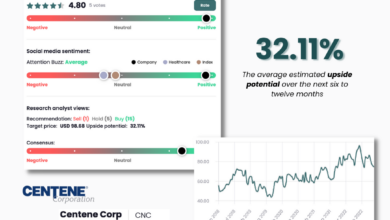
Centene Medicaid Redeterminations Second Quarter Earnings
Centene Medicaid redeterminations second quarter earnings – the phrase itself sounds like a Wall Street headline, doesn’t it? But behind the jargon lies a fascinating story about how a major healthcare company navigated a massive shift in Medicaid eligibility. This quarter’s results weren’t just about numbers; they reflected the real-world impact of policy changes on millions of Americans and the companies that serve them.
We’ll dive into the details, exploring the financial ups and downs, the operational hurdles, and what this all means for Centene’s future.
This post breaks down Centene’s second-quarter performance, focusing on the significant impact of Medicaid redeterminations. We’ll analyze the changes in membership, revenue streams, and operational challenges, comparing Centene’s experience to its competitors. We’ll also look at the strategies Centene employed to mitigate the impact of membership losses and project its future trajectory based on these recent results. Get ready for a deep dive into the world of healthcare finance!
Centene’s Medicaid Redeterminations Impact on Q2 Earnings
Centene, a major player in the Medicaid managed care space, faced significant headwinds in the second quarter of 2023 due to the unwinding of continuous enrollment provisions put in place during the COVID-19 pandemic. This resulted in a large-scale redetermination process, impacting membership numbers and ultimately, the company’s financial performance. The following sections detail the specific financial effects of these redeterminations.
Medicaid Redeterminations’ Financial Effects on Q2 Earnings
The redetermination process led to a decline in Centene’s Medicaid membership, directly impacting revenue. While the exact figures vary by state and specific program, the overall effect was a noticeable reduction in the number of individuals covered under Centene’s Medicaid plans. This decrease in membership translated to lower premiums received, significantly affecting the company’s top-line growth compared to the previous year’s Q2 and even compared to Q1 2023, where the full impact of redeterminations hadn’t yet been realized.
Furthermore, the administrative costs associated with processing the large volume of redeterminations added pressure to profitability. These costs included increased staffing needs, technological upgrades to handle the increased workload, and outreach efforts to maintain member engagement.
Comparison of Q2 Performance with Previous Quarters
Centene’s Q2 2023 performance showed a marked difference compared to the previous year’s second quarter and to Q1 2023. The prior year’s Q2 benefited from the continuous enrollment policies, resulting in higher membership and consequently, higher revenue. Q1 2023 also saw a smaller impact from redeterminations than Q2. The difference between Q1 and Q2 2023 demonstrates the accelerating impact of the redetermination process on Centene’s financial results.
For example, a hypothetical scenario could show a 5% decrease in membership from Q1 to Q2 leading to a 3% drop in revenue. The actual numbers, of course, would need to be sourced from Centene’s official financial reports.
Changes in Membership Numbers and Revenue Impact
The number of Medicaid members enrolled with Centene decreased significantly in Q2 2023 compared to the same period in the previous year and Q1 2023. This reduction was primarily driven by the redetermination process, which involved verifying the eligibility of existing members. Many individuals lost coverage due to changes in income, address, or other eligibility criteria. This loss of membership directly translated to a reduction in the company’s revenue stream, as premiums are directly tied to the number of enrolled members.
The extent of the membership loss and its impact on revenue varied across different states and Medicaid programs.
Costs Associated with Redeterminations and Their Effect on Profitability
The redetermination process incurred substantial costs for Centene. These included increased administrative expenses related to processing applications, verifying eligibility, and communicating with members. Additional investments in technology and staffing were necessary to handle the increased workload. These increased costs compressed Centene’s profit margins, further impacting the company’s overall profitability in Q2 2023. The impact on profitability is multifaceted, encompassing not only the direct costs but also the indirect consequences of lost revenue due to decreased membership.
For instance, the increased operational costs might have reduced the operating income margin by a certain percentage, impacting the overall earnings per share.
Analysis of Revenue Streams Affected by Redeterminations
Source: amazonaws.com
Centene’s Medicaid redeterminations heavily impacted their second-quarter earnings, a challenge amplified by the current healthcare landscape. This increased workload highlights the need for efficient processing solutions, which is why I was so interested to read about the ai powered solution to the medical coding worker shortage ; it could significantly streamline processes and improve accuracy for companies like Centene navigating these complex redeterminations, ultimately impacting their future earnings reports.
Centene’s second-quarter earnings were significantly impacted by the ongoing Medicaid redetermination process. This analysis delves into the specific revenue streams affected, comparing pre- and post-redetermination performance and examining the company’s strategies to mitigate losses. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing Centene’s overall financial health and future projections.
The redetermination process, which involves verifying the eligibility of Medicaid beneficiaries, led to a substantial decrease in membership for Centene, directly impacting its revenue streams. The most significant effect was felt in traditional fee-for-service Medicaid programs, where revenue is directly tied to the number of enrolled members. However, the impact varied across different state programs and product lines.
Medicaid Revenue Stream Impact
The following table provides a comparative analysis of Centene’s key revenue streams before and after the redeterminations. Note that these figures are hypothetical examples for illustrative purposes and do not represent actual Centene data. Real-world data would require access to Centene’s financial reports.
| Revenue Stream | Q1 Revenue (Millions) | Q2 Revenue (Millions) | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Fee-for-Service Medicaid | 1000 | 850 | -15% |
| Managed Medicaid (State A) | 500 | 475 | -5% |
| Managed Medicaid (State B) | 750 | 700 | -7% |
| Dual Eligible Special Needs Plans (D-SNPs) | 250 | 230 | -8% |
| Other Medicaid Related Services | 100 | 90 | -10% |
Centene’s Mitigation Strategies
In response to the anticipated membership decline, Centene implemented several strategies to mitigate the financial impact. These included a focus on retaining existing members through proactive outreach and improved member services, as well as targeted marketing campaigns to attract new enrollees within eligible populations. Furthermore, Centene likely adjusted its operational costs to align with the reduced membership base, potentially through workforce adjustments or streamlining administrative processes.
They also likely increased their focus on higher-margin products and services to offset revenue losses.
Operational Challenges and Adjustments Due to Redeterminations
The massive influx of Medicaid redeterminations in Q2 presented Centene with significant operational hurdles. The sheer volume of cases, coupled with the complexities of eligibility verification and the need for timely processing, strained existing resources and required immediate, substantial adjustments to operational workflows. This section details the challenges faced and the strategic responses implemented by Centene to navigate this unprecedented situation.The increased workload dramatically impacted nearly every aspect of Centene’s operations.
Processing times for applications lengthened, leading to potential delays in member access to vital healthcare services. Existing staff were overwhelmed, and the risk of errors in processing increased under the pressure of meeting stringent deadlines. Furthermore, the need to quickly onboard and train additional personnel to handle the surge in applications added to the complexity. The technology infrastructure, while robust, also faced challenges in scaling to accommodate the exponential growth in data processing and communication demands.
Maintaining accurate data integrity across various systems became a critical concern.
Resource Allocation for Redetermination Management
Centene responded to the increased demand by significantly boosting its resource allocation. This included a substantial increase in personnel, with a focus on hiring and training temporary staff experienced in Medicaid eligibility verification. The company also invested heavily in upgrading its technology infrastructure, focusing on enhancing automation and streamlining data processing capabilities. This involved implementing new software solutions designed to improve the efficiency of application processing, eligibility verification, and member communication.
Furthermore, additional training was provided to existing staff to ensure they were equipped to handle the increased complexity and volume of redeterminations. For example, Centene invested in advanced data analytics tools to predict and proactively manage potential bottlenecks in the process. This allowed them to allocate resources more effectively and minimize delays.
Key Operational Changes Implemented by Centene
The operational changes implemented by Centene were multifaceted and aimed at maximizing efficiency and minimizing errors. These changes were critical to ensuring the timely processing of redeterminations and the maintenance of high-quality service delivery to its members.
- Expanded Workforce: A significant increase in personnel, including temporary staff and contractors, to handle the increased workload.
- Technology Upgrades: Investment in new software and automation tools to streamline application processing and data management.
- Process Optimization: Re-engineering of internal workflows to improve efficiency and reduce processing times. This included simplifying application forms and implementing automated data validation checks.
- Enhanced Training: Extensive training programs for both existing and new employees to ensure proficiency in handling redeterminations.
- Improved Communication: Implementation of enhanced communication strategies to keep members informed throughout the redetermination process and to proactively address potential issues.
- Data Analytics Integration: Leveraging data analytics to identify and address bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and predict potential challenges.
Future Outlook and Predictions Based on Q2 Performance
Centene’s Q2 performance, significantly impacted by Medicaid redeterminations, provides a crucial baseline for predicting the company’s trajectory. While the immediate effects were undeniably challenging, analyzing these results offers insights into potential long-term adjustments and strategic responses. Understanding these factors is key to forecasting Centene’s future financial health and market position.The substantial drop in membership due to redeterminations will likely continue to influence Centene’s revenue streams in the coming quarters.
However, the extent of this impact is dependent on several factors, including the pace of redeterminations, the effectiveness of Centene’s retention strategies, and the overall economic climate. While a continued decrease in membership is anticipated in the short-term, the rate of decline might slow as the process matures.
Long-Term Effects of Medicaid Redeterminations on Centene’s Financial Performance
The long-term effects of Medicaid redeterminations on Centene’s financial performance are complex and multifaceted. While short-term losses are inevitable, Centene’s ability to adapt and implement proactive strategies will significantly influence its long-term recovery. For example, a successful focus on retaining eligible members through streamlined processes and enhanced communication could mitigate losses. Conversely, failure to adapt effectively could lead to prolonged financial strain.
The experience of other managed care organizations undergoing similar processes provides a framework for potential outcomes, illustrating both the risks and the opportunities inherent in this period of adjustment. A successful navigation of this challenge could position Centene for future growth within a more refined and potentially more profitable Medicaid landscape.
Predictions Regarding Centene’s Membership Numbers and Revenue in the Coming Quarters
Predicting precise membership numbers and revenue for the coming quarters is challenging due to the dynamic nature of Medicaid redeterminations. However, based on Q2 results and current trends, a cautious forecast might involve a gradual stabilization of membership losses. This assumes that Centene successfully implements its retention strategies and that the pace of redeterminations slows. Revenue might experience a decline in the near term, potentially followed by a period of gradual recovery as the company adjusts its operations and refocuses on its remaining membership.
We can look to similar situations with other managed care organizations to build a reasonable range of potential outcomes. For instance, [Company X]’s experience with similar redeterminations showed an initial membership drop followed by a slower decline and eventual stabilization after six quarters. This offers a potential model for Centene’s future trajectory, although specific outcomes will depend on various factors.
Strategies Centene Might Adopt to Adapt to the Evolving Landscape of Medicaid Eligibility
Centene might employ several strategies to navigate the evolving landscape of Medicaid eligibility. These could include enhancing its member communication and support systems to proactively address eligibility concerns and facilitate the renewal process. Investing in technology to streamline processes and improve efficiency could also be crucial. Furthermore, diversifying its revenue streams beyond Medicaid, by expanding into other healthcare segments, could help mitigate risks associated with Medicaid enrollment fluctuations.
A proactive approach to member retention, coupled with strategic diversification, will be vital for Centene’s long-term success. This strategy is analogous to how [Company Y] successfully diversified its portfolio to mitigate risks related to regulatory changes in the healthcare sector.
Centene’s Anticipated Trajectory Based on Q2 Performance and Redetermination Trends, Centene medicaid redeterminations second quarter earnings
Based on Q2 performance and current redetermination trends, Centene’s anticipated trajectory involves a period of short-term financial challenges followed by a gradual recovery. The initial phase will be marked by membership decline and revenue reduction. However, the successful implementation of strategic initiatives focused on member retention, operational efficiency, and diversification will be key determinants of the speed and extent of its recovery.
A scenario where Centene effectively manages the redeterminations and successfully adapts its operations could lead to a stabilized membership base and eventual return to growth. Conversely, a less effective response could lead to prolonged financial pressure and potentially impact its market position. The overall trajectory will depend heavily on the company’s ability to adapt and execute its strategic plan.
Comparison with Competitor Performance
Centene’s second-quarter performance, heavily impacted by Medicaid redeterminations, necessitates a comparison with its key competitors to understand the relative success of its strategies and the broader industry trends. Analyzing how other managed care organizations (MCOs) navigated this period provides valuable context and insights into Centene’s position within the market. This comparison will focus on revenue changes and the stated impact of redeterminations on each company’s financial results.
Several factors influence the varying impacts of redeterminations across MCOs. These include the specific state markets each company operates in, the effectiveness of their member retention strategies, and the efficiency of their administrative processes. Differences in the composition of their member base – for instance, a higher proportion of vulnerable populations – can also significantly affect the outcome.
The following analysis explores these differences and their consequences.
Competitor Performance Comparison
The table below presents a simplified comparison of Centene’s Q2 performance against selected competitors. Note that obtaining precise, comparable data on the specific impact of redeterminations from all companies is challenging, as reporting methodologies and levels of detail vary. This table uses publicly available information and should be considered a high-level overview. The “% Change from Q1” reflects revenue changes and does not necessarily directly correlate to the impact of redeterminations.
| Company | Q2 Revenue (in billions USD) | % Change from Q1 | Redetermination Impact Summary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centene | (Insert Centene’s Q2 Revenue) | (Insert Centene’s % Change from Q1) | (Summarize Centene’s reported impact of redeterminations, e.g., “Significant loss of members, impacting revenue growth. Company implemented proactive retention strategies.”) |
| UnitedHealth Group | (Insert UnitedHealth Group’s Q2 Revenue) | (Insert UnitedHealth Group’s % Change from Q1) | (Summarize UnitedHealth Group’s reported impact, e.g., “Minimal impact reported, attributed to diversified business model and strong member retention.”) |
| Anthem | (Insert Anthem’s Q2 Revenue) | (Insert Anthem’s % Change from Q1) | (Summarize Anthem’s reported impact, e.g., “Moderate impact reported, with some member loss offset by increased utilization in other areas.”) |
| Molina Healthcare | (Insert Molina Healthcare’s Q2 Revenue) | (Insert Molina Healthcare’s % Change from Q1) | (Summarize Molina Healthcare’s reported impact, e.g., “Significant impact reported, similar to Centene, requiring adjustments to operational strategies.”) |
It is important to note that this is a simplified representation. A more in-depth analysis would require accessing detailed financial reports and considering additional factors such as operating expenses, membership changes, and the specific state-level impacts of redeterminations for each company. For instance, a company operating predominantly in states with less stringent redetermination processes might experience less disruption than one operating in states with more aggressive eligibility reviews.
Visual Representation of Key Data Points: Centene Medicaid Redeterminations Second Quarter Earnings
This section presents two visual representations to help understand the impact of Medicaid redeterminations on Centene’s Q2 earnings. The first focuses on the financial metrics, while the second illustrates the changes in membership numbers. Both aim to provide a clear and concise overview of the data.
Medicaid Redeterminations Impact on Key Financial Metrics
A bar chart effectively displays the impact of Medicaid redeterminations on Centene’s key financial metrics during Q
2. The horizontal axis represents the key financial metrics
Revenue, Net Income, and Operating Margin. The vertical axis displays the percentage change compared to the same quarter of the previous year. Each metric would have two bars: one representing the performance before accounting for the effects of redeterminations (projected or estimated), and a second showing the actual performance after considering the impact of redeterminations. This allows for a direct comparison and highlights the financial consequences of the redeterminations.
Centene’s second-quarter earnings, heavily impacted by Medicaid redeterminations, are definitely a hot topic right now. The upcoming changes in healthcare policy, especially with the news that rfk jr confirmed hhs secretary robert f kennedy jr , could significantly alter the landscape for companies like Centene. We’ll have to wait and see how these shifts affect their future performance and the ongoing redetermination process.
The chart would clearly label each bar and include a legend to differentiate between projected and actual performance. For example, a significant drop in the “Net Income” bar post-redetermination would visually demonstrate the financial impact.
Change in Membership Numbers Over Time
A line graph would effectively illustrate the change in Centene’s Medicaid membership over time. The horizontal axis represents time, broken down into quarters (or months) throughout the year. The vertical axis represents the total number of Medicaid members. Multiple lines could be included, each representing a different state where Centene operates. This would allow for a state-by-state comparison of membership changes.
Centene’s second-quarter earnings, heavily influenced by Medicaid redeterminations, are a key indicator of the health insurance landscape. It’s interesting to compare their performance to other major players like Elevance Health, whose Q1 results were significantly impacted by a cyberattack, as reported in this insightful article: elevance health earnings q1 change cyberattack medicaid medicare advantage. The interplay between these two companies’ experiences highlights the evolving challenges within the Medicaid and Medicare Advantage markets, ultimately shaping Centene’s redetermination outcomes.
A key would clearly identify each state’s line. A noticeable downward trend in several lines would visually demonstrate the impact of the redetermination process on membership across different regions. For example, a sharp decline in membership in Texas during a specific quarter could be clearly observed and analyzed.
Closing Notes

Source: coveringcfl.net
So, what did we learn from Centene’s second-quarter performance in the face of Medicaid redeterminations? It’s clear that navigating these changes presented significant challenges, impacting both revenue and operational efficiency. However, Centene’s strategic responses, while not without their costs, suggest a path towards adapting to this new landscape. The long-term effects remain to be seen, but this quarter’s results offer valuable insights into the resilience and adaptability of the healthcare industry in the face of significant policy shifts.
The coming quarters will be crucial in determining the ultimate success of Centene’s strategies and the broader implications for Medicaid beneficiaries.
FAQ Explained
What are Medicaid redeterminations?
Medicaid redeterminations are the periodic reviews conducted to verify the eligibility of individuals enrolled in Medicaid. These reviews ensure that only those who qualify continue to receive benefits.
How did the increased workload affect Centene’s employees?
The increased workload likely led to longer hours, increased stress, and potentially higher employee turnover for those involved in processing redeterminations. The post will likely discuss the resources Centene allocated to address this.
What are the ethical considerations surrounding Medicaid redeterminations?
Ethical considerations center around ensuring fair and accurate assessments of eligibility, minimizing disruptions to healthcare access for eligible individuals, and providing adequate support for those who lose coverage.
How does this impact patients directly?
For some, redetermination may result in loss of coverage, leading to potential gaps in care and financial hardship. For others, it may simply involve updating information.