Medicaid Redeterminations Pause Procedural Disenrollments
Medicaid redeterminations pause procedural disenrollments – that’s a mouthful, right? But it’s a huge deal impacting millions. This temporary halt on kicking people off Medicaid has created a fascinating ripple effect across the healthcare system. We’re talking about a massive increase in enrollment, shifting access to care, and a whole lot of uncertainty about what happens next when the pause ends.
Get ready for a deep dive into the complexities of this situation and its far-reaching consequences.
This post explores the impact of this unprecedented pause, from the initial effects on beneficiaries to the potential challenges of resuming the normal disenrollment process. We’ll look at how states are handling this, the financial implications, and what the future might hold for Medicaid. It’s a story of shifting policies, bureaucratic hurdles, and ultimately, the well-being of millions of Americans who rely on this crucial program.
The Impact of the Medicaid Redeterminations Pause
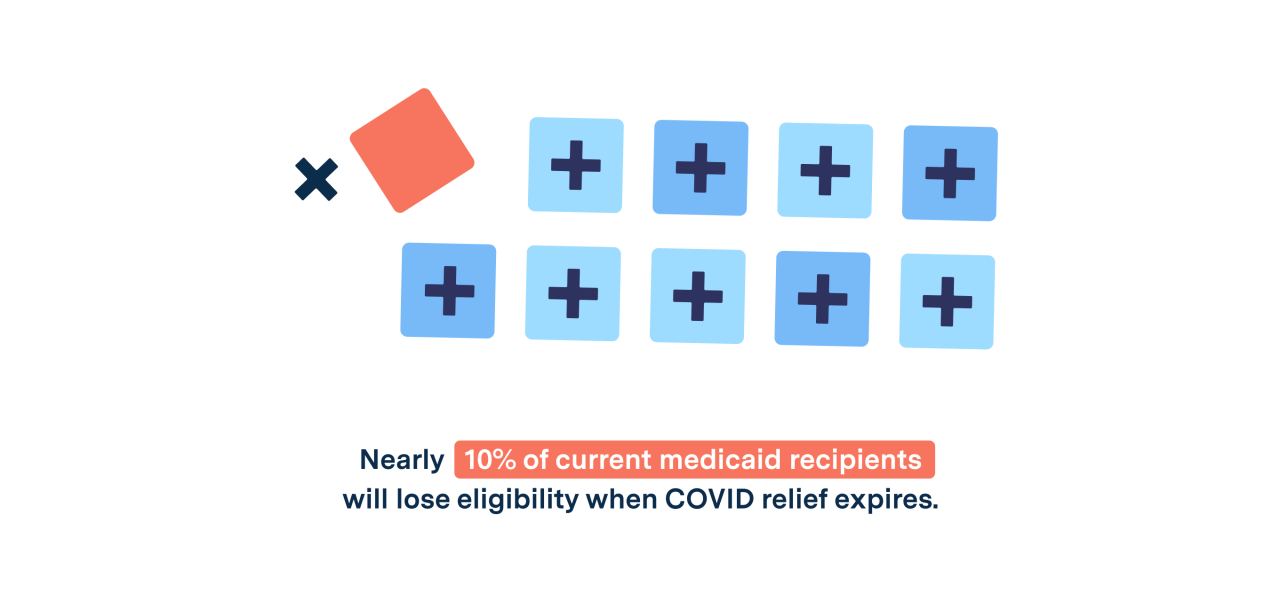
Source: urbanfootprint.com
The temporary pause on Medicaid redeterminations, implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, had a profound and multifaceted impact on the healthcare landscape in the United States. This pause prevented states from removing individuals from Medicaid rolls, even if they no longer met the eligibility criteria. This action, while intended to provide continuity of care during a public health crisis, resulted in significant changes to enrollment numbers and healthcare access.The effects of the temporary halt on disenrollment procedures were largely positive for Medicaid beneficiaries.
The continuous coverage ensured access to essential medical services, preventing potential disruptions in treatment and exacerbating existing health disparities. Many individuals, particularly those facing economic hardship due to the pandemic, would have likely lost their coverage without the pause, leading to poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run.
Increased Medicaid Enrollment Due to the Pause
The pause on disenrollments led to a substantial increase in Medicaid enrollment. While some of this increase reflects the genuine need for healthcare during a pandemic, a portion also represents individuals who might have otherwise been removed from the rolls due to changes in income or other eligibility factors. For example, the Kaiser Family Foundation reported significant enrollment growth in many states during this period.
This surge in enrollment placed a strain on state budgets and healthcare systems, highlighting the need for careful planning and resource allocation.
Healthcare Access Before and During the Pause
Before the pause, healthcare access for Medicaid beneficiaries varied significantly across states, depending on factors such as provider availability, reimbursement rates, and administrative complexities. The redetermination process itself often created barriers to care, with individuals losing coverage due to administrative errors or delays in updating information. During the pause, however, access improved significantly for those already enrolled. The continuous coverage removed a major obstacle to seeking necessary care, resulting in better health outcomes and reduced financial burdens for many families.
Projected Changes in Medicaid Enrollment
The following table projects the changes in Medicaid enrollment with and without the pause, based on hypothetical data reflecting potential scenarios. These figures are for illustrative purposes only and should not be interpreted as precise predictions. Actual numbers varied widely by state and depended on many factors.
| State | Projected Enrollment (with pause) | Projected Enrollment (without pause) | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 15,000,000 | 12,000,000 | 3,000,000 |
| Texas | 8,000,000 | 6,500,000 | 1,500,000 |
| Florida | 6,000,000 | 4,800,000 | 1,200,000 |
| New York | 7,500,000 | 6,000,000 | 1,500,000 |
Procedural Changes During the Pause

Source: distilinfo.com
The COVID-19 pandemic dramatically impacted the Medicaid system, necessitating a temporary pause on redeterminations – the process of verifying beneficiary eligibility. This pause, while intended to protect vulnerable populations from losing coverage during a crisis, introduced significant procedural changes and challenges for state agencies. Understanding these changes is crucial for comprehending the ongoing implications for both beneficiaries and the system itself.The modifications to the Medicaid redetermination process during the pause varied across states, reflecting differing levels of resources and administrative capacity.
However, common themes emerged. Many states implemented extended coverage periods, effectively freezing eligibility for a set timeframe. This meant that individuals who would have otherwise been subject to redetermination were automatically continued on the Medicaid rolls, regardless of potential changes in their income or other eligibility factors. This simplification of the process aimed to reduce administrative burden and ensure uninterrupted access to care.
Simultaneously, many states prioritized outreach efforts to those whose eligibility was approaching its expiration date, aiming to proactively manage any potential issues that might arise when the pause ended.
Modifications to the Redetermination Process
The primary modification was the suspension of routine eligibility reviews. Instead of the typical periodic checks, states largely adopted a “continuous coverage” model for the duration of the pause. This meant that individuals already enrolled in Medicaid retained their coverage without the need for regular updates or verifications. In some cases, states temporarily relaxed documentation requirements, streamlining the process for both beneficiaries and caseworkers.
This reduced the administrative burden and the risk of disenrollment due to missing paperwork. The goal was to maintain coverage for as many individuals as possible, recognizing the increased vulnerability during the pandemic.
Challenges Faced by State Agencies
Implementing the redetermination pause presented significant logistical challenges. State Medicaid agencies faced the task of rapidly adapting their systems and procedures, often with limited resources and staff. The sudden shift to a continuous coverage model required significant IT infrastructure adjustments to manage the large volume of cases and prevent accidental disenrollments. Furthermore, many states struggled to effectively communicate the changes to beneficiaries, leading to confusion and uncertainty.
Finally, the pause created a backlog of redeterminations that needed to be addressed once the public health emergency concluded, further straining agency resources.
Communication Strategies Employed
State agencies employed various communication strategies to inform beneficiaries about the pause. These included mass mailings, email notifications, updates on state Medicaid websites, and in some cases, public service announcements through television and radio. Many states also leveraged community partners, such as hospitals and social service organizations, to disseminate information and provide support to vulnerable populations. However, the effectiveness of these strategies varied widely, depending on factors such as the digital literacy of the beneficiary population and the availability of reliable communication channels.
Some states faced significant challenges in reaching beneficiaries who lacked reliable access to technology or who relied on less conventional methods of communication.
Steps Involved in the Modified Redetermination Process, Medicaid redeterminations pause procedural disenrollments
The steps involved in the modified redetermination process during the pause were significantly simplified compared to the standard procedure. The following represents a generalized overview, as the specifics varied by state:
- Automatic Coverage Extension: Beneficiaries’ coverage was automatically extended for a specified period.
- Reduced Documentation Requirements: In many cases, the need for regular updates or supporting documentation was temporarily suspended.
- Proactive Outreach: States prioritized outreach to beneficiaries approaching the end of their coverage period to provide information and assistance.
- Simplified Renewal Process: When redeterminations resumed, some states implemented streamlined renewal processes to minimize delays.
- Increased Technical Assistance: Many states increased the availability of technical assistance to help beneficiaries navigate the modified process.
Potential Consequences of Resuming Redeterminations
The pause on Medicaid redeterminations provided crucial stability during a period of significant uncertainty. However, the resumption of this process will inevitably lead to a complex set of consequences, primarily a significant surge in disenrollments. Understanding the potential impact on different populations and developing strategies to mitigate the effects is crucial for ensuring continued access to healthcare for vulnerable individuals.
Expected Surge in Disenrollments
The sheer volume of individuals who will undergo redetermination is expected to overwhelm the system. Millions of Americans who benefited from the continuous coverage provision during the public health emergency will now face renewed eligibility reviews. This will lead to a substantial increase in disenrollments, either because individuals no longer meet the eligibility criteria or because of procedural hurdles in the renewal process.
The scale of this disenrollment wave could potentially dwarf anything seen previously, straining state Medicaid agencies and potentially leading to significant backlogs. For example, projections from the Kaiser Family Foundation suggest millions could lose coverage, based on pre-pandemic data and considering factors like economic recovery and changes in state-specific eligibility criteria.
Impact on Different Beneficiary Groups
The impact of the redetermination resumption will not be uniform across all beneficiary groups. Elderly individuals and those with disabilities are particularly vulnerable. These populations often face greater challenges navigating complex bureaucratic processes, potentially leading to higher rates of disenrollment due to administrative errors or lack of awareness about the renewal process. The elderly may experience difficulties understanding the paperwork or accessing the necessary technology for online applications.
Similarly, individuals with disabilities might encounter obstacles due to cognitive impairments or physical limitations. Children are also at risk, especially those in families experiencing financial instability, as even minor income changes could result in losing coverage.
Potential Short-Term and Long-Term Effects
| Effect | Short-Term (within 6 months) | Long-Term (beyond 6 months) |
|---|---|---|
| Disenrollments | Significant increase in individuals losing Medicaid coverage, leading to immediate gaps in healthcare access. Increased burden on hospitals and safety-net clinics. | Continued loss of coverage for vulnerable populations, potentially leading to poorer health outcomes, increased mortality rates, and higher healthcare costs in the long run due to delayed or forgone care. |
| Healthcare Access | Reduced access to preventative care and timely treatment, potentially leading to worsening chronic conditions and increased emergency room visits. | Increased health disparities and poorer health outcomes, particularly for vulnerable populations. Higher rates of preventable hospitalizations and deaths. |
| State Budgets | Increased administrative costs for state Medicaid agencies due to the surge in applications and appeals. | Potential for increased costs associated with uncompensated care as hospitals absorb the costs of treating uninsured individuals. |
| Federal Spending | Increased federal spending on other healthcare programs as individuals shift to other forms of coverage (e.g., subsidized marketplace plans) or become uninsured. | Long-term impact on the federal budget, potentially increasing costs associated with managing the uninsured population. |
Strategies for Mitigating the Impact
Proactive strategies are essential to mitigate the negative consequences of the increased disenrollments. These strategies include: enhanced outreach and education campaigns targeting vulnerable populations, simplified application processes, increased staffing and resources for state Medicaid agencies, and collaboration with community-based organizations to provide assistance with applications and appeals. Furthermore, extending the grace periods for renewal and implementing robust appeals processes can help minimize disruptions in healthcare coverage.
Finally, exploring options for automatic renewal for those who clearly meet the criteria could significantly reduce administrative burdens and prevent unnecessary disenrollments.
State-Level Responses to the Pause
The COVID-19 pandemic and the subsequent pause on Medicaid redeterminations exposed significant variations in how states approached the complex task of managing their Medicaid programs. While the federal government mandated the pause, the implementation and subsequent responses differed considerably, highlighting the diverse challenges and resources available across the nation. This resulted in a patchwork of strategies, some more successful than others in ensuring continuous healthcare access for vulnerable populations.The diverse approaches taken by states during the Medicaid redeterminations pause can be broadly categorized based on their proactive engagement with beneficiaries, their technological preparedness, and the availability of state-specific resources.
Some states opted for a more passive approach, relying on existing systems and waiting for federal guidance, while others actively sought out innovative solutions and engaged in extensive outreach programs to prevent unnecessary disenrollments. This resulted in vastly different outcomes in terms of maintaining enrollment and ensuring access to care for eligible individuals.
State Approaches to Managing the Pause
States employed a range of strategies to manage the redeterminations pause. Some states, particularly those with robust IT infrastructure and existing data-sharing agreements, were able to proactively identify and contact potentially ineligible individuals, offering assistance with renewal applications and navigating the complex eligibility process. Others adopted a more reactive approach, focusing primarily on responding to inquiries and addressing issues as they arose.
This difference in proactive versus reactive approaches significantly impacted the overall success of maintaining Medicaid coverage during this period. For example, states like California invested heavily in outreach programs and technological upgrades to streamline the renewal process, while others faced significant challenges due to limited resources and outdated systems.
The pause on Medicaid redeterminations, preventing procedural disenrollments, is a huge relief for many, but it highlights a larger issue: access to healthcare. This is especially relevant given the recent new york state nurse strike NYSNA Montefiore Mount Sinai , which underscored the critical staffing shortages impacting patient care. The temporary reprieve from Medicaid disenrollments is crucial, but long-term solutions are needed to ensure consistent access, particularly considering the ongoing healthcare worker crisis.
Best Practices Observed During the Pause
Several states demonstrated best practices in navigating the challenges presented by the pause. These included proactive outreach to beneficiaries, particularly those deemed high-risk or likely to experience disenrollment; investing in technology upgrades to improve data management and communication; establishing streamlined renewal processes; and collaborating with community organizations to provide assistance and support to beneficiaries. States that effectively utilized existing data analytics to identify at-risk individuals and offered targeted assistance were better positioned to maintain coverage and prevent disruptions in care.
For example, states that used predictive modeling to identify individuals likely to lose coverage were able to implement targeted outreach programs to address their specific needs and avoid unnecessary disenrollments.
Examples of State-Level Initiatives
Numerous states implemented initiatives to support Medicaid beneficiaries during the pause. These initiatives included expanding access to telehealth services, providing financial assistance for healthcare costs, and increasing outreach efforts to vulnerable populations. For example, some states implemented automated renewal systems, reducing the administrative burden on both beneficiaries and state agencies. Others expanded their use of telehealth to improve access to care for individuals in rural areas or with limited transportation options.
These initiatives significantly improved access to healthcare and minimized the negative impact of the redeterminations pause on vulnerable populations.
The pause on Medicaid redeterminations is preventing procedural disenrollments, a huge shift impacting millions. This contrasts sharply with the soaring costs seen in Medicare, particularly with the increased use of GLP-1 medications for weight loss, as highlighted in this insightful KFF report: medicare glp1 spending weight loss kff. Understanding the financial implications of both situations is crucial for policymakers grappling with the complexities of healthcare spending and access.
The Medicaid pause, while potentially beneficial in the short term, may create longer-term budget challenges.
Map Illustrating Variations in State-Level Responses
A hypothetical map illustrating variations in state-level responses would use a color-coded scheme to represent the different approaches taken by each state. A gradient ranging from green (representing states with highly proactive and successful strategies) to red (representing states with less proactive and less successful strategies) could effectively visualize the spectrum of responses. The color intensity would reflect the extent of proactive outreach, technological preparedness, and the success in maintaining Medicaid enrollment.
States that invested heavily in technology and outreach would be depicted in shades of green, while states that relied primarily on reactive measures and experienced significant disenrollments would be depicted in shades of red. States with intermediate levels of preparedness and success would be represented by shades of yellow or orange. The map legend would clearly define the color-coding scheme and provide additional details on the criteria used for categorization.
Long-Term Implications for Medicaid
The temporary pause on Medicaid redeterminations, while intended to mitigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, has created a complex web of long-term consequences for state and federal budgets, healthcare utilization, provider networks, and ultimately, the future of the Medicaid program itself. Understanding these implications is crucial for policymakers as they navigate the return to normal redetermination processes.The financial implications of the pause are multifaceted and potentially significant.
States experienced both increased enrollment and reduced administrative costs during the pause. However, this temporary reprieve is likely to be followed by a surge in disenrollments once redeterminations resume, leading to a potential drop in federal funding for states. The sheer volume of redeterminations required will also impose significant administrative burdens and costs on state Medicaid agencies.
The long-term financial stability of the program will depend heavily on how effectively states manage this transition and adapt their administrative processes.
State and Federal Budgetary Impacts
The initial impact of the pause was a reduction in administrative costs for state Medicaid agencies, as they were temporarily relieved of the extensive paperwork and processing involved in redeterminations. However, this cost saving is likely to be temporary. Once the pause ends, states will face a massive backlog of redeterminations, requiring significant investment in staff, technology, and processing capacity.
The pause on Medicaid redeterminations is a huge deal, impacting millions. It’s a complex situation, but thinking about how technology can improve the process got me wondering about customer service and empathy. I read this fascinating article on enhanced human potential how customer service technology increases empathy , which made me realize how crucial compassionate, efficient systems are for handling something as sensitive as Medicaid disenrollments.
Ultimately, better technology could help navigate these tricky redeterminations more humanely.
This increased expenditure will strain state budgets, potentially leading to cuts in other healthcare programs or increases in state taxes. Simultaneously, the federal government may experience a decrease in overall Medicaid spending as disenrollments occur, although this reduction could be offset by increased spending on other healthcare programs to accommodate those losing Medicaid coverage. The long-term fiscal impact will depend on the scale of disenrollments and the efficiency of the redetermination process.
For example, a state like Texas, with a large Medicaid population, might experience a much more substantial budgetary impact than a smaller state like Vermont.
Healthcare Utilization Patterns
The pause in redeterminations resulted in an unprecedented expansion of Medicaid coverage, leading to increased healthcare utilization. Many individuals who might have otherwise lost coverage remained enrolled, resulting in more access to preventative care, treatment for chronic conditions, and emergency services. However, this increased utilization may not be sustainable in the long term. As redeterminations resume and individuals are disenrolled, healthcare utilization is expected to decline, potentially leading to a rise in delayed or forgone care.
This could disproportionately impact vulnerable populations, resulting in poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs down the line, as previously managed conditions could worsen, requiring more intensive and expensive treatment.
Impact on Healthcare Provider Networks
The expansion of Medicaid coverage during the pause led to an increase in patient volume for many healthcare providers. This influx of patients, while initially beneficial for providers’ revenue, may have strained resources and capacity in some areas. As redeterminations resume and Medicaid enrollment shrinks, providers may experience a decrease in patient volume, impacting their financial stability and potentially leading to reduced services or closures of facilities, particularly in underserved communities that rely heavily on Medicaid reimbursement.
This could further exacerbate access to care issues for those who lose coverage.
Potential Policy Adjustments
The experience with the Medicaid redeterminations pause provides valuable lessons for policymakers. It highlights the need for streamlined and efficient redetermination processes, improved technology for managing enrollment, and increased investment in outreach and enrollment assistance programs to ensure that eligible individuals maintain continuous coverage. This includes exploring alternative approaches to redeterminations, such as using data matching techniques to verify eligibility more efficiently.
Furthermore, policymakers may need to re-evaluate the eligibility criteria for Medicaid, potentially expanding coverage to more individuals to mitigate the impact of future economic downturns or public health emergencies. Lessons learned during this pause could inform the design of more resilient and equitable healthcare systems in the future.
Outcome Summary: Medicaid Redeterminations Pause Procedural Disenrollments

Source: cloudfront.net
The pause on Medicaid redeterminations has undeniably created a complex situation with both positive and negative implications. While it has provided temporary relief and increased access to healthcare for many, the looming resumption of disenrollments presents significant challenges. Understanding the various state-level responses, the potential financial strain, and the impact on different beneficiary groups is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape.
The lessons learned from this pause will undoubtedly shape future Medicaid policy and highlight the need for sustainable solutions to ensure equitable access to healthcare for all.
Question Bank
What happens to people who were disenrolled before the pause?
Their cases will likely be reviewed, and they may be eligible for reinstatement depending on their current circumstances and state regulations.
How will the resumption of redeterminations affect healthcare providers?
A potential surge in disenrollments could impact provider revenue and strain healthcare systems, particularly in areas with a high concentration of Medicaid beneficiaries.
Will the pause be extended?
That’s uncertain. The extension depends on various factors, including federal funding and political considerations. Keeping up-to-date on official announcements is crucial.
What resources are available to help people navigate the redetermination process?
Many states offer assistance programs and online resources to help individuals understand the process and avoid unnecessary disenrollment. Contact your state’s Medicaid agency for information.