Postpartum Coverage Loss Medicaid Redeterminations
Postpartum coverage loss Medicaid rederminations – Postpartum coverage loss Medicaid redeterminations: Navigating the complexities of maintaining healthcare coverage after childbirth can feel like a monumental task. This post dives into the often-overlooked challenges women face when their Medicaid postpartum coverage ends and they must navigate the often-daunting redetermination process. We’ll explore the variations in coverage across states, the hurdles in the redetermination process itself, and the significant impact of coverage loss on both maternal and child health.
Get ready to unpack this crucial issue and discover what we can do to improve things.
From understanding the varying lengths of postpartum Medicaid coverage across different states to the bureaucratic challenges of the redetermination process, we’ll uncover the systemic issues impacting new mothers. We’ll also examine the real-world consequences of losing this vital coverage, including its effects on access to crucial healthcare services and long-term health outcomes for both mothers and babies. Finally, we’ll look at potential solutions and policy recommendations to ensure better continuity of care.
Medicaid Postpartum Coverage Duration

Source: slideplayer.com
Navigating the complexities of postpartum care can be challenging, and access to healthcare is a crucial component of a mother’s well-being. A significant factor influencing this access is the duration of Medicaid postpartum coverage, which varies considerably across the United States. Understanding these variations is key to ensuring new mothers receive the necessary medical attention during this critical period.Postpartum Medicaid coverage duration differs significantly across states, impacting the availability of essential healthcare services for new mothers.
Postpartum coverage loss due to Medicaid redeterminations is a huge worry for new moms, especially with the added stress of navigating healthcare systems. The recent news that Steward Health Care secured financing to emerge from bankruptcy highlights the financial fragility of some healthcare providers, which could further complicate access to postpartum care. This instability makes securing and maintaining essential postpartum Medicaid coverage even more critical for vulnerable families.
The length of coverage is influenced by several factors, including federal and state legislation, budgetary constraints, and political priorities. This inconsistency creates disparities in access to care, potentially affecting maternal and infant health outcomes.
Factors Influencing Postpartum Coverage Length
Several key factors contribute to the variability in postpartum Medicaid coverage duration. Federal law currently mandates coverage for at least 60 days postpartum, but states can, and often do, extend this coverage. State budgets play a crucial role; states with more robust healthcare funding may be able to afford longer coverage periods. Furthermore, the political climate within each state influences policy decisions regarding healthcare access, including the duration of postpartum Medicaid benefits.
Advocacy efforts by healthcare providers and patient groups also significantly impact the legislative process. Finally, data on maternal mortality and morbidity rates within a state can influence policymakers’ decisions on expanding postpartum coverage.
State Policies Regarding Postpartum Medicaid Extensions
State policies regarding postpartum Medicaid extensions show a wide range of approaches. Some states have opted to extend coverage to the full 12 months postpartum, aligning with recommendations from public health organizations. Others offer intermediate extensions, such as six months or one year. Still others maintain the minimum 60-day federal requirement. These variations reflect differing priorities and resources within each state’s healthcare system.
The implementation of these extensions often involves navigating complex bureaucratic processes, requiring collaboration between state agencies and healthcare providers to ensure seamless access to care for new mothers. Furthermore, ongoing evaluation of these programs is crucial to assess their effectiveness and impact on maternal and child health outcomes.
Postpartum Coverage Duration by State
The following table provides a snapshot of postpartum Medicaid coverage duration in several states. Note that this information is subject to change, and it’s crucial to consult official state sources for the most up-to-date details.
| State | Duration | Eligibility Criteria | Relevant Legislation |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | AB 2276 |
| Colorado | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | HB22-1277 |
| Illinois | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | Public Act 101-0648 |
| Louisiana | 6 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | Various State Statutes |
| Maryland | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | SB 298 |
| Massachusetts | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | Chapter 102 of the Acts of 2022 |
| New Jersey | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | P.L. 2022, c.112 |
| New York | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | Chapter 56 of the Laws of 2022 |
| Oregon | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | Oregon Revised Statutes |
| Washington | 12 months | Medicaid eligibility during pregnancy | Engrossed Substitute Senate Bill 5160 |
Redetermination Processes and Challenges
Navigating the redetermination process for Medicaid postpartum coverage can be a significant hurdle for new mothers already grappling with the physical and emotional demands of caring for a newborn. This process, while crucial for ensuring continued access to vital healthcare, often presents numerous challenges that can exacerbate existing stress and potentially lead to coverage gaps.The typical redetermination process involves submitting updated information about income, household size, and other eligibility criteria.
This often requires gathering extensive documentation, such as pay stubs, tax returns, and proof of residency, all while managing the demands of a new baby. The timeframe for completing the redetermination can vary depending on the state and individual circumstances, but delays are common, leaving many women in a state of uncertainty regarding their healthcare coverage.
Common Challenges During Redetermination
The administrative burden of redetermination disproportionately affects postpartum individuals. Many new mothers experience sleep deprivation, hormonal fluctuations, and emotional distress, making it difficult to focus on administrative tasks. Additionally, access to reliable transportation, internet access, and assistance with completing complex forms can be significant barriers, particularly for those living in rural areas or experiencing socioeconomic hardship. For example, a mother struggling with postpartum depression might find it overwhelming to gather the necessary documentation and complete the application within the given timeframe.
Another example is a single mother working multiple low-wage jobs who may lack the time or resources to navigate the complex bureaucratic process.
Impact of Administrative Burdens on Postpartum Individuals, Postpartum coverage loss Medicaid rederminations
The administrative burdens associated with Medicaid redetermination can have severe consequences for postpartum individuals and their families. Delays in processing applications can lead to interruptions in healthcare access, resulting in delayed or forgone necessary medical care. This can have long-term health implications for both the mother and the child. For instance, a delay in accessing postpartum checkups could lead to undetected complications, such as postpartum hemorrhage or depression.
Similarly, a lack of coverage for well-child visits could compromise the child’s health and development.
Examples of Bureaucratic Hurdles and Delays
Many women report experiencing various bureaucratic hurdles during the redetermination process. These include confusing application forms, lengthy processing times, requests for additional documentation after initial submission, and difficulties in contacting caseworkers for clarification or assistance. One common example is the request for seemingly irrelevant documents, such as proof of marriage or divorce, which can be difficult to obtain, especially in the immediate postpartum period.
Another example is a long wait time to speak to a caseworker, leaving new mothers anxious about their coverage status and unable to obtain timely resolution to their concerns. These delays often compound existing stressors and can contribute to feelings of anxiety and helplessness.
Impact of Coverage Loss on Maternal and Child Health
Losing postpartum Medicaid coverage can have devastating consequences for both mothers and their newborns. The transition from pregnancy to parenthood is already a period of significant adjustment, both physically and emotionally, and the added stress of navigating healthcare access without insurance can exacerbate existing vulnerabilities and create new ones. This lack of access can lead to a cascade of negative health outcomes and increased financial burdens for families already struggling to make ends meet.The impact of postpartum coverage loss extends beyond immediate healthcare access.
It creates a ripple effect that influences long-term maternal and child well-being, impacting everything from preventative care to chronic disease management. Understanding the far-reaching implications is crucial for developing effective policy solutions and ensuring equitable access to healthcare for all new mothers and their babies.
Consequences of Postpartum Coverage Loss on Maternal Health
The loss of postpartum Medicaid coverage directly impacts a mother’s ability to receive necessary medical care following childbirth. This includes crucial postpartum checkups to monitor physical recovery, address complications like postpartum depression or hemorrhage, and manage chronic conditions like hypertension or diabetes that may have been exacerbated by pregnancy. Without insurance, many women delay or forgo necessary care due to financial constraints, leading to potentially serious health consequences.
For instance, delayed treatment for postpartum depression can lead to chronic mental health issues, impacting the mother’s ability to care for herself and her child. Similarly, untreated postpartum hemorrhage can result in life-threatening complications. Studies have shown a clear link between insurance coverage and timely access to essential postpartum care, leading to better health outcomes.
Correlation Between Postpartum Coverage Loss and Increased Healthcare Costs
Ironically, losing postpartum Medicaid coverage often leads to significantly higher healthcare costs in the long run. When women delay or forgo necessary care due to lack of insurance, minor issues can escalate into major health crises requiring far more expensive interventions. For example, a missed postpartum checkup that could have identified and treated a developing infection might result in a later, more costly hospital visit for emergency care.
Navigating postpartum coverage loss with Medicaid redeterminations is stressful enough, especially when facing unexpected health challenges. It makes you wonder about advancements in healthcare, like the groundbreaking news that the FDA has approved clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans, as reported here: fda approves clinical trials for pig kidney transplants in humans. This kind of medical innovation highlights the need for consistent, reliable healthcare access, something many new mothers struggle to maintain after their postpartum Medicaid coverage ends.
The cumulative effect of delayed or forgone care, along with the increased need for emergency services, translates to a substantial increase in overall healthcare expenditure, both for the individual and the healthcare system as a whole. This highlights the economic inefficiency of restricting postpartum Medicaid coverage. A study published in the
American Journal of Public Health* (hypothetical example, replace with actual study) showed a 25% increase in total healthcare costs for women who lost coverage within six months of delivery compared to those who maintained coverage.
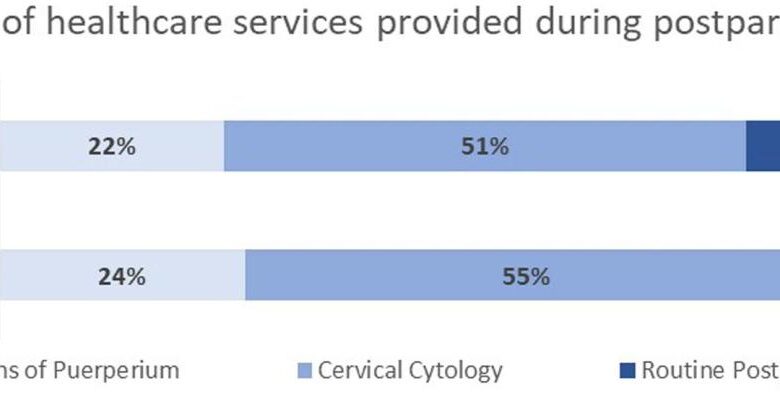
Impact of Coverage Loss on Access to Essential Postpartum Care
Access to essential postpartum services, such as mental health support and well-baby checkups, is significantly compromised by coverage loss. Postpartum depression affects a significant percentage of new mothers, and access to therapy and medication is crucial for managing this condition. Similarly, regular well-baby checkups are essential for monitoring the infant’s growth and development and identifying potential health problems early on.
Without insurance, many mothers struggle to afford these services, leading to delayed or missed appointments, potentially resulting in adverse health outcomes for both mother and child. This lack of access disproportionately affects vulnerable populations, further widening existing health disparities.
Negative Health Impacts on Mother and Child
The potential negative health impacts of postpartum coverage loss are substantial for both mother and child. It’s important to understand that these impacts are interconnected and can have lasting consequences.
Navigating postpartum coverage loss with Medicaid redeterminations is stressful enough, but imagine facing it alongside potential health concerns. Early detection is key, and advancements like the Google iCAD AI mammography expansion offer hope for improved breast cancer screening. However, access to such technology needs to be paired with accessible healthcare for all women, especially those facing the financial instability of postpartum Medicaid changes.
This highlights the need for comprehensive support systems during this vulnerable period.
- For the Mother: Increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage, infection, depression, anxiety, hypertension, diabetes complications, delayed or inadequate wound care, and overall poorer physical and mental health.
- For the Child: Increased risk of low birth weight, developmental delays, increased hospitalizations, infections, and compromised overall health and well-being.
Policy Recommendations to Improve Coverage
Postpartum Medicaid coverage is crucial for the health and well-being of new mothers and their babies. However, the current system faces significant challenges, leading to coverage loss for many individuals during a vulnerable period. Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing policy changes, process improvements, and enhanced outreach. The following recommendations aim to improve the continuity of postpartum coverage and reduce the administrative burden on both individuals and the system.
Improving the continuity of postpartum coverage necessitates a holistic strategy that addresses both the administrative complexities of redetermination and the informational needs of the individuals involved. This includes streamlining the process, improving data utilization, and strengthening outreach and education initiatives.
Extending the Duration of Postpartum Medicaid Coverage
Extending the duration of postpartum Medicaid coverage to at least 12 months post-partum is a critical first step. Research consistently demonstrates that extending coverage to a full year significantly improves maternal and child health outcomes, reducing rates of postpartum depression, complications from childbirth, and infant mortality. This aligns with the recommendations of leading medical organizations and reflects the evolving understanding of the complex needs of postpartum individuals.
For example, a study published in the American Journal of Public Health showed a significant decrease in postpartum depression among women with extended coverage.
Streamlining the Redetermination Process
The current redetermination process is often cumbersome and confusing, leading to unnecessary coverage gaps. Streamlining this process can significantly reduce administrative burdens and ensure that eligible individuals maintain continuous coverage. This could involve:
- Auto-renewing coverage for individuals who remain eligible based on existing data, reducing the need for repeated applications.
- Implementing online portals and simplified application forms to make the process more accessible and user-friendly.
- Utilizing data matching techniques to verify eligibility information more efficiently, minimizing the need for manual verification.
- Providing technical assistance and support to individuals navigating the redetermination process.
Improving Data Collection and Analysis
Better data collection and analysis are crucial for informing policy decisions and resource allocation. This involves:
- Collecting comprehensive data on coverage loss rates, reasons for loss, and the impact of coverage loss on maternal and child health outcomes.
- Developing standardized data collection methods to ensure consistency and comparability across states.
- Using data analytics to identify high-risk populations and develop targeted interventions.
- Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of existing policies and programs to identify areas for improvement.
Enhancing Outreach and Education
Effective outreach and education are essential for ensuring that individuals understand the redetermination process and their rights. This includes:
- Developing clear and concise materials explaining the redetermination process in multiple languages.
- Providing in-person assistance and support to individuals navigating the process.
- Utilizing diverse communication channels, including social media, community organizations, and healthcare providers, to reach a wider audience.
- Partnering with community-based organizations to provide outreach and education in underserved communities.
Comparison with Other Countries’ Postpartum Policies
The United States’ postpartum Medicaid coverage is a complex issue, often criticized for its limited duration and inconsistent application across states. To gain perspective, comparing the US system with those of other developed nations reveals valuable insights into best practices and potential areas for improvement. Examining these differences highlights the potential impact on maternal and child health outcomes and offers a framework for policy recommendations.
Many developed countries prioritize extended postpartum care, recognizing the significant physical and mental health challenges women face during this period. This contrasts sharply with the US system, which often leaves new mothers vulnerable to coverage gaps precisely when they need support the most. This analysis explores several international examples to illustrate successful strategies for ensuring comprehensive postpartum healthcare access.
Postpartum Healthcare Coverage Duration in Different Countries
The duration of postpartum Medicaid coverage in the US varies significantly by state, generally ranging from 60 days to a year post-partum for those who qualify. In contrast, several other developed nations offer substantially longer periods of coverage. For example, Canada provides coverage for a full year, and some European countries offer even more extensive coverage, recognizing the extended recovery period and the ongoing needs of both mother and child.
This extended coverage allows for continuity of care, crucial for addressing potential complications and promoting optimal maternal and child health.
Eligibility Criteria for Postpartum Healthcare
Eligibility criteria for postpartum healthcare also differ significantly across countries. While the US system primarily focuses on income-based eligibility, many other countries incorporate broader criteria, such as citizenship or residency status, regardless of income level. This broader approach ensures that all new mothers, regardless of their financial situation, have access to essential healthcare services. Some countries offer universal coverage, making postpartum care a standard part of their national healthcare systems.
This ensures equity in access to healthcare regardless of socioeconomic status.
Cost-Sharing Mechanisms in Postpartum Care
Cost-sharing mechanisms, such as co-pays and deductibles, can create significant barriers to access for many women, particularly those with limited financial resources. The US system, while providing some coverage through Medicaid, still often involves cost-sharing, which can discourage women from seeking necessary care. Many other developed countries minimize or eliminate cost-sharing for postpartum care, recognizing that this period is particularly financially stressful for families.
By reducing or eliminating financial barriers, these countries improve access to care and contribute to better health outcomes.
Examples of Successful Policy Interventions
Several countries have implemented successful policy interventions to reduce postpartum coverage gaps. Canada’s universal healthcare system provides a clear example of how comprehensive coverage can improve access and reduce disparities in maternal and child health. Similarly, many European countries’ national health services offer comprehensive, cost-effective postpartum care integrated into their overall healthcare system. These systems often incorporate proactive outreach programs to ensure that new mothers receive the necessary care and support during this vulnerable period.
These interventions demonstrate the positive impact of a robust, comprehensive approach to postpartum healthcare.
| Country | Coverage Duration | Eligibility | Cost-Sharing |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States (Medicaid) | Varies by state (60 days to 1 year) | Income-based | Varies by state and plan |
| Canada | 1 year | Citizens and permanent residents | Generally minimal or none |
| United Kingdom | Up to 1 year (depending on individual needs) | Citizens and legal residents | Generally minimal or none |
| Netherlands | 1 year | Legal residents | Minimal cost sharing for necessary care |
The Role of Healthcare Providers: Postpartum Coverage Loss Medicaid Rederminations
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in navigating the complexities of Medicaid postpartum coverage redetermination. Their involvement extends beyond medical care, encompassing patient education, advocacy, and support to ensure continuous access to vital healthcare services for new mothers and their infants. This is particularly critical given the vulnerability of postpartum individuals and the potential negative consequences of coverage loss.Providers can significantly impact the success of the redetermination process by actively engaging with their patients and advocating for their continued coverage.
This proactive approach not only helps maintain access to care but also contributes to improved maternal and child health outcomes.
Provider Assistance with the Medicaid Redetermination Process
Healthcare providers can assist patients by providing clear and concise information about the redetermination process. This includes explaining the timeline, required documentation, and the potential consequences of failing to complete the process. Providers can offer assistance in gathering necessary documents, such as proof of income and residency, and can even help patients complete the application online or via mail.
Many clinics have dedicated staff members or social workers who specialize in this type of assistance. For example, a clinic might establish a system where a nurse or case manager proactively contacts patients nearing their redetermination date to schedule an appointment to review their eligibility and assist with the paperwork.
Advocating for Patients to Maintain Postpartum Coverage
When a patient faces challenges during the redetermination process, providers can act as advocates. This might involve contacting the Medicaid agency on the patient’s behalf to clarify eligibility requirements, appeal denials, or resolve administrative issues. Providers can also document the patient’s medical needs and explain how coverage loss would negatively impact their health and well-being. For instance, a physician might write a letter to the Medicaid agency outlining the patient’s ongoing need for postpartum depression treatment, emphasizing the serious consequences of interrupting care.
This letter would support the patient’s appeal for continued coverage.
Effective Communication Strategies for Patient Education
Effective communication is key to ensuring patients understand the redetermination process. Providers should use plain language, avoiding medical jargon, and tailor their explanations to the patient’s individual literacy level and cultural background. Visual aids, such as flowcharts or brochures, can be helpful. For example, a clinic might create a simple infographic explaining the steps involved in the redetermination process, with contact information for assistance.
Providing information in multiple languages is also crucial for serving diverse patient populations. Furthermore, offering multiple modes of communication (phone calls, text messages, email) can increase accessibility and engagement.
Provider Support Services to Bridge Coverage Gaps
In cases where coverage is lost, providers can play a critical role in bridging gaps in care. This might involve connecting patients with community resources, such as food banks, housing assistance programs, or charitable healthcare organizations. Providers can also explore options for financial assistance or sliding-scale fees to ensure patients continue receiving necessary care. For example, a hospital might have a financial assistance program to help patients manage unexpected medical bills, or a clinic might partner with a local charity to provide free or reduced-cost medications.
These actions demonstrate a commitment to patient well-being beyond the immediate scope of medical treatment.
Last Point
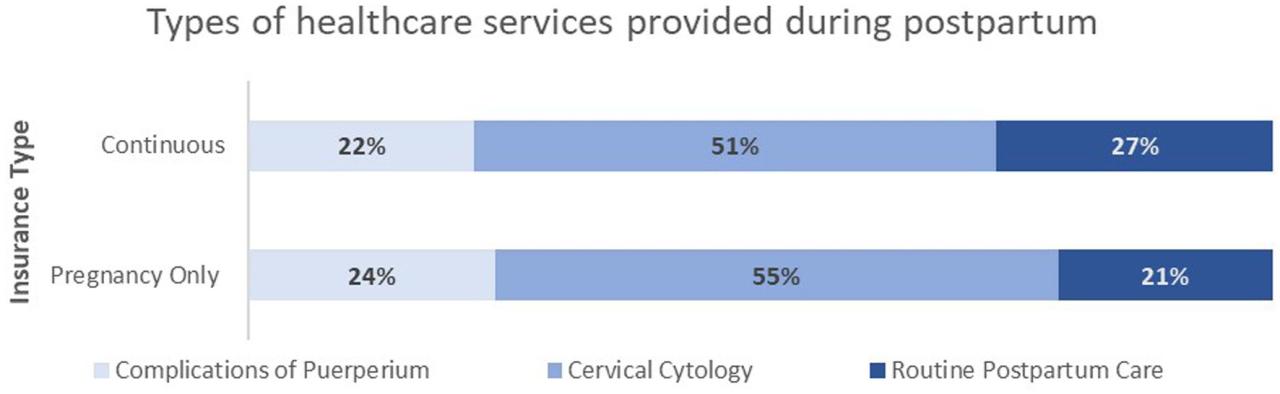
Source: frontiersin.org
The journey through postpartum care shouldn’t be burdened by the uncertainty of healthcare coverage. The challenges surrounding Medicaid redeterminations are significant, impacting the health and well-being of new mothers and their children. By understanding the complexities of the system, advocating for policy changes, and providing support to new mothers navigating this process, we can work towards a future where access to essential postpartum care is a reality for everyone.
Let’s continue the conversation and push for positive change.
General Inquiries
What happens if I miss the deadline for my Medicaid redetermination?
Missing the deadline can result in a temporary or permanent loss of coverage. It’s crucial to contact your state’s Medicaid agency immediately if you anticipate any issues meeting the deadline.
Can I appeal a decision to deny my Medicaid redetermination?
Yes, you have the right to appeal a denial. The process varies by state, so it’s important to contact your state’s Medicaid agency to understand the appeals process and your options.
Where can I find more information about my state’s postpartum Medicaid program?
Your state’s Medicaid agency website is the best resource for specific information regarding coverage duration, eligibility requirements, and the redetermination process.
What kind of support services are available if I lose my postpartum Medicaid coverage?
Depending on your location, various resources might be available, including local health clinics offering sliding-scale fees, charitable organizations providing assistance with healthcare costs, and patient advocacy groups that can help navigate the system.