New York Hospital Cybersecurity Regulation Healthcare
New York hospital cybersecurity regulation healthcare is a critical issue, impacting patient safety and hospital operations. Navigating the complex landscape of HIPAA compliance alongside New York’s specific cybersecurity laws presents significant challenges for hospitals. This post explores the key regulations, common threats, and best practices for ensuring robust data protection in New York’s healthcare facilities. We’ll delve into the potential penalties for non-compliance, explore effective cybersecurity technologies, and examine the crucial role of cybersecurity insurance in mitigating risks.
From ransomware attacks to insider threats, the risks are real and ever-evolving. Understanding the intricacies of these regulations and implementing effective strategies is paramount to protecting sensitive patient data and maintaining the trust of the community. This isn’t just about ticking boxes; it’s about building a culture of cybersecurity within the hospital system.
New York State Cybersecurity Regulations Impacting Healthcare

Source: connection.com
Navigating the complex landscape of cybersecurity regulations is a significant challenge for healthcare providers in New York State. The state has implemented robust regulations to protect sensitive patient data, and understanding these rules is crucial for hospitals to avoid hefty penalties and maintain patient trust. This post will delve into the key aspects of these regulations, their implications, and how they compare to those in other states.
Key Components of New York’s Cybersecurity Regulations for Hospitals
New York’s cybersecurity regulations for healthcare providers, largely driven by the state’s Department of Health (DOH), focus on data breach notification, risk management, and security protocols. These regulations aren’t codified in a single, easily accessible document but rather are derived from a combination of state laws, DOH guidance, and interpretations of federal regulations like HIPAA. Key areas of focus include establishing a comprehensive cybersecurity program, regular risk assessments, employee training, and incident response planning.
The regulations emphasize a proactive approach to security, requiring hospitals to anticipate and mitigate potential threats rather than simply reacting to breaches. Specific requirements often center around data encryption, access controls, and vulnerability management.
Penalties for Non-Compliance with New York’s Cybersecurity Regulations
Failure to comply with New York’s cybersecurity regulations can result in significant penalties. These penalties can vary depending on the severity of the violation and the hospital’s history of compliance. Potential consequences range from substantial fines to suspension or revocation of licenses to operate. In addition to financial penalties, non-compliance can severely damage a hospital’s reputation, leading to a loss of patient trust and potential legal action from affected individuals.
The state actively investigates reported breaches and takes enforcement action against non-compliant entities. The cost of remediation following a data breach, including legal fees, forensic investigation costs, and public relations efforts, can also be substantial, far exceeding any potential fines.
Comparison of New York’s Regulations with Other States
New York’s cybersecurity regulations are among the more stringent in the nation. While many states have adopted breach notification laws based on federal HIPAA requirements, New York’s regulations often go beyond the minimum federal standards, requiring more extensive risk management programs and more proactive security measures. Some states have a more fragmented approach, relying on a patchwork of laws and guidance, whereas New York strives for a more comprehensive and unified regulatory framework.
However, the specific requirements and enforcement mechanisms vary significantly across states, reflecting differing priorities and legislative approaches. For example, some states may place a greater emphasis on specific technologies or industry sectors, while others focus on general security principles.
New York hospitals face stringent cybersecurity regulations, impacting everything from patient data protection to operational efficiency. Understanding the federal guidelines is crucial, and a great resource for this is the hhs healthcare cybersecurity framework hospital requirements cms website, which details the CMS requirements. This framework helps New York hospitals align their practices with national standards, ultimately strengthening their overall cybersecurity posture and patient data security.
Summary of Key Requirements and Penalties
| Requirement | Penalty for Non-Compliance | Example | Enforcement Agency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehensive Cybersecurity Program | Fines, License Revocation | Failure to implement appropriate security controls | New York State Department of Health (DOH) |
| Regular Risk Assessments | Fines, Corrective Action Plans | Failure to identify and mitigate vulnerabilities | DOH |
| Data Breach Notification | Fines, Legal Action | Failure to timely notify individuals of a breach | DOH, Attorney General |
| Employee Training | Fines, Corrective Action Plans | Failure to provide adequate security awareness training | DOH |
HIPAA Compliance in the Context of New York’s Cybersecurity Laws
Navigating the complex landscape of healthcare cybersecurity requires a keen understanding of overlapping and sometimes conflicting regulations. Hospitals in New York State face the dual challenge of complying with both the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and New York’s increasingly stringent cybersecurity laws. Understanding the nuances of each and how they interact is crucial for effective risk management and avoiding significant penalties.The relationship between HIPAA and New York’s cybersecurity regulations isn’t one of simple substitution; rather, it’s one of augmentation and sometimes, even redundancy.
HIPAA sets a national baseline for protecting patient health information (PHI), focusing primarily on the privacy and security of electronic protected health information (ePHI). New York’s laws, however, often go beyond HIPAA’s minimum requirements, imposing more stringent security controls and breach notification protocols. This means that meeting New York’s standards frequently ensures HIPAA compliance, but not always the other way around.
Overlap and Differences Between HIPAA and New York Cybersecurity Laws
HIPAA’s Security Rule Artikels administrative, physical, and technical safeguards for protecting ePHI. These safeguards cover areas like access controls, audit trails, and risk management. New York’s cybersecurity regulations, particularly the recently strengthened ones, expand upon these requirements, often demanding more robust security measures and stricter enforcement. For example, while HIPAA requires risk assessments, New York’s laws may specify the frequency and depth of these assessments, along with mandatory penetration testing and vulnerability scanning.
Similarly, while HIPAA mandates breach notification, New York might have a shorter timeframe for notification and a broader definition of what constitutes a breach. The key difference lies in the scope and stringency of the requirements; New York’s laws are often more prescriptive and demanding.
Areas Where Compliance with One Necessitates Compliance with the Other
Compliance with New York’s cybersecurity regulations often inherently leads to HIPAA compliance. For instance, implementing robust multi-factor authentication (MFA) to meet New York’s requirements will simultaneously fulfill HIPAA’s access control stipulations. Similarly, rigorous data encryption mandated by New York State will also satisfy HIPAA’s requirements for protecting ePHI. However, it’s crucial to remember that New York’s regulations may cover areas not explicitly addressed by HIPAA, such as specific requirements for incident response planning or data retention policies.
Meeting these state-specific requirements will bolster overall security posture, indirectly enhancing HIPAA compliance.
Challenges Hospitals Face in Meeting Both Sets of Regulations
Hospitals face numerous challenges in achieving simultaneous compliance. The sheer volume of regulations, coupled with their evolving nature, can be overwhelming. Maintaining updated security infrastructure, training staff on evolving protocols, and implementing effective risk management programs are significant ongoing investments. Furthermore, resource constraints, including budget limitations and staffing shortages, can hinder hospitals’ ability to effectively manage cybersecurity risks and meet all regulatory obligations.
The lack of standardized cybersecurity frameworks can also create confusion and complicate the compliance process. Finally, the constantly evolving threat landscape necessitates continuous adaptation and investment in new technologies and security measures.
Best Practices for Achieving Simultaneous HIPAA and New York State Compliance
A comprehensive approach is necessary. This includes conducting regular risk assessments that consider both HIPAA and New York State requirements, implementing a robust security awareness training program for all staff, establishing strong vendor management protocols, regularly updating security software and systems, and implementing a comprehensive incident response plan that adheres to both sets of regulations. Leveraging a centralized security information and event management (SIEM) system can streamline monitoring and reporting, simplifying compliance efforts.
Regular audits and penetration testing are also crucial for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring ongoing compliance. Furthermore, engaging with experienced cybersecurity consultants can provide invaluable guidance and support in navigating the complex regulatory landscape. Finally, proactively monitoring for and responding to emerging threats is essential for maintaining a strong security posture and mitigating risks.
Cybersecurity Threats Specific to New York Hospitals
New York hospitals, like healthcare providers nationwide, face a unique set of cybersecurity challenges. The confluence of sensitive patient data, complex medical devices, and a constantly evolving threat landscape creates a high-risk environment. Understanding the specific threats impacting these institutions is crucial for effective risk mitigation and compliance with stringent New York State regulations.
Ransomware Attacks
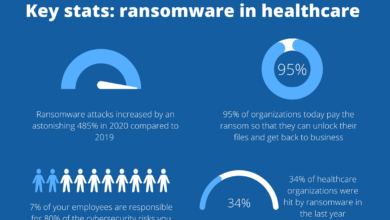
Ransomware attacks remain a significant threat to New York hospitals. These attacks involve malicious software that encrypts critical data, rendering it inaccessible unless a ransom is paid. The impact on patient care can be devastating, delaying diagnoses, disrupting treatment plans, and potentially endangering lives. For example, a ransomware attack could compromise electronic health records (EHRs), preventing doctors from accessing vital patient information during emergencies.
Furthermore, the disruption of hospital operations, including billing and administrative systems, can lead to significant financial losses. The potential for reputational damage and legal repercussions adds to the severity of these attacks.
Phishing and Social Engineering
Phishing attacks, which involve deceptive emails or messages designed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, pose a substantial threat. Hospital employees, often juggling multiple tasks and under pressure, can be more susceptible to these attacks. Successful phishing campaigns can lead to the compromise of credentials, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access to hospital systems and patient data.
Social engineering, a broader term encompassing manipulative tactics to gain access or information, can also be highly effective, exploiting human trust and vulnerabilities. For instance, a cleverly crafted email pretending to be from IT support could trick an employee into revealing their password, providing a backdoor for malicious actors.
Insider Threats
Insider threats, originating from individuals within the hospital, represent a significant but often overlooked risk. This could involve malicious intent, negligence, or unintentional actions. A disgruntled employee, for example, might intentionally leak patient data or sabotage systems. Conversely, an employee who fails to follow security protocols, such as using weak passwords or clicking on suspicious links, can inadvertently create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
The consequences of insider threats can be just as severe as external attacks, potentially leading to data breaches, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
New York hospitals are grappling with increasingly stringent cybersecurity regulations, a crucial aspect of healthcare data protection. The rising costs associated with this, however, highlight a broader issue – efficient resource allocation within the healthcare system. This is especially pertinent considering the findings of the Urban Institute report, which argues that the Medicare Advantage Quality Bonus Program needs reform to better support hospitals facing these challenges.
Ultimately, stronger cybersecurity in New York hospitals requires a more holistic approach to healthcare funding and regulation.
Hypothetical Cybersecurity Breach Scenario
Imagine a scenario where a New York City hospital experiences a sophisticated ransomware attack. The attackers, using a combination of phishing and exploiting a vulnerability in outdated medical imaging software, gain access to the hospital’s network. They encrypt the EHRs, billing system, and radiology images, demanding a substantial ransom for decryption. This attack leads to immediate operational disruptions: surgeries are delayed, patient appointments are canceled, and emergency room operations are severely hampered.
The hospital’s reputation suffers significantly, leading to a decline in patient admissions and potential legal ramifications. The financial impact is substantial, encompassing the ransom payment, the cost of recovery efforts, and the loss of revenue due to service disruptions. This scenario highlights the interconnected nature of cybersecurity threats and their far-reaching consequences for hospitals.
Cybersecurity Technologies and Best Practices for New York Hospitals: New York Hospital Cybersecurity Regulation Healthcare

Source: hospitalmanagement.net
Protecting patient data in New York hospitals requires a multi-layered approach leveraging advanced cybersecurity technologies and robust security protocols. The sheer volume of sensitive information handled, coupled with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, necessitates a proactive and comprehensive strategy. This involves not only the implementation of cutting-edge technologies but also a strong focus on employee training and awareness.
Common Cybersecurity Technologies Used by New York Hospitals
New York hospitals utilize a range of technologies to safeguard patient data, often integrating multiple solutions for a robust defense. These technologies address various aspects of cybersecurity, from network security and data protection to threat detection and response. The specific technologies employed often depend on the size and resources of the hospital, as well as the specific threats they face.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): These systems monitor network traffic for malicious activity, alerting administrators to potential threats and automatically blocking suspicious connections. Many hospitals use a combination of network-based and host-based IDPS solutions for comprehensive protection.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as barriers between the hospital’s internal network and the external internet, controlling the flow of network traffic and blocking unauthorized access. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) offer advanced features like deep packet inspection and application control for enhanced security.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR solutions provide real-time monitoring and protection for individual computers and devices within the hospital network. They detect and respond to malware, ransomware, and other threats at the endpoint level, minimizing the impact of successful attacks.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP tools prevent sensitive patient data from leaving the hospital’s network unauthorized. They monitor data transfers, identify sensitive information, and block or alert on unauthorized attempts to copy, print, or email protected data.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): VPNs create secure connections for remote access to the hospital’s network, encrypting data transmitted between remote users and the hospital’s servers. This protects sensitive information when accessed from outside the hospital network.
Implementation Procedures for Selected Cybersecurity Technologies
Effective implementation is crucial for the success of any cybersecurity technology. Let’s look at the implementation procedures for three key technologies: firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint detection and response.
- Firewalls: Firewall implementation involves careful configuration of rules to control network traffic. This includes defining which ports and protocols are allowed or blocked, creating access control lists (ACLs) to restrict access based on IP addresses or other criteria, and regularly updating firewall rules to address new threats. Hospitals often employ multiple firewalls, creating a layered defense.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Implementing an IDS involves deploying sensors throughout the network to monitor traffic. These sensors analyze network packets for suspicious patterns indicative of malicious activity. The IDS then generates alerts that are reviewed by security personnel. Effective IDS implementation also includes regular tuning of the system to minimize false positives and maximize detection accuracy.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR implementation involves installing agents on each endpoint device (computers, laptops, servers). These agents continuously monitor the device for malicious activity, providing real-time threat detection and response capabilities. Centralized management consoles allow security personnel to monitor and manage all endpoints from a single location. Regular updates and configuration changes are essential for optimal performance.
Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Technologies in Mitigating Specific Threats
Different cybersecurity technologies excel at mitigating specific threats. For example, firewalls are highly effective in preventing unauthorized external access, while intrusion detection systems are crucial for identifying and responding to internal threats or sophisticated attacks that bypass initial defenses. EDR solutions are essential for detecting and responding to endpoint-based threats like malware and ransomware. Data loss prevention (DLP) tools are vital in preventing data breaches involving sensitive patient information.
The effectiveness of these technologies is significantly enhanced when they are integrated and work in concert.
Best Practices for Employee Cybersecurity Training in a New York Hospital
A strong cybersecurity posture relies heavily on well-trained employees. Regular and comprehensive training is essential.
- Regular Security Awareness Training: Conduct regular training sessions covering topics such as phishing scams, social engineering tactics, password security, and safe internet browsing practices.
- Phishing Simulations: Periodically conduct simulated phishing attacks to test employee awareness and identify vulnerabilities. Provide feedback and retraining for those who fall victim to the simulations.
- Tailored Training Based on Roles: Develop training programs specific to different roles within the hospital, focusing on the types of data and systems each role accesses. For example, nurses may require training on protecting patient data in electronic health records (EHRs).
- Emphasis on HIPAA Compliance: Clearly communicate the importance of HIPAA compliance and the legal and ethical implications of data breaches. Explain how employees’ actions can impact patient privacy and the hospital’s reputation.
- Ongoing Education and Updates: Keep employees informed about emerging threats and best practices through newsletters, updates, and reminders. Regular updates ensure employees remain aware of evolving cybersecurity risks.
The Role of Cybersecurity Insurance for New York Hospitals
Given the stringent New York State cybersecurity regulations and the significant HIPAA compliance requirements, coupled with the ever-present threat of cyberattacks, cybersecurity insurance has become a critical component of risk management for New York hospitals. It’s no longer a luxury but a necessity for mitigating the potentially catastrophic financial and reputational consequences of a data breach.Cybersecurity insurance offers crucial protection against the financial burdens associated with a cyberattack, helping hospitals recover from the incident and continue providing essential healthcare services.
The rising frequency and sophistication of cyber threats, targeting sensitive patient data and hospital operations, underscore the importance of this coverage. Without adequate insurance, a single breach could cripple a hospital’s finances, leading to service disruptions and potentially jeopardizing patient care.
Types of Cybersecurity Insurance Coverage
Cybersecurity insurance policies for hospitals typically offer a range of coverage options tailored to the unique risks faced by healthcare providers. These policies aren’t monolithic; they are customizable to meet specific needs. Common coverage areas include:First-party coverage addresses the hospital’s direct losses resulting from a cyberattack. This can include costs associated with data breach notification, credit monitoring for affected individuals, forensic investigations to determine the extent of the breach, legal fees for regulatory compliance, and system restoration.
Third-party coverage protects the hospital from claims made by patients or other third parties who have suffered losses due to the breach, such as lawsuits for negligence or identity theft. This is particularly crucial given the sensitive nature of patient data. Many policies also include coverage for business interruption, compensating for lost revenue during the recovery period following an attack.
Factors Influencing the Cost of Cybersecurity Insurance
Several factors significantly influence the premium a New York hospital will pay for cybersecurity insurance. The size and complexity of the hospital’s IT infrastructure are major considerations. Larger hospitals with more extensive networks and data stores generally face higher premiums due to the increased risk of a larger-scale breach. The hospital’s existing cybersecurity practices and security controls also play a critical role.
Hospitals demonstrating a robust security posture, including strong security awareness training for staff, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits, may qualify for lower premiums. The hospital’s claims history is another important factor. A history of previous cyber incidents will likely result in higher premiums. Finally, the specific coverage amounts and policy limits selected will also impact the overall cost.
A broader range of coverage and higher limits will naturally lead to higher premiums.
Comparison of Cybersecurity Insurance Providers
The cybersecurity insurance market offers a range of providers, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Direct comparison is challenging without specific details on individual hospital needs and risk profiles. However, factors to consider when evaluating providers include: the breadth and depth of coverage offered, the financial strength and stability of the insurer, the responsiveness and expertise of their claims handling team, and the cost of the premium relative to the coverage provided.
It’s essential for hospitals to obtain quotes from multiple providers to compare options and ensure they select a policy that best aligns with their risk profile and budget. Hospitals should also seek independent advice from brokers specializing in healthcare cybersecurity insurance to navigate the complexities of the market and find the most suitable policy.
Data Breach Response Planning in New York Hospitals
Developing a robust data breach response plan is crucial for New York hospitals, not only to meet stringent state and federal regulations but also to protect patient data and maintain public trust. A well-defined plan minimizes the impact of a breach, facilitates a swift recovery, and demonstrates proactive risk management. This plan should be regularly tested and updated to reflect evolving threats and technological advancements.
Developing a Comprehensive Data Breach Response Plan
Creating a comprehensive data breach response plan involves several key steps. First, a thorough risk assessment identifies potential vulnerabilities and likely attack vectors. This informs the development of a prioritized incident response strategy, outlining roles and responsibilities for each team member involved. The plan should clearly define escalation procedures, communication protocols, and legal obligations. Crucially, it needs to detail the technical steps for containing the breach, including isolating affected systems and preventing further data exfiltration.
Finally, the plan should incorporate procedures for data recovery, system restoration, and post-incident analysis to prevent future occurrences. Regular training and drills are essential to ensure all personnel are familiar with the plan and can execute it effectively.
Notification Requirements Under New York Law Following a Data Breach
New York’s data breach notification law, under Article 23-A of the General Business Law, mandates timely notification to affected individuals and, in some cases, the Attorney General. The law requires notification “without unreasonable delay” after discovery of a breach. The notification must include specific information about the breach, including the types of personal information compromised and the steps individuals can take to protect themselves.
New York hospital cybersecurity regulations are crucial for protecting sensitive patient data, especially given the complexities of healthcare IT. Understanding these regulations helps us appreciate the need for robust systems, much like the careful planning required when considering effective strategies, as outlined in this helpful article on strategies to manage Tourette syndrome in children , for managing complex health conditions.
Ultimately, both require proactive planning and consistent vigilance to ensure positive outcomes.
The timeframe for notification depends on the circumstances of the breach and the number of individuals affected. Failure to comply with these notification requirements can result in significant penalties. For example, a hospital might face legal action if it fails to provide timely and accurate notification to affected patients.
Containing and Remediating a Cybersecurity Incident, New york hospital cybersecurity regulation healthcare
Containing and remediating a cybersecurity incident requires a swift and coordinated response. The first step involves isolating affected systems to prevent further data loss or compromise. This might involve disconnecting servers from the network or shutting down specific applications. Next, the incident response team needs to analyze the breach to understand its scope and impact. This involves identifying the source of the breach, the methods used by the attacker, and the extent of data exfiltration.
Based on this analysis, the team can develop a remediation plan, which might include patching vulnerabilities, restoring data from backups, and implementing enhanced security controls. Throughout this process, detailed logging and documentation are crucial for both internal investigation and potential legal proceedings.
Data Breach Response Flowchart
A flowchart visually represents the steps to take during a data breach. It begins with the detection of a potential incident. This triggers an immediate assessment to determine the severity and scope of the breach. The flowchart then branches into actions depending on the assessment, such as isolating affected systems, initiating the incident response team, and contacting legal counsel.
Next, it Artikels steps for containing the breach, investigating its cause, and notifying affected individuals and authorities as required by law. Finally, the flowchart details procedures for remediating the incident, restoring systems, and conducting a post-incident review to improve security practices and prevent future breaches. The flowchart would use symbols like diamonds for decision points, rectangles for processes, and parallelograms for input/output.
A final step would be documenting the entire process.
Final Wrap-Up
Protecting patient data in New York hospitals requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding the intricacies of state and federal regulations, implementing robust cybersecurity technologies, and fostering a culture of security awareness among staff, hospitals can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats. Proactive measures, including comprehensive data breach response plans and adequate cybersecurity insurance, are essential components of a strong security posture.
Staying informed about evolving threats and best practices is an ongoing commitment to safeguarding patient information and ensuring the smooth operation of healthcare facilities.
Detailed FAQs
What are the most common types of cyberattacks targeting New York hospitals?
Ransomware, phishing attacks, and insider threats are among the most prevalent. Ransomware encrypts data, demanding payment for its release. Phishing attempts to trick employees into revealing credentials. Insider threats involve malicious or negligent actions by employees.
How much does cybersecurity insurance cost for a New York hospital?
The cost varies significantly based on factors like hospital size, the complexity of its IT infrastructure, and its existing security measures. It’s best to obtain quotes from multiple insurers to compare coverage and pricing.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with New York’s cybersecurity regulations?
Penalties can be substantial, including significant fines, legal action, and reputational damage. The specific penalties depend on the severity and nature of the violation.
Does HIPAA preempt New York’s cybersecurity regulations?
No, New York’s regulations often complement and build upon HIPAA requirements, meaning hospitals must meet both sets of standards. There’s often overlap, but New York may have stricter requirements in certain areas.