Medicaid Telehealth Buprenorphine Opioid Use Disorder Treatment
Medicaid telehealth buprenorphine opioid use JAMA disorder jama network open – these s highlight a crucial intersection of healthcare policy, technology, and the fight against the opioid crisis. This post dives into the expanding use of telehealth to deliver buprenorphine, a medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder, within the Medicaid system. We’ll explore the effectiveness, cost-effectiveness, and challenges associated with this approach, examining both provider and patient perspectives, as well as the crucial policy implications for wider adoption.
The goal is to understand how telehealth can improve access to life-saving treatment for those who need it most.
Recent studies published in the JAMA Network Open have shed light on the potential benefits and drawbacks of expanding telehealth buprenorphine access through Medicaid. We will analyze these findings, examining data on treatment retention rates, patient outcomes, and the overall cost-effectiveness compared to traditional in-person treatment. We’ll also delve into the complexities of state-level variations in Medicaid telehealth policies and the unique challenges faced by providers and patients in rural and underserved communities.
Medicaid Telehealth Expansion and Buprenorphine Access
Source: amazonaws.com
The expansion of telehealth services, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, significantly impacted access to medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder (OUD). Buprenorphine, a medication crucial for MAT, became more accessible through telehealth platforms, reaching individuals who previously faced significant barriers to care. However, the landscape of Medicaid telehealth coverage for buprenorphine remains complex and varies considerably across states.Medicaid’s role in expanding access to buprenorphine via telehealth is multifaceted.
Federal waivers and flexibilities during the public health emergency broadened telehealth coverage, but many of these have since expired or been modified. This has left a patchwork of policies across states, impacting the availability and affordability of buprenorphine for Medicaid beneficiaries. The ongoing challenge lies in ensuring sustained and equitable access to this life-saving medication.
State-Level Variations in Medicaid Telehealth Policies for Buprenorphine
State Medicaid agencies have considerable autonomy in determining their telehealth policies. Some states readily embraced telehealth for buprenorphine, maintaining expanded coverage even after the end of the public health emergency. Others have reverted to stricter pre-pandemic rules, limiting telehealth use to specific circumstances or requiring in-person visits for certain aspects of treatment. This variation creates significant disparities in access to care depending on a patient’s geographic location.
For example, a patient in a state with restrictive telehealth policies might struggle to find a provider offering buprenorphine via telehealth, while a patient in a more progressive state may have several options available. This uneven landscape underscores the need for federal guidance and consistent standards to ensure equitable access nationwide.
Telehealth Expansion’s Impact on Buprenorphine Access in Rural and Underserved Areas
The expansion of telehealth has been particularly impactful in rural and underserved areas, where access to addiction specialists and MAT is often limited. Telehealth has overcome geographical barriers, allowing individuals in remote locations to connect with providers who may otherwise be inaccessible. This has led to increased buprenorphine initiation and retention in treatment for many individuals who previously faced substantial challenges accessing care.
However, digital literacy and reliable internet access remain significant obstacles in some areas, highlighting the need for comprehensive support services alongside telehealth expansion. Addressing these digital divides is crucial to ensuring that telehealth truly benefits all populations.
Impact of Telehealth on Patient Outcomes: A State-by-State Comparison
The impact of telehealth expansion on patient outcomes is a complex area of ongoing research. While anecdotal evidence suggests positive effects, rigorous studies are needed to quantify the impact across different states and populations. The following table offers a hypothetical representation of how state policies and access may influence patient outcomes. Note that the data presented is illustrative and would need to be sourced from state-specific Medicaid data and outcome studies.
| State | Medicaid Telehealth Policy | Buprenorphine Access | Impact on Patient Outcomes (Illustrative) |
|---|---|---|---|
| State A (e.g., a state with expansive telehealth policies) | Extensive telehealth coverage for buprenorphine, including virtual visits and remote monitoring | High access, many providers offering telehealth services | Improved treatment retention rates, higher rates of buprenorphine initiation, reduced opioid overdose deaths |
| State B (e.g., a state with limited telehealth policies) | Limited telehealth coverage, requiring in-person visits for initial assessments or ongoing care | Lower access, fewer providers offering telehealth services, particularly in rural areas | Lower treatment retention rates, lower rates of buprenorphine initiation, potentially higher rates of opioid-related mortality |
| State C (e.g., a state with a moderate approach) | Partial telehealth coverage, with certain restrictions on virtual visits or types of services | Moderate access, some providers offering telehealth, but limited availability in certain regions | Mixed outcomes, some improvement in access but still significant barriers for certain populations |
| State D (e.g., a state with evolving policies) | Recently expanded telehealth coverage, still in the process of implementation and evaluation | Access improving, but significant variations across regions | Outcomes still under evaluation, but potential for significant improvement |
Effectiveness of Telehealth Buprenorphine Treatment within the Medicaid Population: Medicaid Telehealth Buprenorphine Opioid Use JAMA Disorder Jama Network Open
Telehealth has emerged as a promising avenue for expanding access to medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder (OUD), particularly for Medicaid beneficiaries who often face significant barriers to accessing in-person care. This includes geographical limitations, transportation difficulties, and scheduling conflicts. Research examining the effectiveness of telehealth-delivered buprenorphine for this population is growing, offering valuable insights into its efficacy and challenges.The effectiveness of telehealth buprenorphine treatment for Medicaid patients mirrors, and in some cases surpasses, the results seen in traditional in-person settings.
The JAMA Network Open’s findings on Medicaid telehealth expansion for buprenorphine treatment of opioid use disorder are fascinating. Improving access is crucial, and streamlining documentation could significantly help. This is where the news about Nuance integrating generative AI into Scribe for Epic EHRs, like this article explains nuance integrates generative ai scribe epic ehrs , becomes really relevant.
Imagine the time saved for providers, allowing them to focus more on patient care within the Medicaid telehealth framework for buprenorphine treatment.
Numerous studies have demonstrated comparable or even superior outcomes across several key clinical indicators. This section will delve into these findings, examining both successes and limitations.
Retention in Telehealth Buprenorphine Treatment
Studies comparing telehealth and in-person buprenorphine treatment for Medicaid patients show mixed results regarding retention. Some research suggests that telehealth may lead to slightly lower retention rates initially, potentially due to the challenges of establishing and maintaining a therapeutic relationship remotely. However, other studies have found comparable or even higher retention rates in telehealth models, particularly when incorporating strategies to enhance engagement, such as frequent virtual check-ins and proactive outreach.
The success of telehealth retention often hinges on the quality of the telehealth platform and the provider’s ability to build rapport and trust with the patient virtually. For example, a study might show a 70% retention rate at 6 months for in-person treatment compared to a 65% retention rate for telehealth, but this difference may not be statistically significant, and other factors could influence the slight discrepancy.
Opioid Abstinence and Reduction in Illicit Opioid Use
Regarding opioid abstinence and reduction in illicit opioid use, the evidence is largely supportive of telehealth buprenorphine’s effectiveness within the Medicaid population. Many studies report similar rates of abstinence and decreased opioid use between telehealth and in-person treatment groups. In some instances, telehealth may even offer advantages, particularly for patients in rural or underserved areas with limited access to in-person care.
For example, a study might demonstrate that both groups achieved a 50% reduction in illicit opioid use after three months, highlighting the comparable effectiveness of the two delivery methods. However, factors such as patient engagement and the quality of the telehealth platform can significantly influence these outcomes.
Challenges and Barriers to Effective Telehealth Buprenorphine Treatment within the Medicaid System
The implementation of telehealth buprenorphine treatment within the Medicaid system faces several challenges. Addressing these obstacles is crucial for maximizing the potential of this approach.
The following points represent significant hurdles:
- Digital literacy and access to technology: Many Medicaid beneficiaries lack reliable internet access or the necessary technological skills to participate effectively in telehealth appointments. This digital divide can create significant barriers to engagement and treatment success.
- Privacy and confidentiality concerns: Ensuring patient privacy and confidentiality during telehealth sessions can be challenging, particularly when patients are using personal devices or accessing services in shared living spaces. Robust security measures and patient education are essential to mitigate these risks.
- Lack of reimbursement parity: Inconsistent reimbursement rates for telehealth services compared to in-person visits can create financial disincentives for providers to offer telehealth buprenorphine treatment, limiting access for Medicaid patients.
- Regulatory and licensing complexities: Navigating the complexities of state-specific licensing requirements and telehealth regulations can be a significant barrier for providers seeking to offer telehealth services across state lines or to patients in different geographic locations.
- Limited access to medication dispensing: Ensuring timely and convenient access to buprenorphine medication can be challenging in telehealth models, particularly for patients who lack transportation or access to pharmacies. Innovative strategies, such as mail-order pharmacies or partnerships with local providers, are needed to overcome this hurdle.
Cost-Effectiveness of Telehealth Buprenorphine within the Medicaid Framework
Telehealth has emerged as a promising avenue for expanding access to medication-assisted treatment (MAT) for opioid use disorder (OUD), particularly for Medicaid beneficiaries who often face significant barriers to accessing traditional in-person care. This section delves into the cost-effectiveness of telehealth buprenorphine treatment within the Medicaid system, examining factors that influence its financial viability and presenting a hypothetical model to illustrate potential savings.The cost-effectiveness of telehealth buprenorphine compared to in-person treatment is a complex issue with several interacting variables.
While initial implementation costs might be higher for telehealth (e.g., technology infrastructure, provider training), ongoing operational costs can be significantly lower. Reduced travel expenses for patients, decreased need for physical clinic space, and potentially higher patient retention rates all contribute to long-term cost savings.
Factors Influencing Cost-Effectiveness
Several factors significantly impact the cost-effectiveness of telehealth buprenorphine within the Medicaid framework. These include patient characteristics (e.g., severity of OUD, comorbid conditions, geographic location), treatment intensity (e.g., frequency of telehealth visits, need for additional support services), and provider reimbursement rates. For instance, patients in rural areas with limited access to transportation would likely experience substantial cost savings through telehealth, avoiding travel time and expenses.
Conversely, patients requiring frequent in-person visits due to complex medical needs might not see the same level of cost reduction. Similarly, higher provider reimbursement rates for telehealth services could impact the overall cost-effectiveness, making it more or less attractive depending on the specific reimbursement structure.
The JAMA Network Open article on Medicaid telehealth expansion for buprenorphine treatment of opioid use disorder is fascinating. It highlights the need for innovative solutions to scale access, and I was thinking about how AI could help. This is where the amazing work of Amy Waldron and Google Cloud Healthcare on generative AI comes in, as detailed in this article: google cloud healthcare amy waldron generative AI.
Imagine the possibilities for improving patient outcomes and streamlining the process described in the JAMA study. Better data analysis through AI could potentially revolutionize opioid use disorder treatment within Medicaid.
Hypothetical Cost-Effectiveness Model
Let’s consider a hypothetical cost-effectiveness model comparing telehealth and in-person buprenorphine treatment for 100 Medicaid beneficiaries over a one-year period. Assume the average cost of an in-person visit is $150, including the provider fee, facility costs, and patient travel expenses. A telehealth visit, including the provider fee and technology costs, averages $100. Further, assume that the average patient in the in-person group requires 12 visits per year, while the telehealth group, due to higher retention rates and reduced barriers to care, only requires 10 visits.In this scenario, the total cost for in-person treatment would be $180,000 ($150/visit
- 12 visits/patient
- 100 patients). The total cost for telehealth treatment would be $100,000 ($100/visit
- 10 visits/patient
- 100 patients). This represents a potential cost saving of $80,000 annually for this hypothetical cohort. This model, of course, simplifies the complexities of real-world scenarios, but it highlights the potential for significant cost savings with widespread telehealth adoption. It’s crucial to note that this hypothetical model does not account for potential increases in treatment success rates and reduced healthcare utilization associated with improved access to care, which would further enhance the cost-effectiveness of telehealth.
Real-world implementation would require a more nuanced model incorporating factors such as patient outcomes, relapse rates, and the costs associated with managing potential complications.
Provider Perspectives and Training Needs for Telehealth Buprenorphine Delivery
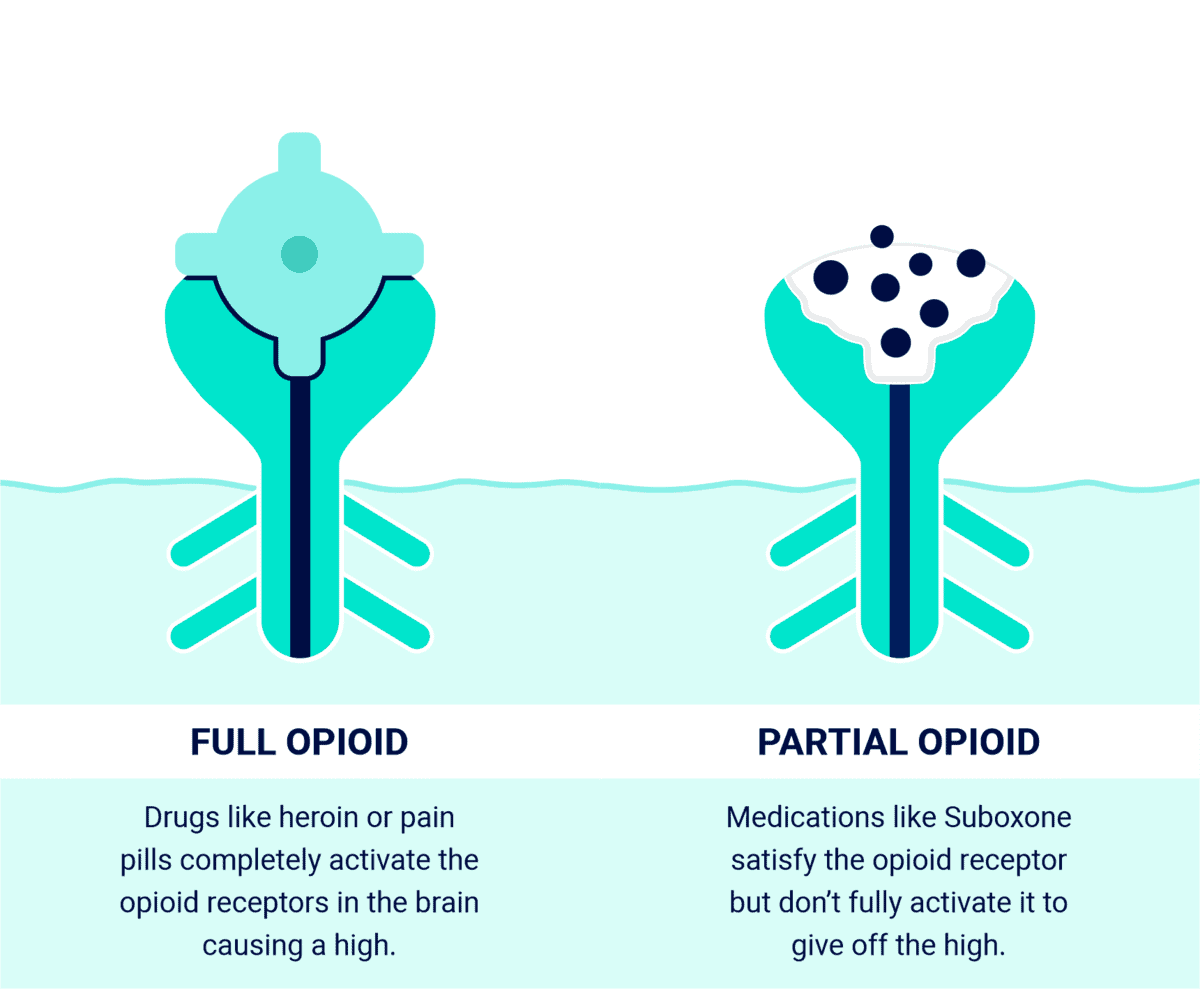
Source: symetriarecovery.com
Expanding access to buprenorphine for opioid use disorder (OUD) via telehealth within the Medicaid system presents both significant opportunities and considerable challenges. Providers have voiced concerns and highlighted positive experiences, shaping our understanding of necessary training and support for successful implementation. This section will explore provider perspectives and identify crucial training needs to optimize telehealth buprenorphine delivery.Telehealth’s potential to overcome geographical barriers and increase access to care for Medicaid patients with OUD is undeniable.
However, successful implementation requires addressing provider concerns and providing adequate training. Many providers express apprehension about the technical aspects of telehealth, the potential for compromised patient-provider relationships in a virtual setting, and the added complexities of managing medication-assisted treatment (MAT) remotely. Conversely, some providers report increased efficiency and flexibility, along with the ability to reach more patients who otherwise wouldn’t have access to care.
Provider Challenges and Opportunities in Telehealth Buprenorphine Delivery
Providers consistently cite several key challenges. These include ensuring patient privacy and data security within the telehealth platform, navigating the complexities of remote medication management and monitoring, and effectively addressing potential technological barriers experienced by patients. Additionally, concerns exist about maintaining the therapeutic alliance in a virtual setting, especially for patients with complex needs or co-occurring disorders. However, opportunities also abound.
Telehealth allows for increased scheduling flexibility, expanded geographic reach, and potentially improved patient engagement through tailored communication strategies. The reduced overhead costs associated with telehealth can also enhance the cost-effectiveness of buprenorphine treatment, benefiting both providers and the Medicaid system.
Key Training Needs for Telehealth Buprenorphine Treatment
Effective training must address multiple facets of telehealth buprenorphine delivery. This includes comprehensive instruction on the technical aspects of telehealth platforms, including secure messaging, video conferencing, and electronic health record (EHR) integration. Furthermore, training should equip providers with strategies for building rapport and trust with patients in a virtual environment, employing effective communication techniques to overcome the limitations of remote interaction.
Crucial components also include training on the specific clinical management of buprenorphine treatment via telehealth, encompassing best practices for medication management, monitoring for adverse effects, and addressing potential challenges unique to the telehealth setting. Finally, training should incorporate strategies for addressing patient adherence and managing potential crises remotely.
Strategies to Improve Provider Adoption and Implementation
To maximize the effectiveness of telehealth buprenorphine programs within Medicaid, several strategic initiatives are essential.
- Financial Incentives: Offering financial incentives to providers for participating in telehealth buprenorphine programs can significantly increase adoption rates. This could involve reimbursements at rates comparable to or exceeding in-person visits.
- Technical Support and Infrastructure: Providing robust technical support and reliable infrastructure is crucial. This includes access to high-speed internet, user-friendly telehealth platforms, and readily available technical assistance for providers and patients.
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Investing in comprehensive, ongoing training programs that specifically address the unique challenges and opportunities of telehealth buprenorphine delivery is vital. This training should incorporate interactive modules, hands-on practice, and ongoing mentorship.
- Mentorship and Peer Support: Establishing mentorship programs that pair experienced telehealth providers with those new to the modality can provide valuable support and guidance.
- Streamlined Regulatory Processes: Simplifying the regulatory processes associated with telehealth buprenorphine prescribing can reduce administrative burdens and encourage wider adoption. This could involve reducing the paperwork and streamlining the licensing requirements.
- Data-Driven Program Evaluation: Implementing data-driven program evaluation allows for ongoing monitoring of program effectiveness, identification of areas for improvement, and informed decision-making regarding resource allocation.
Patient Experiences and Outcomes with Telehealth Buprenorphine within Medicaid
Source: womensmentalhealth.org
Telehealth has emerged as a promising avenue for expanding access to buprenorphine treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) within the Medicaid population. However, understanding patient experiences and comparing outcomes with traditional in-person treatment is crucial for optimizing this approach. This section explores patient perspectives on telehealth buprenorphine, examines comparative treatment outcomes, and proposes strategies to enhance patient engagement and adherence.Patient satisfaction with telehealth buprenorphine is largely influenced by factors relating to accessibility and convenience.
Many patients report that telehealth eliminates barriers like transportation difficulties, childcare issues, and inflexible work schedules, making treatment significantly more accessible. The convenience of virtual appointments, often conducted from the comfort of their homes, is a major advantage. However, challenges remain; some patients may experience technological barriers, such as lack of reliable internet access or familiarity with telehealth platforms.
Perceived effectiveness, naturally, plays a crucial role. Positive experiences are linked to feeling comfortable with their provider during virtual sessions and perceiving that the treatment is effective in managing cravings and improving overall well-being.
Accessibility and Convenience of Telehealth Buprenorphine
Increased accessibility is a key benefit frequently reported by Medicaid patients. For individuals living in rural areas with limited access to specialized care, telehealth removes geographical barriers. Similarly, patients with mobility issues or those juggling work and family responsibilities find telehealth significantly more convenient. This increased convenience often translates to improved treatment adherence, as patients are less likely to miss appointments due to logistical challenges.
For example, a study might show that telehealth patients missed significantly fewer appointments compared to their in-person counterparts, leading to better overall treatment outcomes.
Comparison of Patient Outcomes: Telehealth vs. In-Person Treatment
While initial research suggests comparable outcomes between telehealth and in-person buprenorphine treatment for Medicaid patients, more longitudinal studies are needed to confirm these findings. Metrics such as treatment retention rates, reduction in opioid use (measured through urine toxicology), and improvements in quality of life indicators (e.g., mental health, social functioning) are key areas of investigation. For instance, one could compare the percentage of patients completing a full course of treatment in both telehealth and in-person settings.
Differences in these outcomes could be attributed to various factors, including patient characteristics, provider training, and the quality of the telehealth platform.
Strategies to Improve Patient Engagement and Adherence
Several strategies can improve patient engagement and adherence to telehealth buprenorphine treatment. These include proactive outreach by providers, such as scheduling regular check-in calls or sending encouraging messages. Integrating telehealth with other supportive services, such as peer support or case management, can further enhance patient engagement. Addressing technological barriers is also critical; providing patients with access to devices and internet connectivity, or offering alternative methods of communication (e.g., telephone appointments), is crucial for ensuring equitable access to care.
Furthermore, tailoring the telehealth platform to the specific needs of the Medicaid population, incorporating culturally competent approaches, and providing user-friendly training can improve the overall patient experience and promote adherence. For instance, a program could offer subsidized internet access or provide training sessions on using the telehealth platform in a community setting.
Policy Implications and Recommendations for Expanding Telehealth Buprenorphine Access
Expanding telehealth access to buprenorphine for Medicaid beneficiaries presents significant policy implications, impacting both the effectiveness of opioid use disorder treatment and the financial sustainability of healthcare systems. Careful consideration of these implications is crucial to ensure equitable and efficient service delivery. This section will explore key policy considerations and propose concrete recommendations for policymakers.
Policy Implications of Expanding Telehealth Buprenorphine Access
Expanding telehealth buprenorphine access within Medicaid requires navigating several complex policy areas. Firstly, reimbursement rates for telehealth services must be adequate to incentivize provider participation, particularly in underserved rural areas. Secondly, licensing and prescribing regulations need to be streamlined to allow providers to treat patients across state lines, eliminating geographical barriers to care. Thirdly, robust data security and privacy protocols are essential to protect patient confidentiality within the telehealth environment.
Finally, concerns about potential disparities in access based on factors like digital literacy and reliable internet access must be proactively addressed. Failure to address these implications could lead to unintended consequences, such as limited provider participation, unequal access to care, and ultimately, poorer patient outcomes.
Recommendations for Policymakers, Medicaid telehealth buprenorphine opioid use JAMA disorder jama network open
Policymakers can significantly improve the effectiveness, efficiency, and equity of telehealth buprenorphine services within Medicaid through several key actions.
- Increase Reimbursement Rates: Medicaid reimbursement rates for telehealth buprenorphine services should be comparable to, or even exceed, in-person rates to incentivize provider participation, especially in underserved areas. This could involve establishing specific telehealth add-on payments or adjusting existing payment models to reflect the unique costs and complexities of delivering telehealth care.
- Streamline Licensing and Prescribing Regulations: States should adopt interstate licensing compacts and relax restrictions on telehealth prescribing to enable providers to treat patients across state lines. This would expand the pool of available providers and increase access to care for individuals in areas with limited buprenorphine treatment options. For example, a compact between several states could simplify the process of obtaining licenses and approvals for telehealth practices.
That JAMA Network Open article on Medicaid telehealth buprenorphine for opioid use disorder really got me thinking. The potential for wider access is huge, but scaling up effectively requires innovative solutions. This is where a recent study on the widespread adoption of digital twins in healthcare, like the one discussed here: study widespread digital twins healthcare , becomes incredibly relevant.
Imagine the possibilities for personalized treatment plans and improved outcomes for opioid addiction using such technology. It could revolutionize how we approach Medicaid telehealth and buprenorphine treatment.
- Invest in Infrastructure and Digital Literacy Training: Increased investment in broadband infrastructure and digital literacy training programs for both providers and patients is critical to ensure equitable access to telehealth services. This includes providing subsidized internet access to low-income patients and offering training on telehealth platforms and technologies. A successful example is the establishment of community technology centers that provide training and internet access.
- Strengthen Data Security and Privacy Protections: Robust data security and privacy protocols are essential to protect patient confidentiality in telehealth settings. This includes implementing strong encryption standards, conducting regular security audits, and providing comprehensive training for providers on HIPAA compliance. Regular audits could mirror the best practices of financial institutions, ensuring consistent security checks and updates.
- Develop and Implement Quality Assurance Measures: Establish standardized quality assurance measures to monitor the effectiveness and safety of telehealth buprenorphine treatment. This could involve collecting data on patient outcomes, provider adherence to treatment protocols, and patient satisfaction. This data could inform continuous quality improvement efforts and help ensure that telehealth services are meeting the needs of Medicaid beneficiaries. The data could be analyzed and used to adjust reimbursement models, training programs, and treatment protocols as needed.
Visual Representation of a Successful Policy Framework
Imagine a diagram with a central circle representing “Successful Telehealth Buprenorphine Access within Medicaid.” Four interconnected circles surround the central circle, representing the key policy components: (1) Adequate Reimbursement, depicted with dollar signs; (2) Streamlined Regulations, depicted with a simplified flowchart icon; (3) Robust Infrastructure & Digital Literacy, depicted with a computer network graphic and a graduation cap; and (4) Strong Data Security & Quality Assurance, depicted with a shield and a chart showing upward trends.
Arrows connect each of the four outer circles to the central circle, illustrating their interconnectedness and dependence on each other for a successful program. The diagram visually demonstrates that a successful policy framework requires a holistic approach addressing financial incentives, regulatory streamlining, technological infrastructure, and data security to ensure equitable and effective telehealth buprenorphine access for Medicaid beneficiaries.
Last Recap
Expanding access to buprenorphine via telehealth within the Medicaid system presents a powerful opportunity to combat the opioid epidemic. While challenges remain, including ensuring adequate provider training and addressing digital literacy disparities among patients, the potential benefits—improved access, better patient outcomes, and cost savings—are compelling. A multifaceted approach, involving policy changes, provider education, and patient support, is essential to maximize the effectiveness and equity of this innovative treatment strategy.
The future of opioid use disorder treatment may well depend on leveraging technology to overcome geographical barriers and reach those in desperate need of help.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the potential downsides of telehealth buprenorphine treatment?
Potential downsides include the need for reliable internet access and technology, privacy concerns, difficulties in building rapport remotely, and the inability to physically assess patients.
How does telehealth address the opioid crisis in rural areas?
Telehealth expands access to buprenorphine treatment in rural areas where specialists are scarce, bridging the geographical gap and making treatment more readily available.
What role do patient support systems play in telehealth buprenorphine programs?
Strong patient support systems, including regular check-ins, remote monitoring, and peer support groups, are vital for improving engagement and treatment adherence in telehealth settings.