Medicaid Redeterminations States Lessons Learned (KFF Survey)
Medicaid redeterminations states lessons learned kff survey – Medicaid redeterminations: states’ lessons learned KFF survey – Navigating the complex landscape of Medicaid redeterminations across the US is a challenge, but a crucial one for ensuring access to healthcare. This KFF survey sheds light on the varied approaches states have taken, the successes they’ve achieved, and the hurdles they’ve faced. We’ll delve into the key findings, exploring everything from enrollment impacts to technological innovations and effective communication strategies.
The Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) survey provides invaluable insights into the real-world experiences of states undergoing Medicaid redeterminations post-pandemic. We’ll examine how different states tackled the process, the successes and failures encountered, and the resulting impact on Medicaid enrollment and access to care. We’ll also look at the experiences of Medicaid recipients, the resource allocation challenges, and the role of technology in streamlining the process.
This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about the people whose lives are directly affected.
Overview of Medicaid Redeterminations

Source: globaljusticerc.org
Medicaid redeterminations, the process of reviewing eligibility for Medicaid benefits, have become a significant focus of attention recently, particularly given the unwinding of the continuous coverage requirement implemented during the COVID-19 public health emergency. This process, while crucial for maintaining the fiscal integrity of the program, presents considerable challenges for both states and beneficiaries. Understanding the mechanics and complexities of redeterminations is key to navigating this critical period for the Medicaid system.The process of Medicaid redetermination varies across states, reflecting differences in state-specific regulations, administrative capacity, and technological infrastructure.
Generally, it involves a review of a beneficiary’s income, assets, household size, and other factors to determine continued eligibility for Medicaid benefits. States employ a variety of methods, ranging from automated systems that compare data with other state and federal databases to more manual processes requiring extensive paperwork and human intervention. The level of technology and automation employed directly impacts the efficiency and accuracy of the redetermination process.
Medicaid Redetermination Timeline
The timeline for Medicaid redeterminations is not uniform across all states, but typically involves several key stages. First, a notice is sent to the beneficiary informing them of the need for a redetermination. The beneficiary then has a specific timeframe to submit updated information regarding their income, assets, and household composition. This is followed by a review period, during which state agencies verify the information provided and determine eligibility.
If eligibility is denied, the beneficiary has the right to appeal the decision, which often involves a further review process and potentially a hearing. The entire process, from initial notification to final appeal resolution, can take several months, and delays are common, especially in states with high caseloads and limited resources. For example, some states have reported backlogs of several months in processing redetermination applications, leading to significant delays in benefits.
Challenges and Opportunities Highlighted by the KFF Survey
The Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF) survey on state-level Medicaid redetermination experiences revealed several key challenges and opportunities. One significant challenge is the sheer volume of redeterminations required, potentially overwhelming state agencies with limited staff and resources. Another challenge is ensuring accurate and timely processing of applications, particularly given the complexities of verifying information and handling appeals. This is compounded by the potential for high disenrollment rates, impacting access to crucial healthcare services for vulnerable populations.
The survey also highlighted opportunities for states to improve their processes through enhanced technology, improved outreach and communication strategies, and streamlined appeals processes. For example, proactive outreach through text messaging and other digital channels could reduce delays and improve communication with beneficiaries. Furthermore, investing in technology that automates certain aspects of the process can significantly increase efficiency and reduce administrative burden.
States also need to ensure sufficient staff training to handle the complexities of the redetermination process and adequately support beneficiaries.
State-Level Variations in Approaches
The Medicaid redetermination process, while federally mandated, has seen significant variation in implementation across states. This stems from differences in state-specific populations, existing IT infrastructure, and the resources available to manage the complex logistical challenges involved. Understanding these variations is crucial to identifying best practices and areas for improvement in ensuring continuous access to vital healthcare coverage.The methods employed by states range from fully automated systems leveraging existing data matching technologies to more manual processes requiring significant human intervention.
Some states have prioritized proactive outreach to beneficiaries, while others have relied more heavily on passive renewal processes. This diversity in approach has led to a wide range of outcomes, highlighting the need for a more standardized, yet adaptable, national framework.
State-Specific Approaches to Medicaid Redeterminations
The following table compares the approaches of five states, illustrating the diversity of strategies and outcomes. It’s important to note that data on success rates and challenges are often self-reported and may not fully capture the complexities of each state’s experience. Further research is needed for a complete understanding of the nuances in each state’s implementation.
| State | Method | Success Rate (Estimated) | Challenges Faced |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | Combination of automated systems and human review, with significant emphasis on outreach and assistance programs. | High (estimates vary, but generally above 80%) | High volume of renewals, language barriers, technological challenges in data integration. |
| Texas | Primarily automated system, with less emphasis on proactive outreach. | Moderate (estimates around 60-70%) | High disenrollment rates due to lack of outreach, difficulties in verifying income and eligibility information. |
| Florida | Mixed approach with a significant human component, utilizing caseworkers for complex cases. | Moderate to High (estimates around 70-80%) | Staffing shortages, high caseloads, challenges in reaching beneficiaries with limited digital access. |
| New York | Significant investment in technology and automation, combined with robust outreach efforts. | High (estimates above 85%) | System capacity issues during peak periods, ensuring data accuracy across multiple systems. |
| Arizona | Automated system supplemented by targeted outreach to vulnerable populations. | Moderate (estimates around 70%) | Challenges in data integration with other state agencies, reaching geographically dispersed populations. |
Best Practices and Innovative Strategies
States that have successfully navigated the challenges of redeterminations often share common characteristics. Proactive outreach, particularly to vulnerable populations, has proven crucial in preventing unnecessary disenrollments. Investing in robust IT systems that can effectively manage large volumes of data and streamline the process is another key element. Finally, a collaborative approach, involving state agencies, community organizations, and healthcare providers, is essential for ensuring a smooth and equitable process.
Innovative strategies include leveraging technology for automated verification of income and eligibility, using multilingual communication channels, and partnering with community organizations to provide in-person assistance.
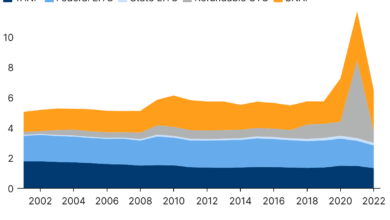
Impact on Medicaid Enrollment
Source: kff.org
The ongoing Medicaid redetermination process, triggered by the end of the COVID-19 public health emergency, has significantly impacted Medicaid enrollment numbers across the United States. States are experiencing varying degrees of disenrollment, with the implications for access to healthcare varying considerably depending on factors like the state’s approach to redetermination, its existing social safety net, and the characteristics of its Medicaid population.
Understanding these variations is crucial for assessing the overall impact on healthcare access and equity.The sheer scale of the redetermination effort is unprecedented. Millions of individuals are undergoing reviews of their eligibility, leading to a potential surge in disenrollments. This isn’t simply a matter of administrative processes; it directly impacts individuals’ access to essential medical services, including preventative care, chronic disease management, and treatment for serious illnesses.
The consequences of losing Medicaid coverage can be severe, ranging from delayed or forgone care to financial hardship due to mounting medical bills.
The KFF survey on Medicaid redeterminations revealed significant challenges for states. Understanding the impact on vulnerable populations is crucial, especially considering pre-existing conditions like high blood pressure, a major risk factor; learning about other risk factors that make stroke more dangerous helps us anticipate potential health crises resulting from lost coverage. These insights are vital as states navigate the complexities of Medicaid enrollment and ensure access to critical healthcare services.
State-Specific Enrollment Changes
The impact of redeterminations on Medicaid enrollment varies considerably from state to state. Some states, with proactive outreach and streamlined processes, have experienced relatively smaller drops in enrollment. Others, facing bureaucratic hurdles and limited resources, have seen significantly higher disenrollment rates. For instance, some states have reported relatively stable enrollment figures, demonstrating the effectiveness of their redetermination strategies. Conversely, other states have experienced substantial decreases, highlighting challenges in navigating the complex process.
These differences underscore the critical role of state-level policies and administrative capacity in mitigating the negative consequences of redeterminations.
Visual Representation of Enrollment Trends, Medicaid redeterminations states lessons learned kff survey
Imagine a bar graph showing Medicaid enrollment changes across five states (State A, State B, State C, State D, State E) over a three-year period. The x-axis represents the year (pre-redetermination, during redetermination, post-redetermination). The y-axis represents the number of Medicaid enrollees (in millions). State A, with a robust outreach program, shows a slight decrease during redetermination but maintains relatively stable enrollment afterwards.
State B shows a more substantial drop during redetermination, with a slower recovery afterwards. State C experiences a sharp decline followed by a minimal recovery. State D displays a gradual decrease throughout the entire period. State E shows a large initial drop but a subsequent stabilization and a modest increase. The different bar heights for each state visually represent the variation in the impact of redeterminations on enrollment.
The graph clearly illustrates the diverse experiences of states in managing the redetermination process and its impact on Medicaid enrollment.
Implications for Healthcare Access
Increased disenrollment from Medicaid due to redeterminations directly translates to reduced access to healthcare for vulnerable populations. This can lead to poorer health outcomes, increased hospitalizations, and higher healthcare costs in the long run. For example, individuals losing coverage may delay or forgo necessary medical care, leading to worsening chronic conditions or untreated acute illnesses. This can result in more expensive emergency room visits and hospitalizations down the line, ultimately increasing the overall healthcare burden on the system.
The potential for increased health disparities is also a significant concern, as disenrollment disproportionately affects marginalized communities who already face significant barriers to accessing quality healthcare.
Experiences of Medicaid Recipients
The KFF survey sheds light on the often-challenging experiences of Medicaid recipients navigating the redetermination process. The complexities of the system, coupled with individual circumstances, created significant hurdles for many individuals attempting to maintain their coverage. Understanding these difficulties is crucial for improving the process and ensuring equitable access to healthcare.
The survey revealed a range of difficulties faced by Medicaid recipients, which can be broadly categorized into issues with navigation, paperwork, and communication. These challenges often compounded each other, creating significant barriers to successful redetermination.
Navigation of the Redetermination Process
Many individuals struggled to understand the process itself. The information provided was often unclear, confusing, or inaccessible. This led to missed deadlines, incomplete applications, and ultimately, loss of coverage.
- Difficulty finding relevant information online or through state agencies.
- Lack of clear and concise instructions regarding the required documentation and steps involved.
- Inconsistent information across different channels, leading to confusion and frustration.
- Complex online portals that were difficult to navigate, especially for those with limited digital literacy.
Paperwork Requirements and Burden
The sheer volume and complexity of the paperwork required for redetermination proved overwhelming for many recipients. This was particularly challenging for individuals with limited literacy skills, disabilities, or those facing unstable living situations.
- Difficulty obtaining and providing the necessary documentation (e.g., income verification, proof of residency).
- Lengthy and complicated application forms that were difficult to understand and complete accurately.
- Lack of assistance in completing the paperwork, especially for individuals with limited English proficiency or disabilities.
- Concerns about the security and confidentiality of sensitive personal information.
Communication Challenges
Effective communication is vital for a smooth redetermination process. However, many recipients reported difficulties communicating with state agencies, resulting in delays, misunderstandings, and ultimately, loss of coverage.
- Difficulty reaching state agencies by phone or email.
- Long wait times for assistance.
- Inconsistent or unclear communication from state agencies regarding the status of their applications.
- Lack of communication in multiple languages or accessible formats for individuals with disabilities.
Successful Outreach and Support Programs
While many states faced challenges, some implemented successful outreach and support programs to help recipients navigate the redetermination process. These programs often included:
- Simplified application processes: Streamlining the application process and reducing the amount of paperwork required. For example, some states pre-filled applications with existing data, reducing the burden on recipients.
- Multi-lingual assistance: Providing application assistance and information in multiple languages to cater to diverse populations. This could involve translated materials and multilingual staff.
- Community-based outreach: Partnering with community organizations to provide in-person assistance with application completion and navigation. This included events and workshops in easily accessible locations.
- Technology-based solutions: Utilizing technology to improve communication and access to information. This might involve user-friendly online portals, text message reminders, and online chat support.
Resource Allocation and Staffing
The success of Medicaid redeterminations hinges critically on the resources—both financial and human—allocated to the process. States faced vastly different challenges in managing this complex undertaking, with resource allocation significantly influencing the efficiency and accuracy of their redetermination efforts. A sufficient budget and appropriately trained staff are not simply desirable; they are essential for a smooth and equitable process.The KFF survey revealed significant state-to-state variation in how resources were deployed for Medicaid redeterminations.
The KFF survey on Medicaid redeterminations highlighted significant state-level challenges. Access to healthcare, a key concern, could be dramatically impacted by advancements like the recent FDA approval of clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as reported here. This breakthrough, while promising, also raises questions about equitable access and affordability, issues directly relevant to the Medicaid redetermination process and its impact on vulnerable populations.
Some states invested heavily in technology upgrades, hiring additional staff, and providing extensive training, while others relied on existing infrastructure and personnel, leading to considerable differences in outcomes. This disparity underscores the crucial role of proactive planning and adequate funding in ensuring a successful redetermination process.
State Resource Allocation Strategies
Several distinct strategies emerged regarding resource allocation. Some states prioritized technology investments, developing sophisticated systems for managing applications and automating data verification. This approach, while initially costly, aimed to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error. Other states opted for a more labor-intensive approach, hiring temporary staff to handle the increased workload. This strategy, while potentially less expensive upfront, often faced challenges related to training and maintaining consistent performance across a large and potentially less-experienced workforce.
Finally, some states adopted a hybrid approach, combining technology upgrades with targeted staff augmentation.
Staffing Levels and Training
The number of staff dedicated to redeterminations varied dramatically across states. States with larger Medicaid populations and more complex eligibility criteria generally employed larger teams. However, even within similar populations, staffing levels differed significantly, reflecting differing approaches to resource allocation and priorities. Training programs also varied considerably. Some states offered extensive training programs covering all aspects of the redetermination process, including eligibility criteria, procedural guidelines, and effective communication techniques.
Others provided limited training, relying on staff to learn on the job. This difference in training directly impacted the quality and consistency of the redeterminations conducted.
Impact of Adequate Resource Allocation
Adequate resource allocation demonstrably impacted the efficiency and effectiveness of the redeterminations. States with sufficient funding and well-trained staff generally experienced higher rates of accurate and timely processing. They also reported lower error rates and fewer appeals. In contrast, states with limited resources faced longer processing times, higher error rates, and increased appeals, leading to delays in benefit determination and increased administrative burdens.
For example, State X, which invested heavily in both technology and staff training, processed 90% of redeterminations within the allotted timeframe, while State Y, with limited resources, only processed 60%. This difference highlights the direct correlation between resource allocation and successful redetermination outcomes.
Technological Solutions and Innovations
The Medicaid redetermination process, already complex, has been significantly impacted by the sheer volume of renewals required. This has highlighted the crucial role of technology in streamlining operations and ensuring accuracy. States have increasingly turned to technological solutions to manage the increased workload, improve communication with recipients, and ultimately, prevent unnecessary disenrollments. The adoption and effectiveness of these technologies vary widely, however, reflecting differences in state resources and infrastructure.The implementation of technological solutions has aimed to automate various aspects of the redetermination process, from initial data collection and verification to communication with applicants and final decision-making.
These advancements have the potential to significantly reduce administrative burdens, enhance efficiency, and improve the overall experience for both state agencies and Medicaid recipients. However, challenges remain, including ensuring equitable access to technology for all recipients and addressing potential privacy concerns related to data management.
State-Level Technology Adoption in Medicaid Redeterminations
Several states have leveraged technology to improve their Medicaid redetermination processes. These efforts range from simple improvements in data management systems to the implementation of sophisticated online portals and automated verification tools. The success of these initiatives depends on several factors, including the quality of the technology, the level of staff training, and the integration of technology across different state agencies.
Some states have chosen to partner with private technology companies to develop customized solutions, while others have opted for off-the-shelf software.
Examples of Technological Tools and Their Effectiveness
The following list details various technological tools employed and assesses their effectiveness based on available data and anecdotal evidence. Effectiveness is highly dependent on implementation and integration with existing systems.
The KFF survey on Medicaid redeterminations revealed some surprising state-level variations in enrollment changes. It made me think about how individual needs, like nutritional requirements, also differ. For example, I was reading this fascinating article on are women and men receptive of different types of food and game changing superfoods for women , which highlights how diverse dietary needs can be.
Understanding these individual differences, whether it’s healthcare access or nutritional preferences, is crucial for effective policy and support systems, just like in navigating the complexities of Medicaid redeterminations.
- Online Portals: Many states have developed online portals allowing recipients to update their information, submit documents, and track their application status. While generally well-received for convenience, some recipients, particularly those with limited digital literacy, may face challenges navigating these portals. Effectiveness varies based on user-friendliness and accessibility features.
- Automated Data Matching: Systems that automatically compare Medicaid application data with other state and federal databases (e.g., IRS, Social Security Administration) can significantly reduce manual verification efforts. This leads to faster processing times and reduces the risk of human error. However, data accuracy and privacy concerns need to be carefully addressed.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Some states are exploring the use of AI and ML to automate tasks such as document review and eligibility determination. While promising for increased efficiency and accuracy, the implementation of these technologies is still in its early stages and requires significant investment in infrastructure and expertise. The potential for bias in AI algorithms also needs careful consideration.
- SMS and Email Communication: States utilize SMS and email to send reminders, updates, and important information to recipients. This improves communication and reduces the likelihood of missed deadlines. Effectiveness depends on recipients’ access to these technologies and their preference for communication methods.
Successful State Implementations
While comprehensive data on state-level success is still emerging, several states have demonstrated promising results through technological innovation. For example, some states that have implemented robust online portals with user-friendly interfaces and multilingual support have reported higher rates of successful redeterminations and reduced administrative costs. States that have effectively integrated data matching systems have also seen improvements in processing speed and accuracy.
Specific examples, however, often remain confidential due to data privacy concerns or are not consistently reported across states.
Communication Strategies and Public Awareness: Medicaid Redeterminations States Lessons Learned Kff Survey

Source: amchp.org
The success of Medicaid redeterminations hinges critically on effective communication. States employed a variety of strategies to inform recipients about the process, ranging from simple mailers to sophisticated multi-channel campaigns. However, the effectiveness of these strategies varied significantly, impacting enrollment and creating challenges for both recipients and state agencies. Analyzing these communication strategies and identifying areas for improvement is crucial for ensuring equitable access to vital healthcare coverage.The methods used by states to reach Medicaid recipients were diverse.
Many relied heavily on mailed notices, often supplemented by email or text message reminders. Some states leveraged social media, public service announcements, and partnerships with community organizations. However, the KFF survey highlighted significant disparities in the sophistication and reach of these campaigns. Some states invested heavily in multilingual materials and outreach to underserved communities, while others relied on more limited, less accessible methods.
This resulted in a wide range of understanding and participation rates among Medicaid recipients.
Effectiveness of Communication Strategies
The effectiveness of state communication strategies varied considerably. While some states reported high rates of recipient understanding and timely participation, others struggled with low response rates and high disenrollment numbers due to missed deadlines or confusion about the process. Factors influencing effectiveness included the clarity and accessibility of materials, the frequency and timing of communications, and the availability of multilingual and culturally competent support.
States with more comprehensive, multi-channel campaigns, particularly those engaging community partners, tended to report better outcomes. For example, states using plain language materials and offering multiple communication channels (phone, email, text, in-person assistance) generally saw higher completion rates. Conversely, states relying solely on mailed notices often experienced higher disenrollment rates, particularly among recipients with limited literacy or digital access.
Improving Public Awareness and Outreach
Effective public awareness campaigns must be tailored to the specific needs and characteristics of the target population. This necessitates a multi-pronged approach that includes: Utilizing multiple communication channels to reach individuals with varying levels of digital literacy and language preferences. This might include mail, email, text, phone calls, social media, and partnerships with community organizations and trusted local leaders.
Developing clear, concise, and culturally appropriate materials that are easy to understand, regardless of literacy level or language background. Providing multiple avenues for assistance, including multilingual call centers, in-person assistance at community locations, and online resources. Targeting outreach efforts to specific vulnerable populations, such as elderly individuals, people with disabilities, and those with limited English proficiency. Partnering with community-based organizations and trusted local leaders to build trust and ensure effective dissemination of information.
Regularly monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of communication strategies and adapting them as needed based on feedback and data. These measures are crucial to improving both participation and understanding of the redetermination process.
Wrap-Up
The KFF survey on Medicaid redeterminations paints a complex picture, highlighting the need for adaptable and empathetic approaches. While some states have demonstrated success in navigating the challenges, others still grapple with significant hurdles. Ultimately, the success of redetermination efforts hinges on effective communication, adequate resource allocation, and a commitment to ensuring that vulnerable populations maintain access to essential healthcare.
The lessons learned from this process are vital for shaping future policy and ensuring a more equitable healthcare system for all.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of Medicaid redeterminations?
Medicaid redeterminations ensure that only eligible individuals continue to receive benefits, preventing waste and fraud while identifying those who may have become ineligible due to changes in income or other circumstances.
How long does the redetermination process typically take?
The timeframe varies significantly by state, but it generally involves several steps, from initial application to potential appeals, often taking several weeks or even months.
What support is available for Medicaid recipients during redetermination?
Support varies by state but may include assistance with paperwork, navigating the process, and appeals. Some states offer dedicated helplines or online resources.
What are some common reasons for disenrollment during redeterminations?
Common reasons include failure to submit required paperwork, changes in income that exceed eligibility thresholds, or difficulty navigating the complex process.