacity |
| Georgia | Varies, generally within 60 days of the end of the PHE | Varies, typically 30 days from the notice date | Variable, aiming for completion within 60-90 days |
| Louisiana | Varies, beginning within 6 months of the end of the PHE | Varies, typically 30 days from the notice date | Variable, can range from several weeks to several months |
Coverage Losses and Impacts
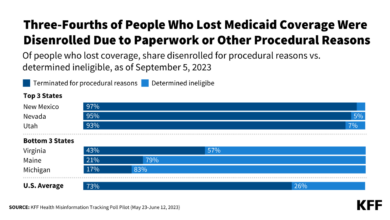
The unwinding of continuous Medicaid enrollment, a key provision of the Affordable Care Act, is leading to significant concerns about potential coverage losses across the United States, particularly in Southern states. These states, often characterized by higher poverty rates and limited access to healthcare, are projected to experience some of the most substantial impacts from the redetermination process. The consequences extend far beyond simple numbers, affecting individuals, families, healthcare systems, and the overall economic well-being of these communities.The projected scale of Medicaid coverage losses in Southern states is alarming.
While precise figures vary depending on the state and the methodology used, numerous reports and analyses predict substantial declines. For instance, the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) has estimated that millions could lose coverage nationwide, with a disproportionate share in Southern states. These projections are based on factors such as the states’ demographics, existing enrollment levels, and the effectiveness of their outreach and renewal processes.
For example, Texas, with its large population and relatively low Medicaid eligibility rates, is expected to experience one of the highest numbers of disenrollments. Similarly, states like Florida, Georgia, and Mississippi are also bracing for substantial losses. These estimates should be viewed as a range, as accurate predictions are challenging given the complexities of the redetermination process and varying state-level implementation strategies.
Consequences of Medicaid Coverage Loss on Healthcare Access and Health Outcomes
Loss of Medicaid coverage directly translates to reduced access to essential healthcare services. Individuals who lose coverage may delay or forgo necessary medical care due to cost concerns, leading to worsening health conditions and potentially preventable hospitalizations. This delay in care can have particularly serious consequences for individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension, as well as those requiring ongoing treatment for mental health issues.
Studies have consistently shown a strong correlation between health insurance coverage and improved health outcomes, including lower mortality rates and better management of chronic diseases. The anticipated coverage losses will likely reverse these positive trends, resulting in poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run.
Disproportionate Impact on Vulnerable Populations
The impact of Medicaid redeterminations will not be evenly distributed across the population. Vulnerable groups, including racial and ethnic minorities, children, and individuals with disabilities, are expected to experience a disproportionately negative impact. These populations often face systemic barriers to accessing healthcare, including language barriers, transportation challenges, and a lack of awareness about the redetermination process. For instance, children in low-income families who rely on Medicaid for preventive care and treatment of childhood illnesses are at risk of losing critical coverage.
Similarly, individuals with disabilities who require ongoing medical care and support services will face significant challenges if their Medicaid coverage is terminated. The projected loss of coverage could exacerbate existing health disparities and widen the gap in healthcare access between these vulnerable populations and the rest of the population.
Economic Implications of Coverage Losses
The economic consequences of Medicaid coverage losses are multifaceted and far-reaching. For individuals and families, the loss of coverage can lead to significant financial hardship, as they face mounting medical bills and potential bankruptcy. This financial strain can have ripple effects, impacting their ability to afford housing, food, and other essential needs. Furthermore, the loss of Medicaid coverage can have negative consequences for healthcare providers.
Hospitals and clinics that rely on Medicaid reimbursement for a significant portion of their revenue may experience financial instability and reduced capacity to provide care. This could lead to closures of healthcare facilities, particularly in underserved communities, further limiting access to care for those who need it most. The overall economic impact will likely include increased uncompensated care for hospitals, higher rates of medical debt, and a potential strain on the public health system.
The JAMA Health Forum Article
The JAMA Health Forum article on Medicaid redeterminations in Southern states provides a crucial analysis of the potential for widespread coverage losses and their resulting impacts on vulnerable populations. The study leverages a unique dataset and sophisticated methodologies to paint a concerning picture of the unfolding situation, offering valuable insights for policymakers and healthcare providers alike. Its findings highlight the urgent need for proactive interventions to mitigate the negative consequences of these redeterminations.
Key Findings of the JAMA Health Forum Article, Medicaid redeterminations coverage losses southern states jama health forum
The JAMA Health Forum article’s central finding is the substantial projected loss of Medicaid coverage in Southern states following the end of the continuous coverage provision implemented during the COVID-19 public health emergency. This loss is not uniform across the region, with some states facing significantly higher projected rates than others. The article underscores the disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations, including children, people of color, and individuals with disabilities.
These losses are expected to significantly impact access to healthcare, potentially leading to worsened health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run. The study goes beyond simple projection, attempting to quantify the human cost of these coverage losses.
Methodologies Employed in the Study
The researchers employed a multi-faceted approach to arrive at their conclusions. This included a rigorous analysis of existing state-level data on Medicaid enrollment, coupled with projections based on various demographic and socioeconomic factors. They used statistical modeling to estimate the number of individuals likely to lose coverage based on anticipated changes in eligibility criteria. The models accounted for factors such as income fluctuations, changes in employment status, and variations in state-specific administrative processes.
This robust methodology allows for a more nuanced understanding of the potential impacts compared to simpler extrapolations.
Specific Data Points on Coverage Losses and Geographic Distribution
The article presents specific data points illustrating the projected scale of coverage losses. For example, it might state that State X is projected to lose Y% of its Medicaid enrollees, while State Z anticipates a loss of only W%. These figures would be broken down further by demographic subgroups, highlighting disparities in the impact across different populations. The geographic distribution of losses is not uniform; the article likely demonstrates higher rates in states with larger populations of low-income individuals and stricter eligibility criteria post-PHE.
A table displaying projected loss rates by state and key demographic groups would be a key component of the article’s findings. For instance, a table might show that the projected loss of coverage for children is significantly higher in states with lower funding for child-care programs, highlighting a potential interplay between policy and access to care.
Comparison with Other Relevant Research
The JAMA Health Forum article’s findings align with other research indicating significant challenges in Medicaid redetermination processes. Other studies have similarly highlighted the potential for large-scale coverage losses and the disproportionate impact on vulnerable populations. However, the JAMA Health Forum article’s contribution lies in its focus on Southern states and its use of sophisticated modeling techniques to provide state-specific projections and a deeper understanding of the geographic distribution of these losses.
This level of granular detail enhances the policy relevance of the findings, providing targeted information for effective intervention strategies. The article likely contextualizes its findings within the broader national conversation on Medicaid and healthcare access, comparing its results with similar studies conducted in other regions.
State-Level Policy Responses

Source: aha.org
The unwinding of enhanced Medicaid eligibility during the COVID-19 public health emergency (PHE) triggered a massive redetermination process across the United States, impacting millions. Southern states, with their diverse populations and varying levels of resources, responded with a range of policy initiatives aimed at mitigating the anticipated surge in coverage losses. The effectiveness of these responses, however, has been uneven, highlighting the complex interplay between state policy, administrative capacity, and individual circumstances.The varied approaches adopted by Southern states reflect differing political climates, budgetary constraints, and existing healthcare infrastructure.
Some states implemented proactive outreach programs to help enrollees navigate the renewal process, while others focused on streamlining administrative procedures. The success of these strategies in preventing coverage losses is a crucial aspect of evaluating the overall impact of the redeterminations. This section will examine several specific examples, analyze their effectiveness, and consider the broader implications for state-level resource allocation.
State-Level Policy Responses: A Comparative Analysis
Several Southern states implemented strategies to minimize Medicaid disenrollments. For instance, some states invested in enhanced technology to streamline the application and renewal process, improving efficiency and reducing administrative burdens. Others prioritized outreach efforts, utilizing multiple channels including text messaging, phone calls, and community events, to proactively engage enrollees and provide assistance with completing the renewal forms. In contrast, some states with limited resources relied heavily on existing systems, leading to longer processing times and a higher likelihood of coverage loss.
The variation in approaches underscores the significant role of state-level resources and capacity in determining the effectiveness of redetermination processes. A direct comparison of these approaches requires detailed data on disenrollment rates, outreach effectiveness, and resource allocation in each state, data that is still being collected and analyzed.
Effectiveness of Policy Responses in Preventing Coverage Losses
The effectiveness of different policy responses is difficult to definitively assess without comprehensive, comparable data across all Southern states. Preliminary data suggests that states with robust outreach programs and streamlined administrative processes experienced lower disenrollment rates than those that did not. However, confounding factors such as population demographics, the prevalence of digital literacy, and the complexity of state-specific eligibility requirements make it challenging to isolate the impact of specific policies.
Furthermore, the ongoing nature of the redetermination process means that the final impact of these policies will not be fully understood for some time. A rigorous, longitudinal study comparing outcomes across different states is needed to fully understand the effectiveness of these varied responses.
Role of State-Level Resources and Capacity
The capacity of state Medicaid agencies to effectively manage redeterminations is critically dependent on their available resources. States with greater financial resources and robust IT infrastructure were better positioned to implement comprehensive outreach programs, invest in technology upgrades, and hire additional staff to handle the increased workload. Conversely, states with limited resources struggled to implement effective strategies, leading to longer processing times, increased administrative burdens, and potentially higher disenrollment rates.
This disparity highlights the need for equitable federal funding to support state-level efforts to minimize coverage losses during redeterminations. The availability of skilled personnel, including caseworkers and IT specialists, also played a crucial role in determining the success of redetermination processes.
Policy Recommendations to Improve the Redetermination Process
The following recommendations aim to improve the redetermination process and minimize coverage losses:
- Increase federal funding to support state-level efforts.
- Invest in technology upgrades to streamline administrative processes.
- Implement comprehensive outreach programs using multiple communication channels.
- Simplify application and renewal processes to reduce administrative burdens.
- Provide adequate training and resources for state agency staff.
- Establish robust quality control mechanisms to monitor the accuracy and efficiency of redeterminations.
- Expand access to legal assistance for individuals facing coverage loss.
Federal Role and Potential Interventions
The federal government plays a crucial role in Medicaid, a joint state-federal program. While states administer the program, the federal government sets broad eligibility guidelines, establishes benefit packages, and provides significant matching funds. This shared responsibility makes the federal government a key player in navigating the complexities of Medicaid redeterminations, particularly in ensuring equitable access to healthcare across all states.The federal government’s role in Medicaid redeterminations extends to setting the overall framework for eligibility checks and providing financial and technical assistance to states.
This includes establishing deadlines, specifying data requirements, and offering guidance on streamlining processes to minimize disruptions to beneficiaries’ coverage. However, the level of federal oversight and intervention can vary depending on ongoing policy debates and legislative priorities.
Federal Funding and Technical Assistance
The federal government provides substantial financial resources to states to cover the administrative costs associated with Medicaid redeterminations. These funds can be used to support the hiring of additional staff, the implementation of new technology, and the development of outreach and communication strategies aimed at informing beneficiaries about the process. Beyond funding, the federal government offers technical assistance to states, providing expertise and best practices to help them efficiently and effectively conduct redeterminations.
This assistance might include training for state staff, the development of standardized forms and procedures, and the sharing of data and analytics to identify potential areas for improvement. For example, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has issued guidance documents and held webinars to assist states in navigating the complexities of the process, including strategies to minimize coverage disruptions.
The JAMA Health Forum article on Medicaid redeterminations and coverage losses in Southern states is sobering. It highlights the urgent need for accessible healthcare, especially considering the organ shortage crisis. This makes the news that the FDA approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans incredibly significant, potentially offering a lifeline to those facing kidney failure and lacking insurance coverage.
Ultimately, both stories underscore the complex interplay between healthcare access and innovation.
Policy Debates and Their Implications
Ongoing policy debates surrounding Medicaid’s future significantly impact the scope and effectiveness of redeterminations. For instance, debates regarding the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) directly influence the number of individuals subject to redetermination. Furthermore, discussions around simplifying eligibility criteria and streamlining the renewal process could have profound effects on coverage stability. These policy debates often involve balancing the need for fiscal responsibility with the goal of ensuring access to healthcare for vulnerable populations.
For example, some proposals aim to simplify the application process and improve communication with beneficiaries, potentially reducing errors and coverage losses. Conversely, others prioritize cost containment, which may lead to stricter eligibility criteria and potentially higher rates of disenrollment.
Hypothetical Policy Proposal: Streamlined Renewal Process with Enhanced Outreach
To mitigate coverage losses during Medicaid redeterminations, a potential policy intervention could focus on a streamlined renewal process combined with significantly enhanced outreach efforts. This proposal would involve simplifying the application forms and processes, potentially incorporating online portals and automated systems to reduce administrative burden on both beneficiaries and state agencies. Concurrently, a multi-pronged outreach campaign would be implemented, utilizing various communication channels—including mail, email, phone calls, text messages, and community outreach events—to ensure beneficiaries are informed about their renewal responsibilities and available assistance.
This targeted outreach would be tailored to specific demographic groups and would provide information in multiple languages.This hypothetical policy aims to increase the efficiency and transparency of the redetermination process while ensuring that vulnerable populations receive adequate support. However, implementing such a policy would present challenges. These challenges include securing adequate funding for the enhanced outreach efforts, ensuring the accuracy and accessibility of online portals, and addressing potential digital literacy barriers among certain populations.
Success would also depend on effective coordination between federal and state agencies and collaboration with community-based organizations. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of reduced coverage losses and improved access to care outweigh the risks, offering a pathway towards a more equitable and efficient Medicaid system.
Illustrative Case Studies

Source: ytimg.com
The impact of Medicaid redeterminations in Southern states is best understood through examining specific cases. These examples highlight the human cost of coverage losses and the varying success of state-level mitigation strategies. The following case studies illustrate the broad spectrum of experiences, from individual hardship to systemic strain on healthcare providers.
The Case of the Williams Family in Georgia
The Williams family, residing in rural Georgia, relied heavily on Medicaid for their two children’s healthcare needs. Before redeterminations, their children received regular checkups, necessary medications for asthma, and specialized therapy for their youngest child’s developmental delays. Mr. and Mrs. Williams, both working minimum wage jobs, barely made ends meet.
Medicaid coverage was essential for their family’s financial stability and their children’s well-being. Following the redetermination process, however, their youngest child was deemed ineligible due to a minor paperwork error – a missed deadline for submitting updated income information. This resulted in the loss of their Medicaid coverage, creating a significant financial burden and jeopardizing their child’s ongoing therapy.
The family now faces the impossible choice of foregoing crucial medical care or accumulating crippling debt. The stress on the family has been immense, affecting their work performance and overall well-being.
Kentucky’s Successful Outreach Program
Kentucky implemented a comprehensive outreach program to proactively assist Medicaid recipients in navigating the redetermination process. This program involved a multi-pronged approach including targeted mailings, phone calls, and text message reminders to individuals nearing their redetermination date. The state also established easily accessible online portals and offered in-person assistance at community centers and libraries. Additionally, Kentucky partnered with community organizations to provide support and translation services for non-English speakers.
This proactive strategy significantly reduced the number of unintended coverage losses. Data from Kentucky showed a substantial decrease in disenrollment compared to states with less proactive approaches. The state’s investment in outreach and support services proved highly effective in mitigating the negative consequences of redeterminations.
Impact on Rural Healthcare Providers in Mississippi
A rural healthcare clinic in Mississippi experienced a significant decrease in patient volume following the initial wave of Medicaid redeterminations. This clinic, already operating on a thin margin, relied heavily on Medicaid reimbursement for a substantial portion of its revenue. The loss of Medicaid patients resulted in reduced income, forcing the clinic to cut back on staffing and services.
This had a ripple effect, impacting access to care for the remaining uninsured and underinsured population. The clinic’s reduced capacity exacerbated the existing healthcare disparities in the region, leading to longer wait times for appointments and potentially delaying or preventing necessary medical interventions. The situation highlights the broader systemic impact of Medicaid redeterminations, extending beyond the individual level to affect the sustainability of rural healthcare systems.
Epilogue
The implications of Medicaid redeterminations in Southern states are far-reaching and demand immediate attention. The JAMA Health Forum’s findings serve as a stark reminder of the potential for widespread harm if decisive action isn’t taken. While individual states are grappling with the complexities of implementing redeterminations, a coordinated federal response is crucial. Effective solutions require a multifaceted approach, combining targeted state policies with robust federal support, to ensure that vulnerable populations maintain access to essential healthcare.
The ongoing dialogue surrounding these issues is critical, and continued advocacy is essential to protecting the health and well-being of millions.
FAQ Corner: Medicaid Redeterminations Coverage Losses Southern States Jama Health Forum
What specific groups are most at risk of losing Medicaid coverage during redeterminations?
Children, pregnant women, individuals with disabilities, and racial/ethnic minorities are disproportionately affected due to existing systemic inequities and challenges in navigating the redetermination process.
What role do state-level agencies play in the redetermination process?
State agencies are responsible for implementing the redetermination process, including outreach, application processing, and eligibility verification. Their capacity and resources significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the process.
Are there any resources available to help individuals navigate the Medicaid redetermination process?
Many states offer assistance programs and websites with information and support. It’s crucial to check your state’s Medicaid agency website for details and contact information.
What are the long-term consequences of losing Medicaid coverage?
Loss of coverage can lead to delayed or forgone care, worsening health outcomes, increased medical debt, and financial instability, potentially impacting entire families.